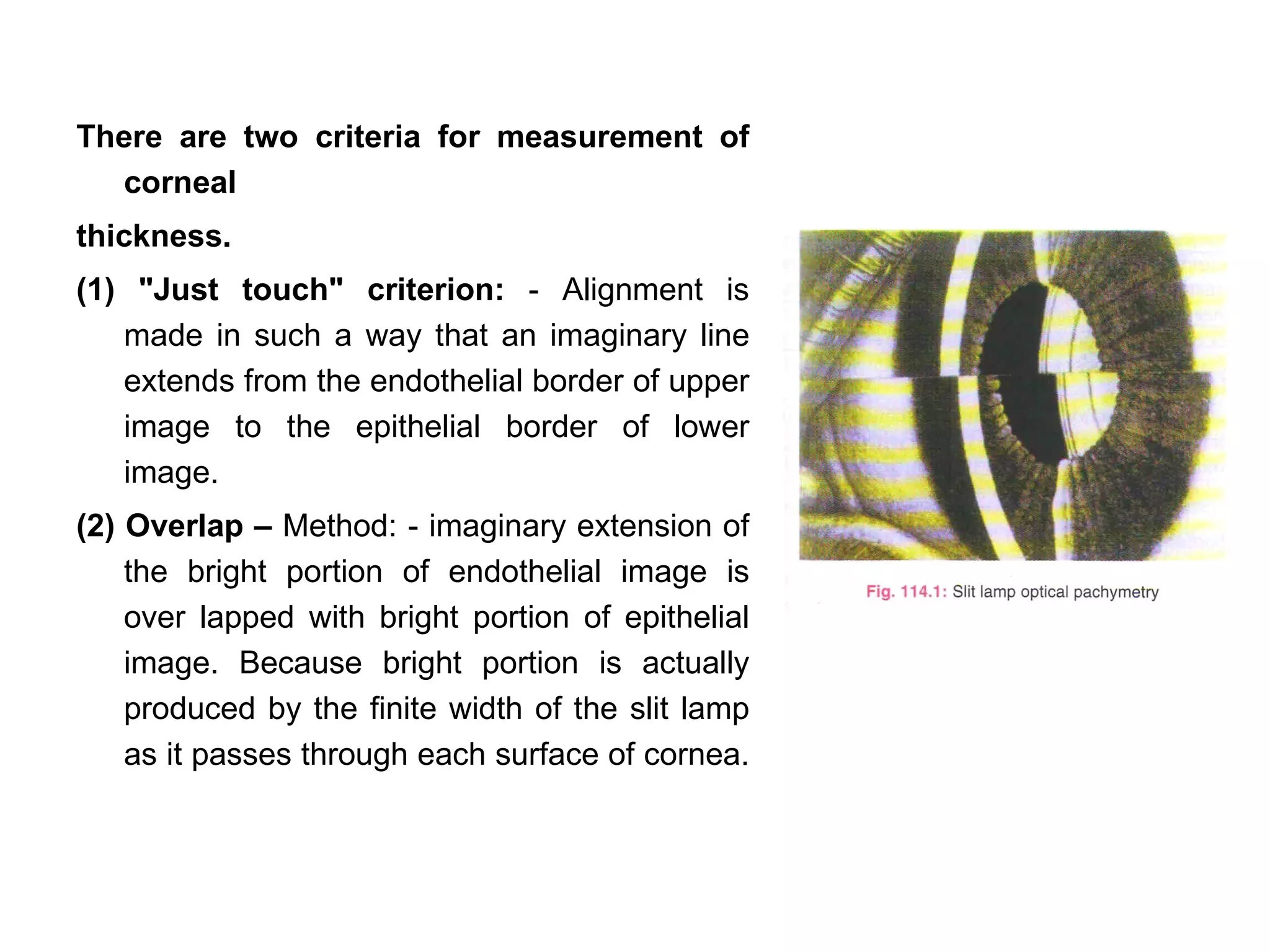
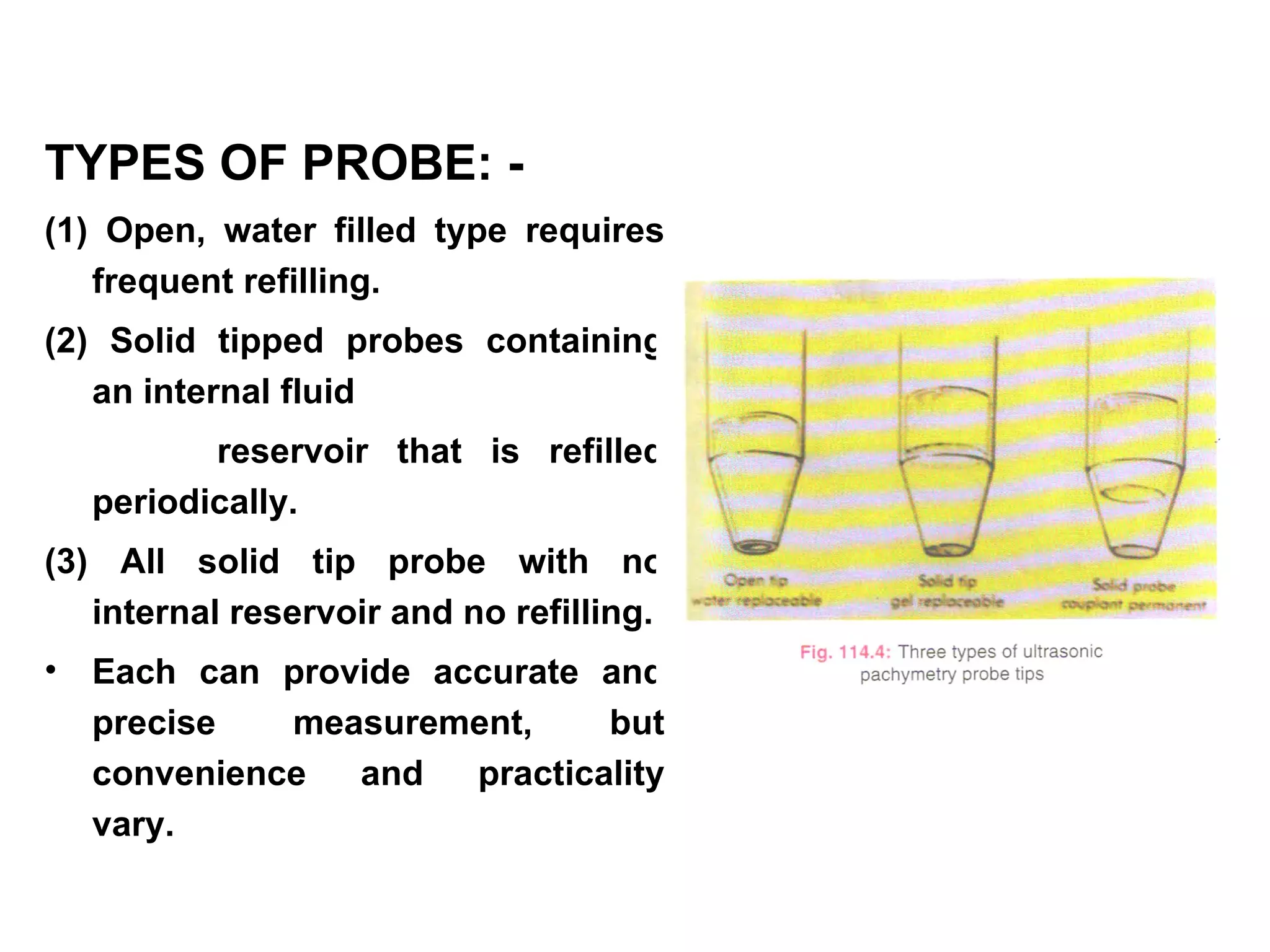
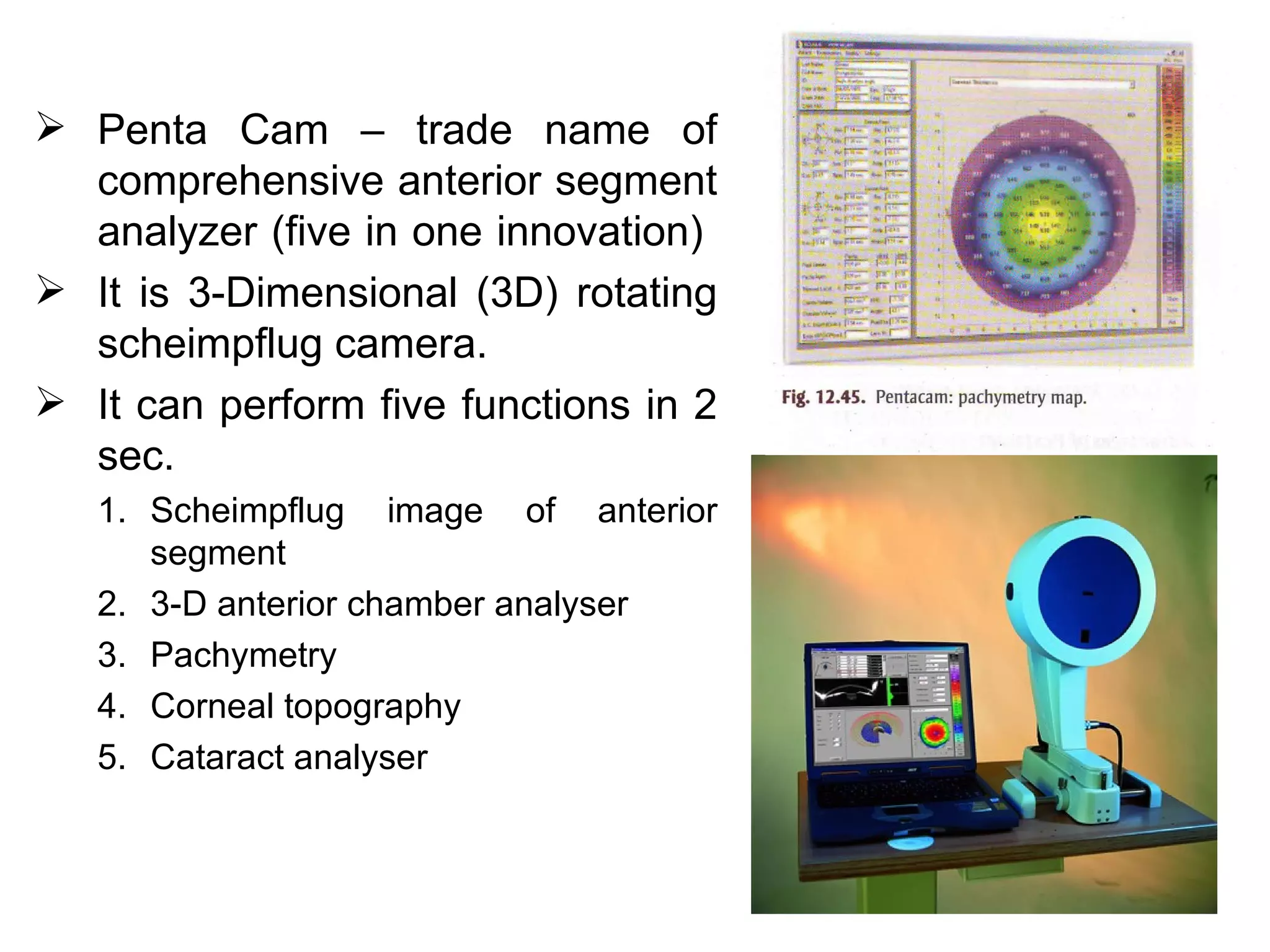
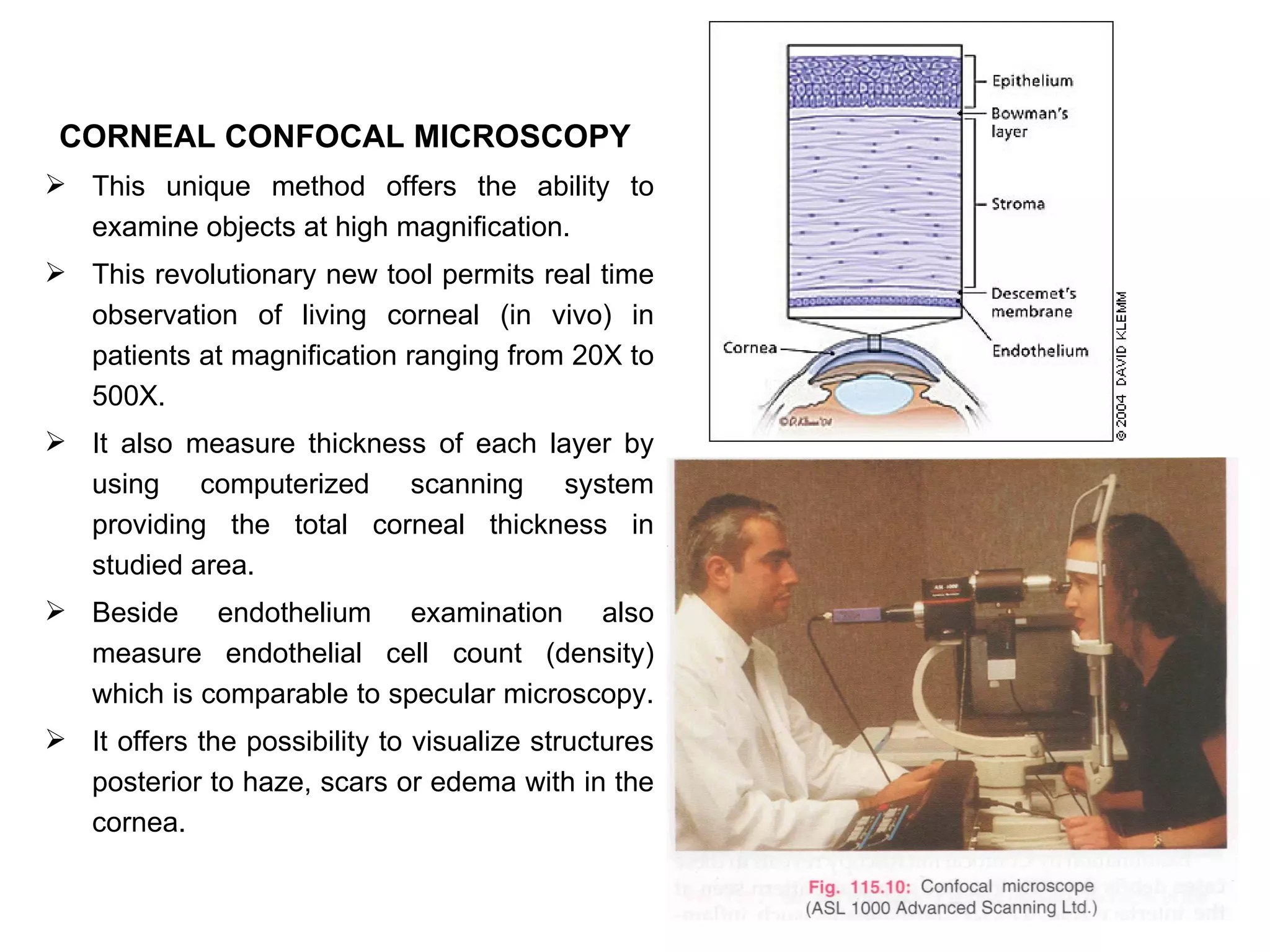
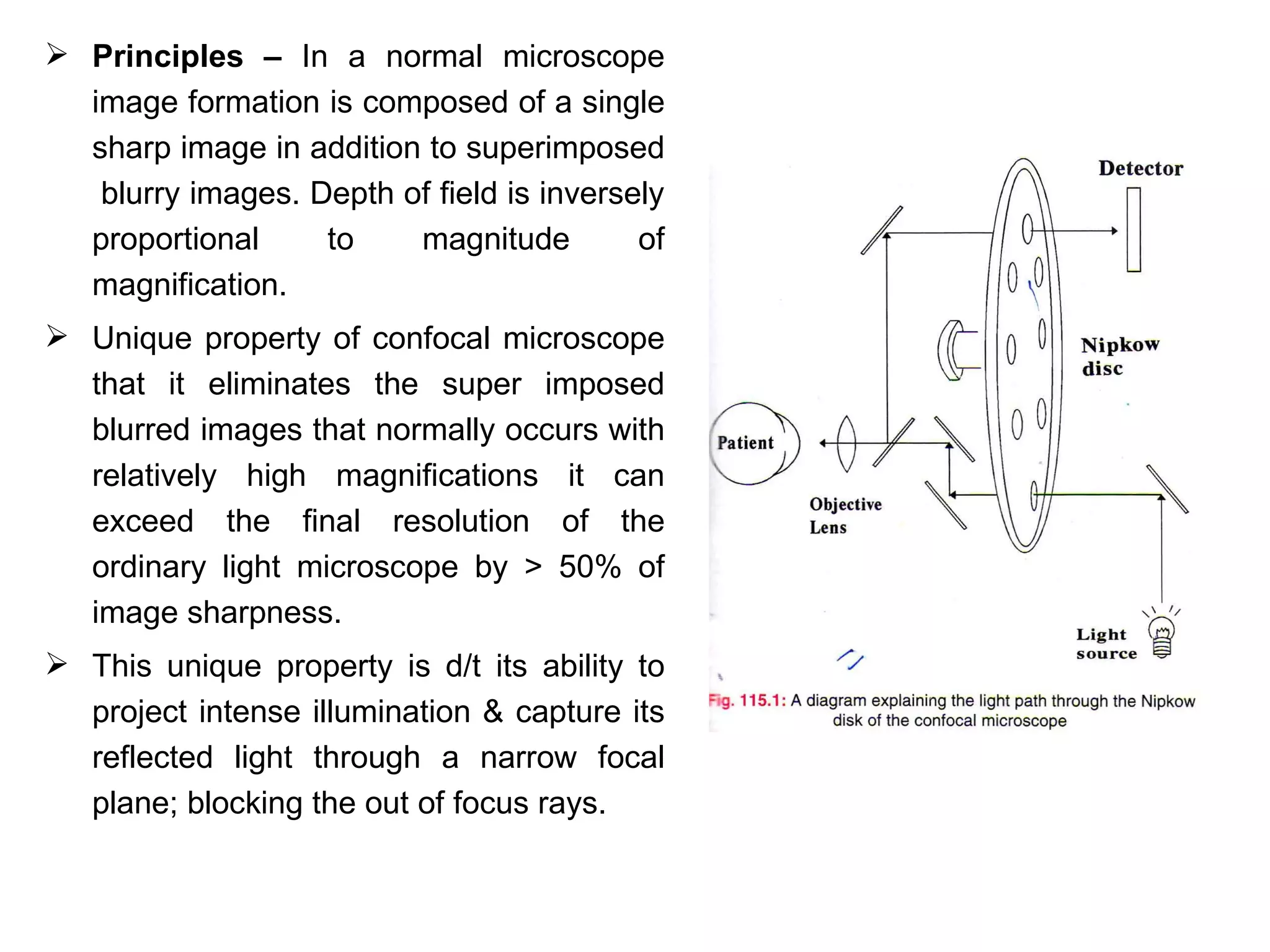
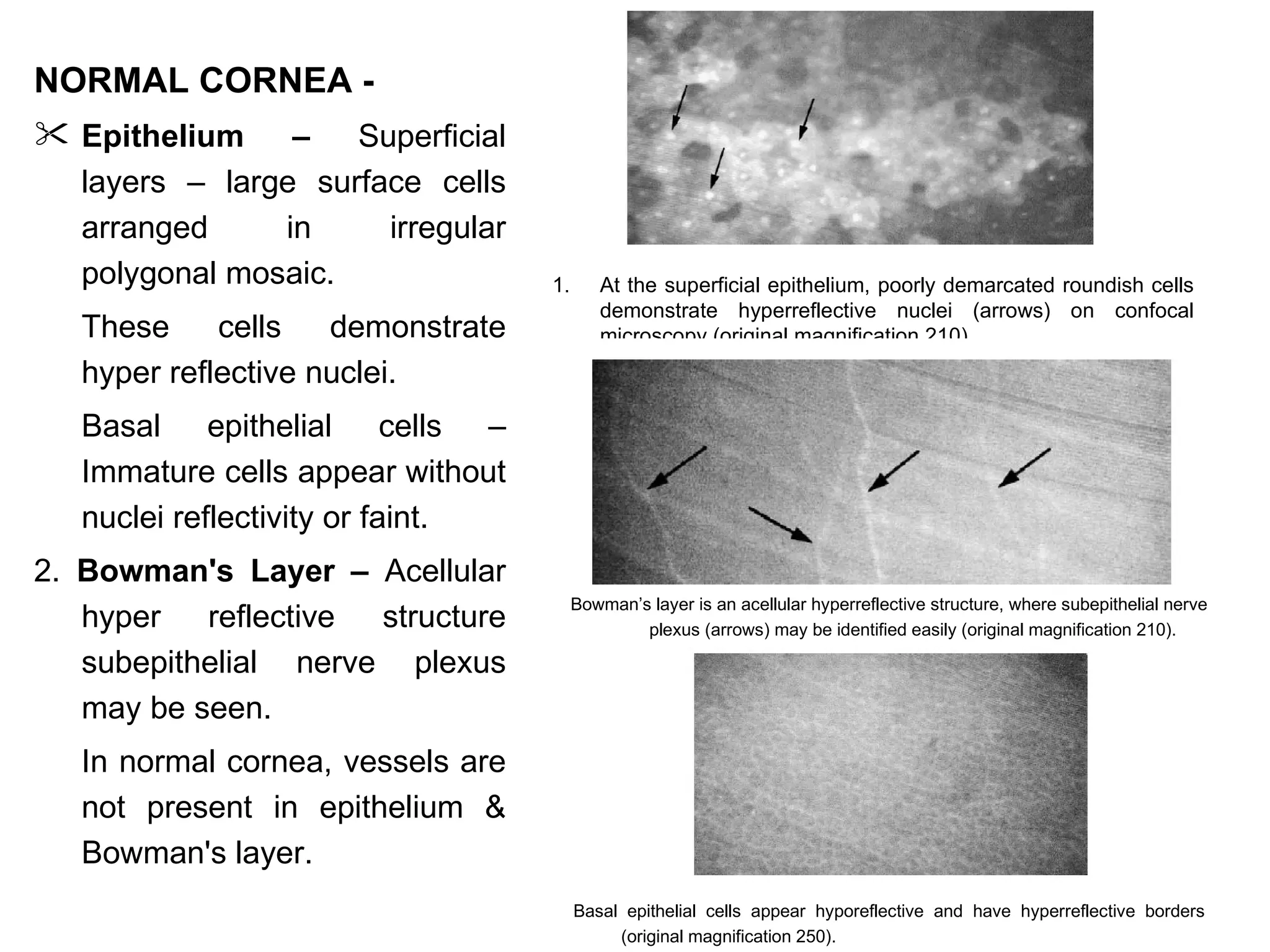
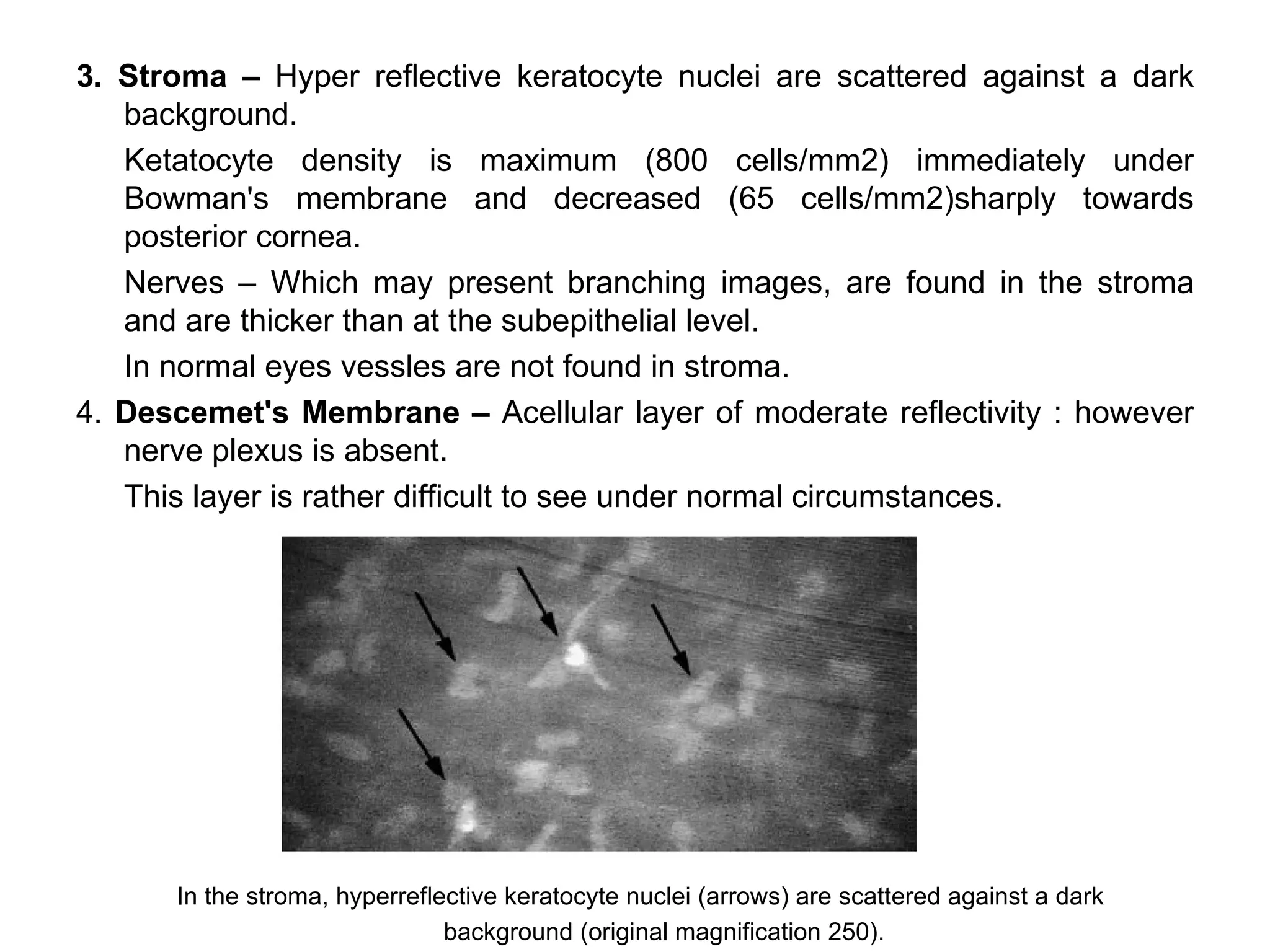
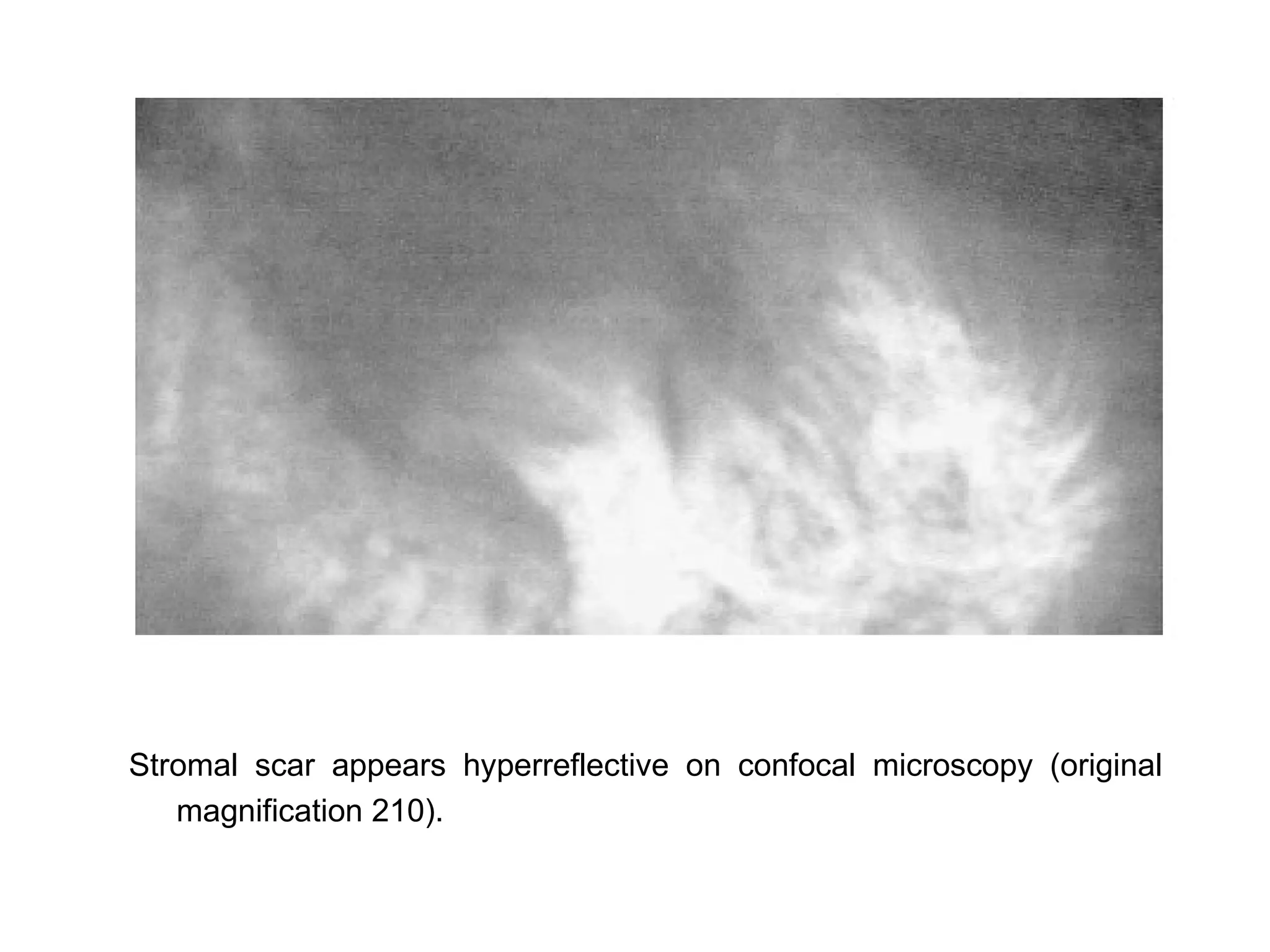
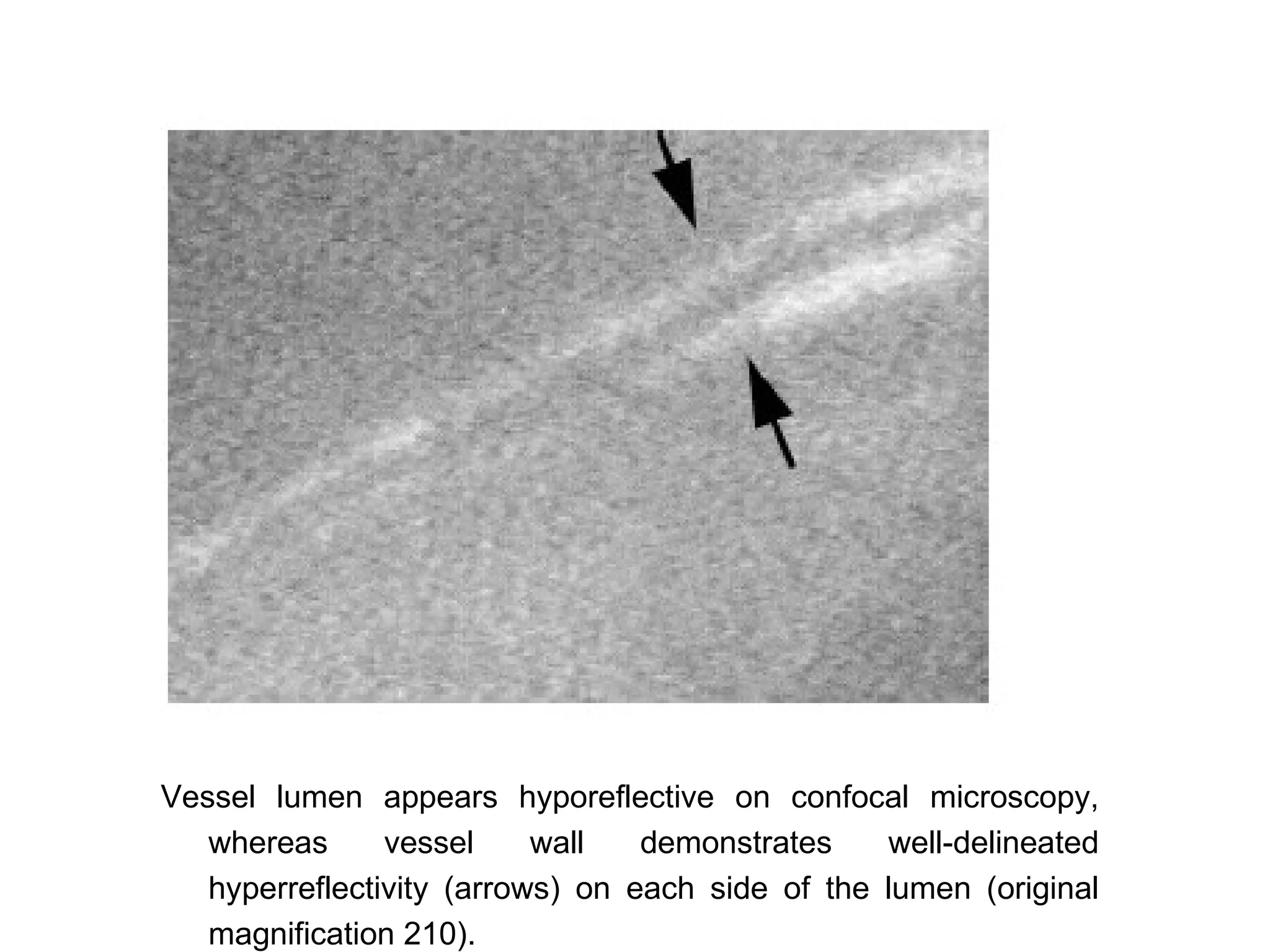
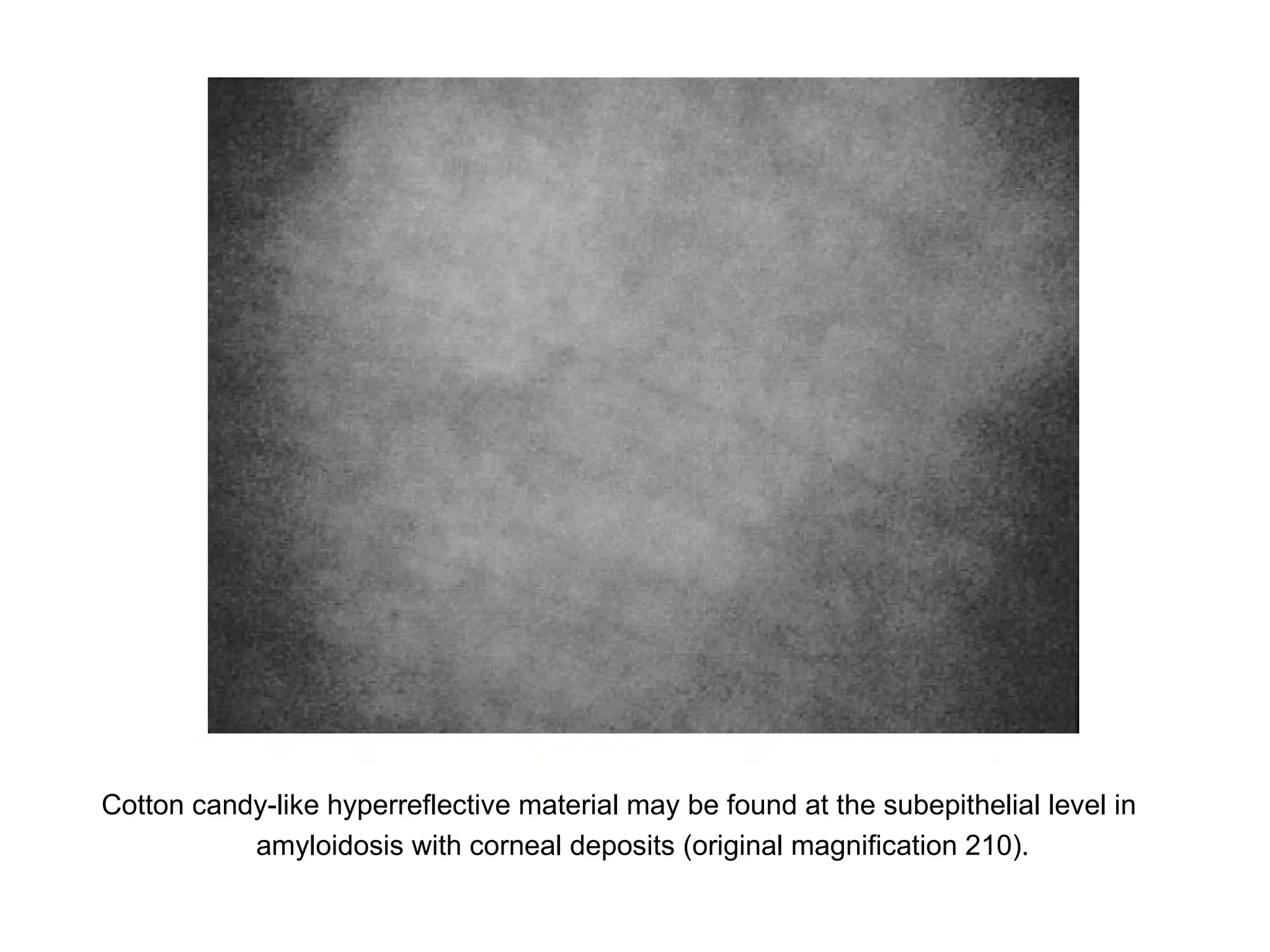
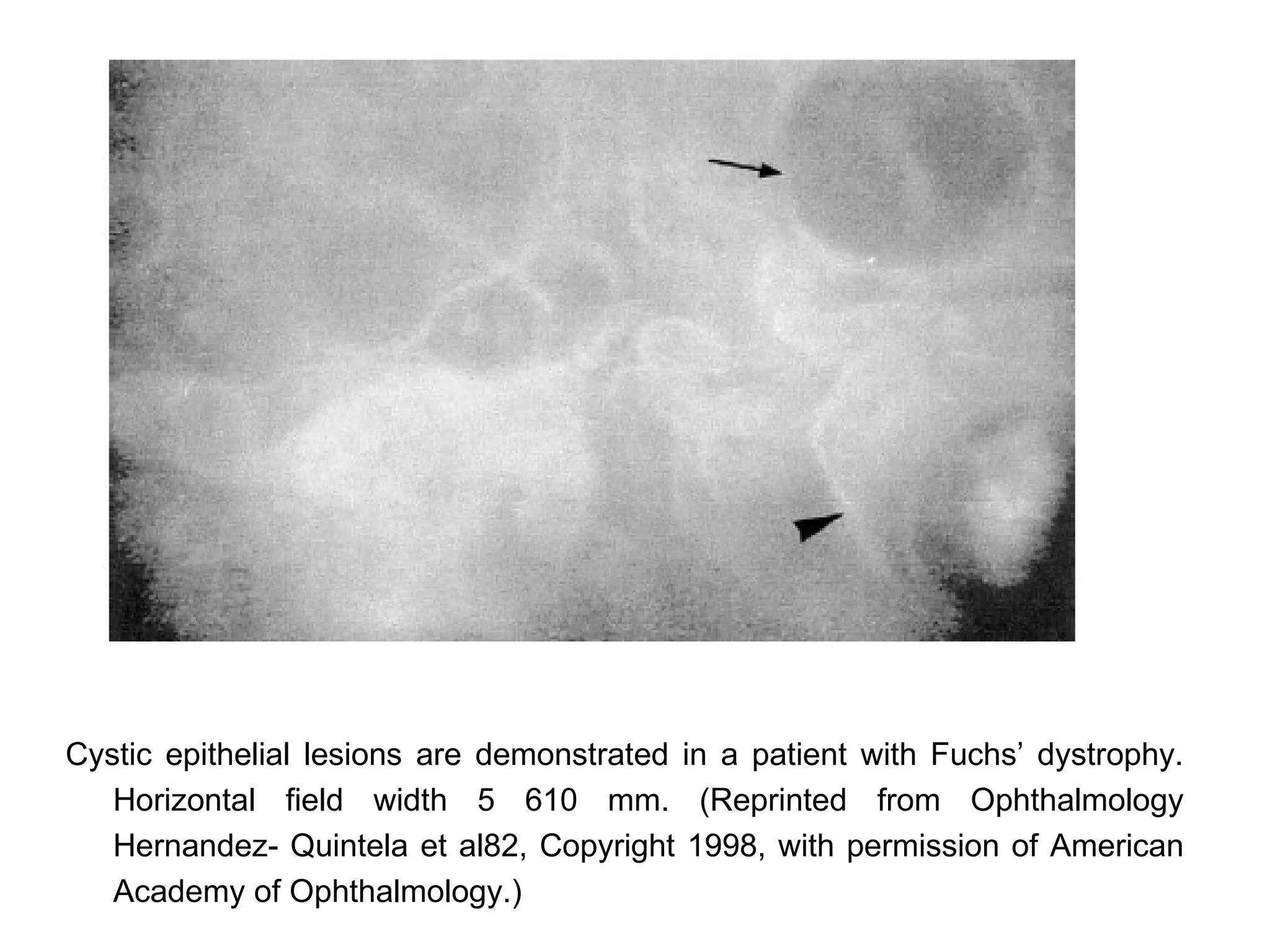
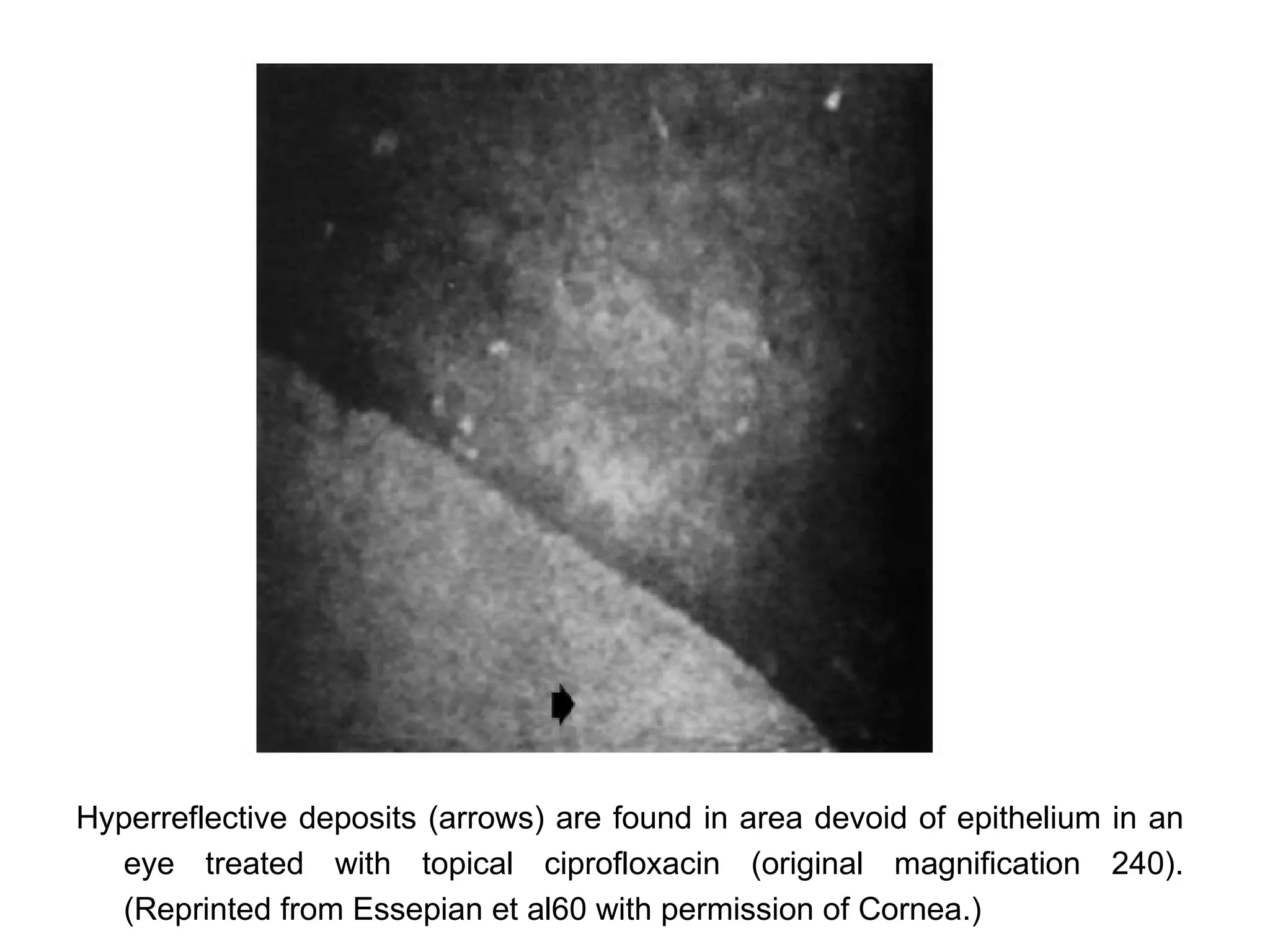
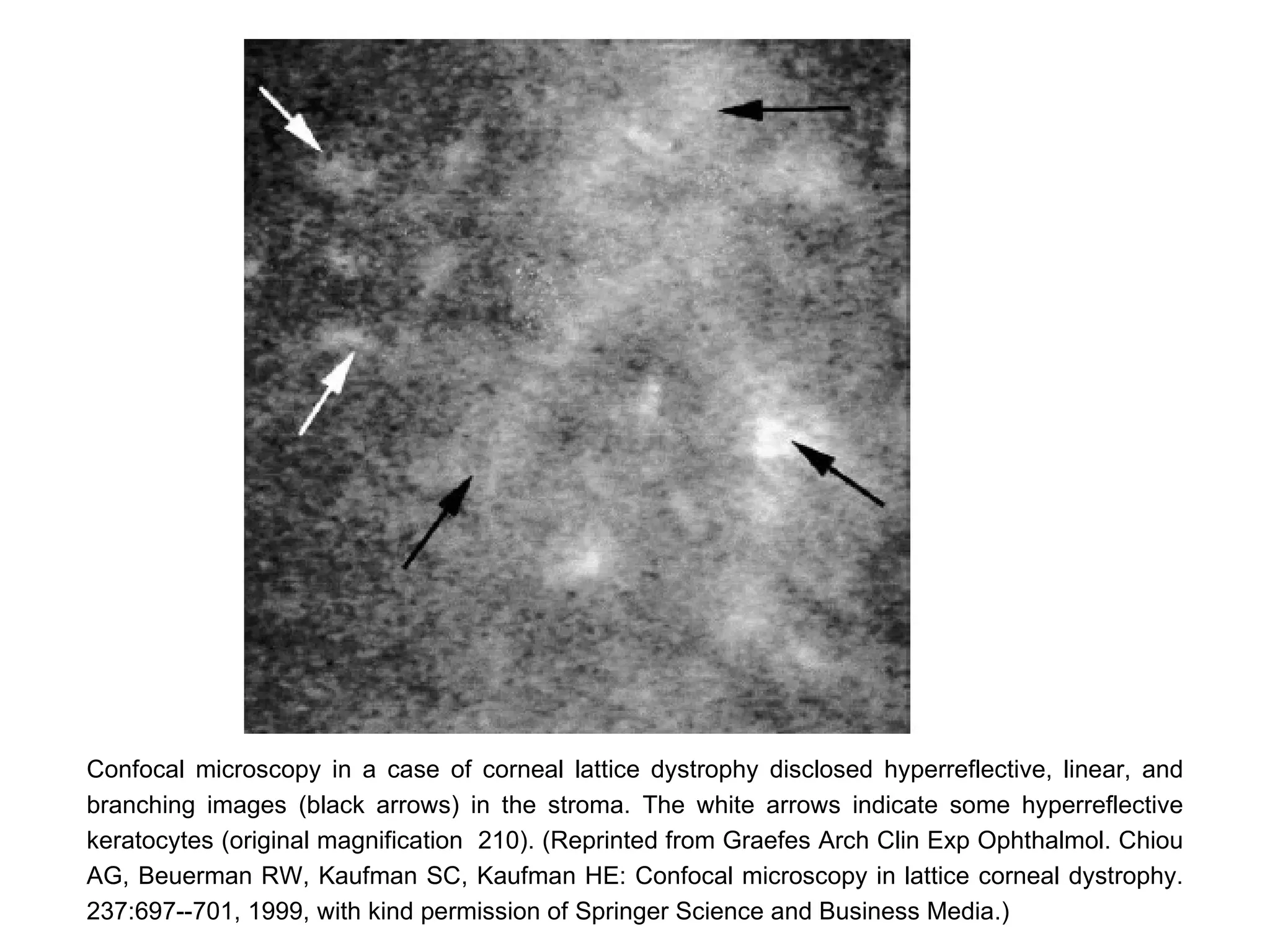
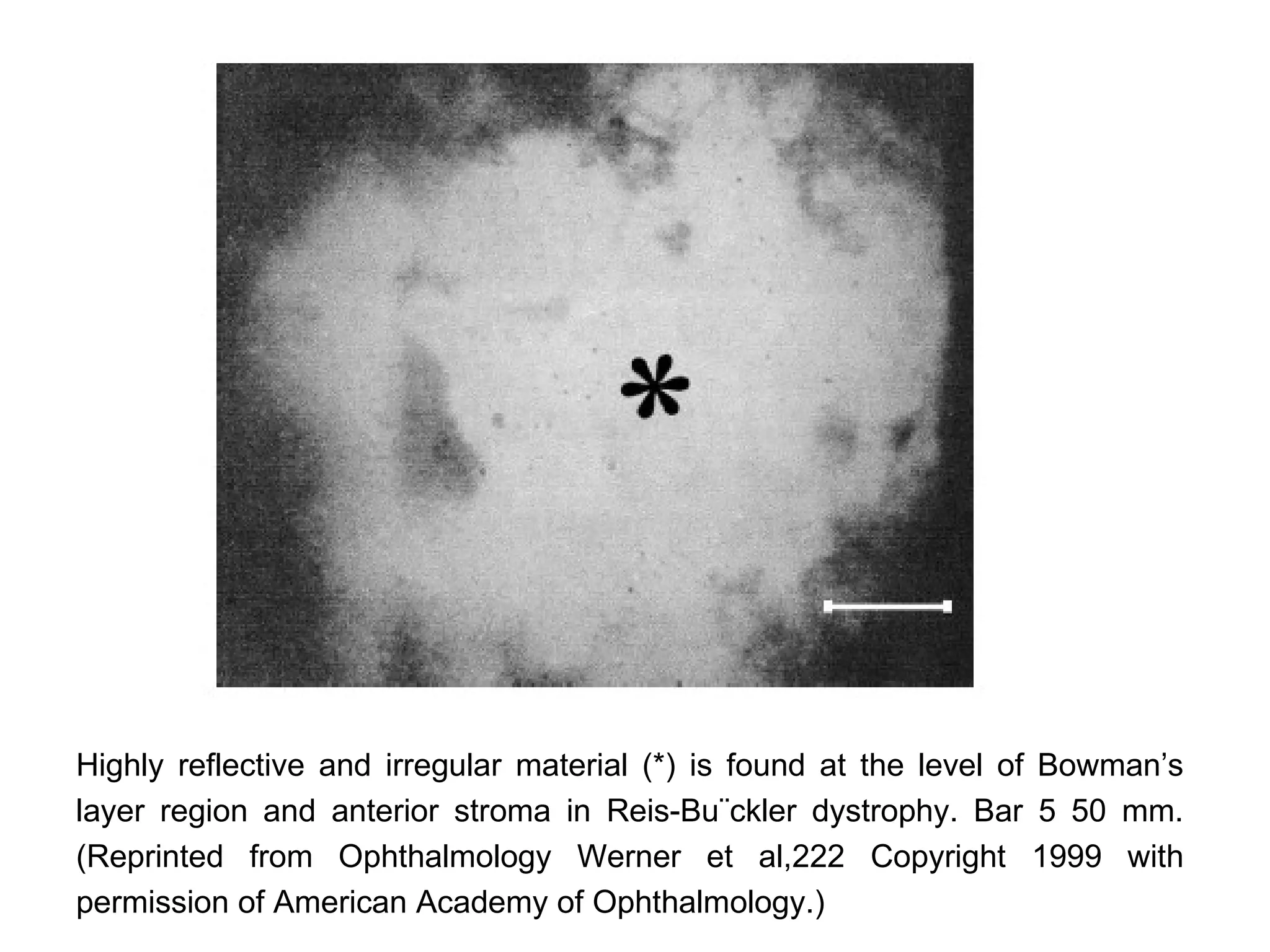
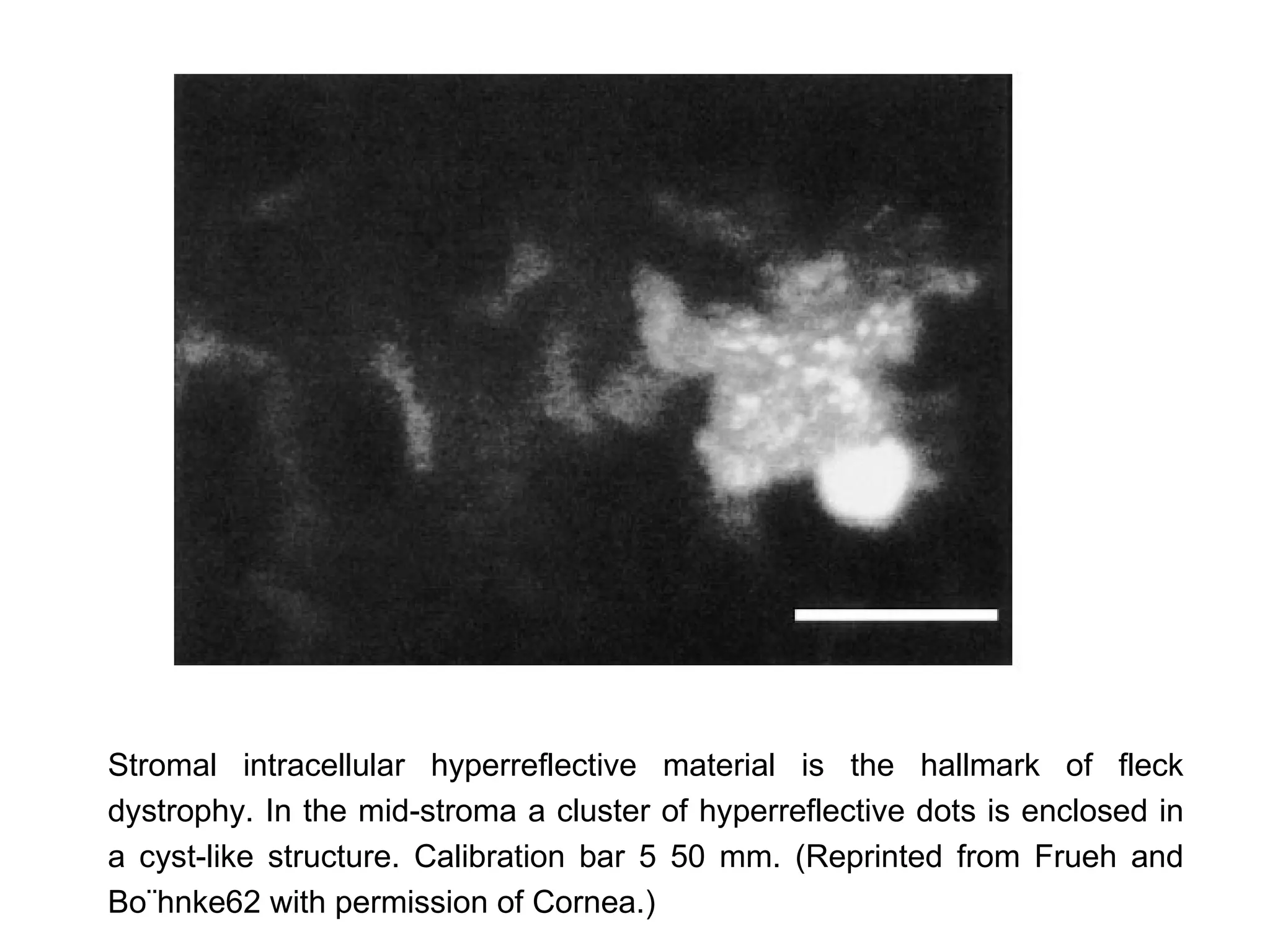
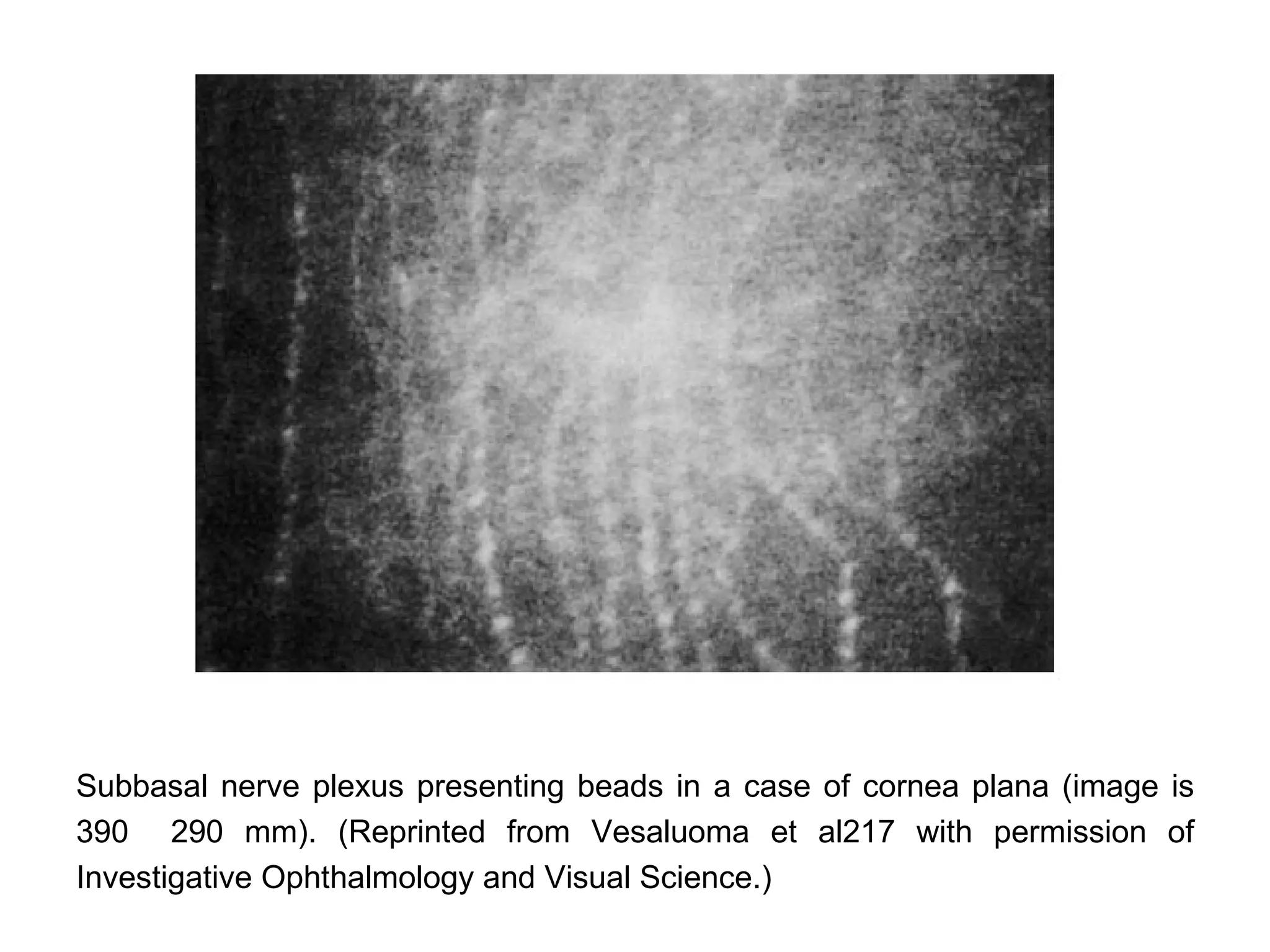
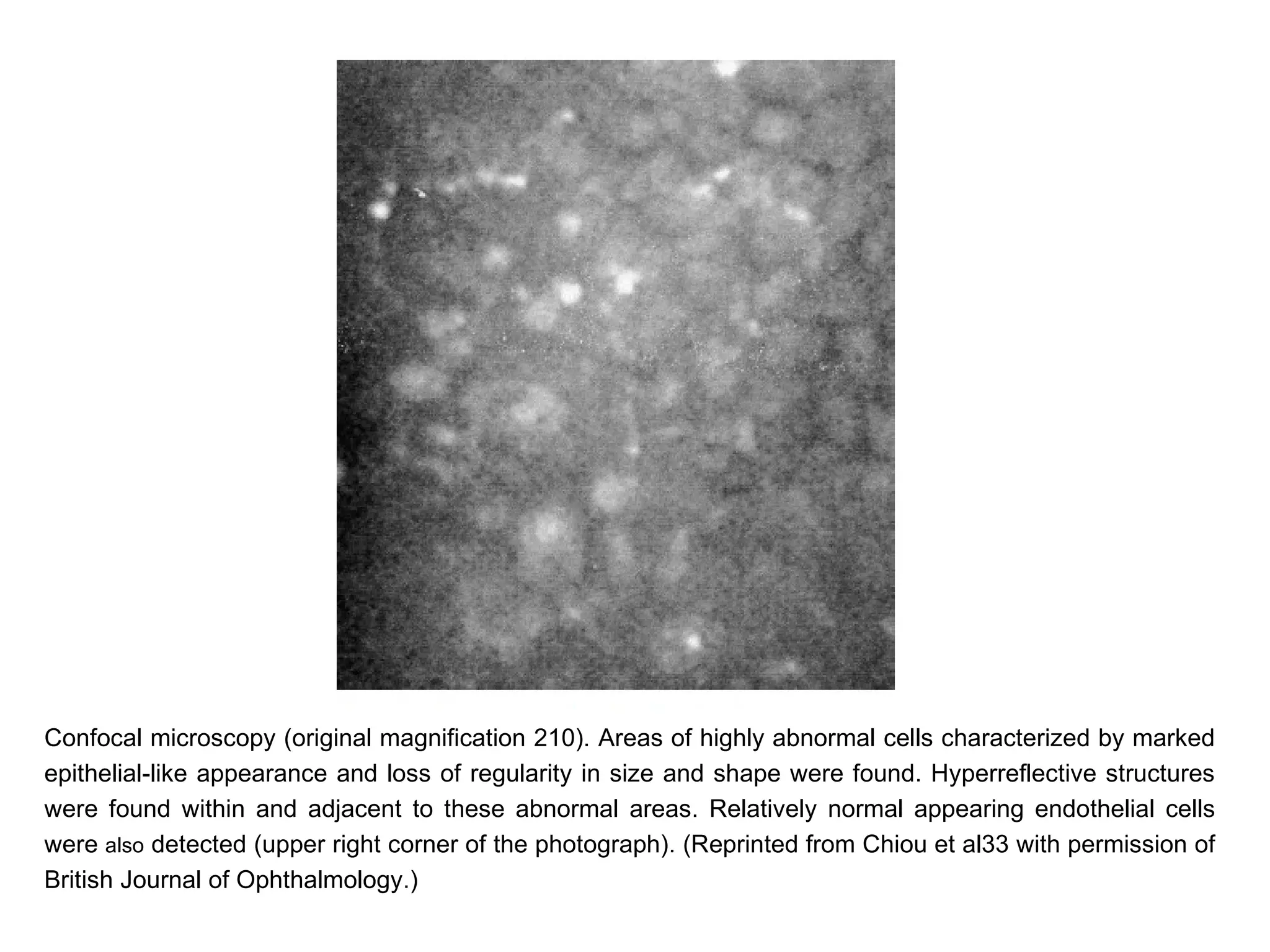
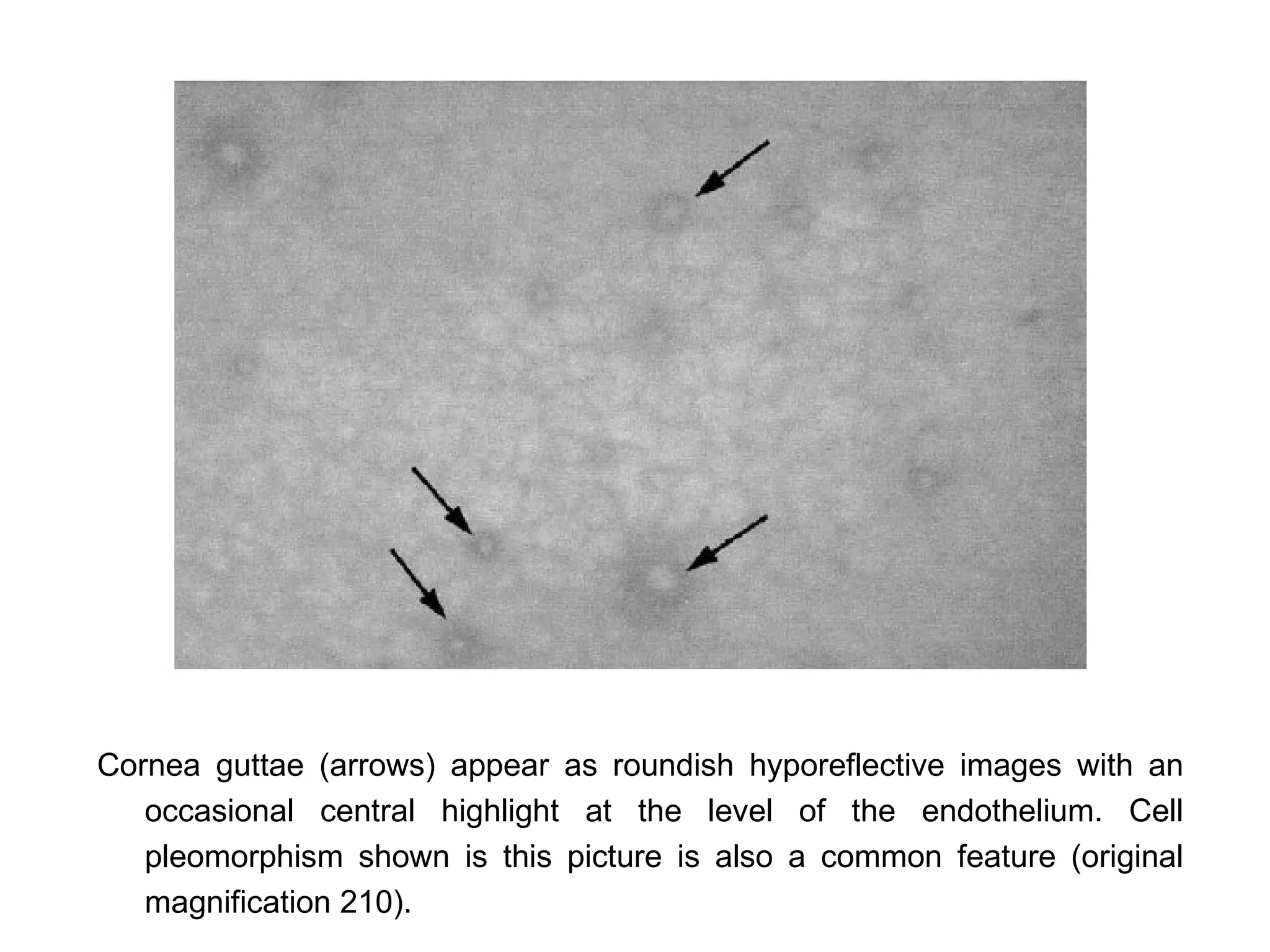
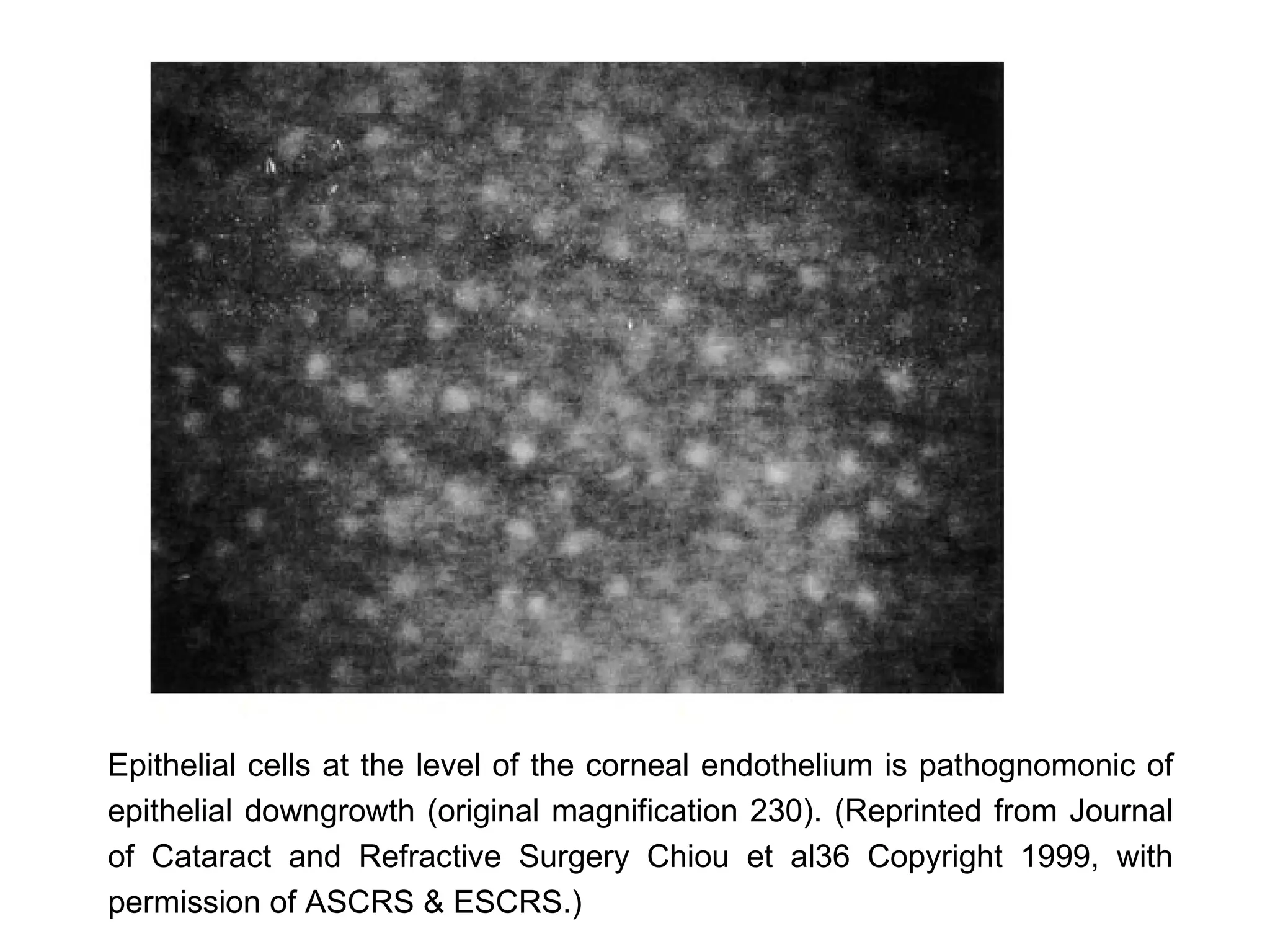
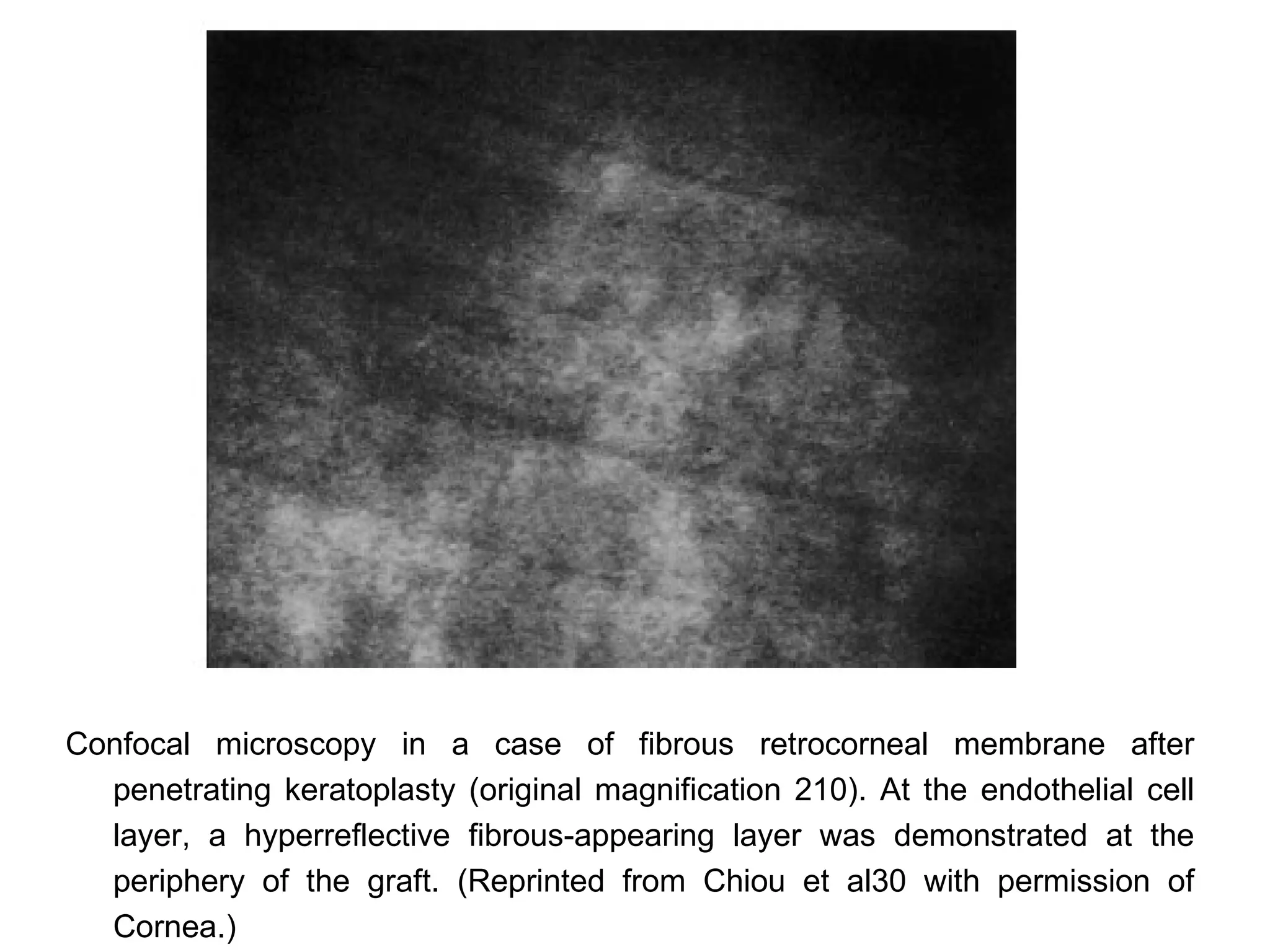
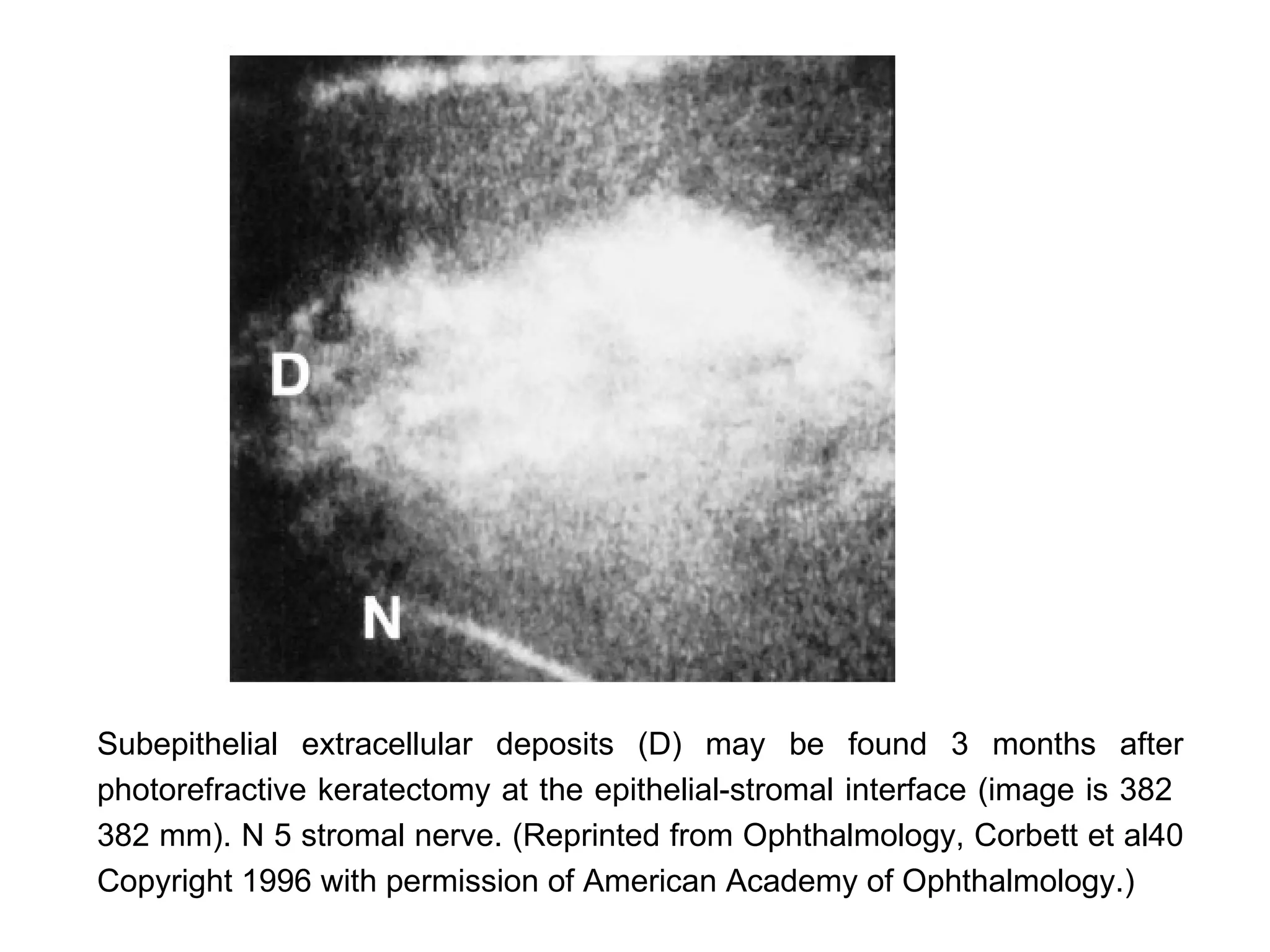
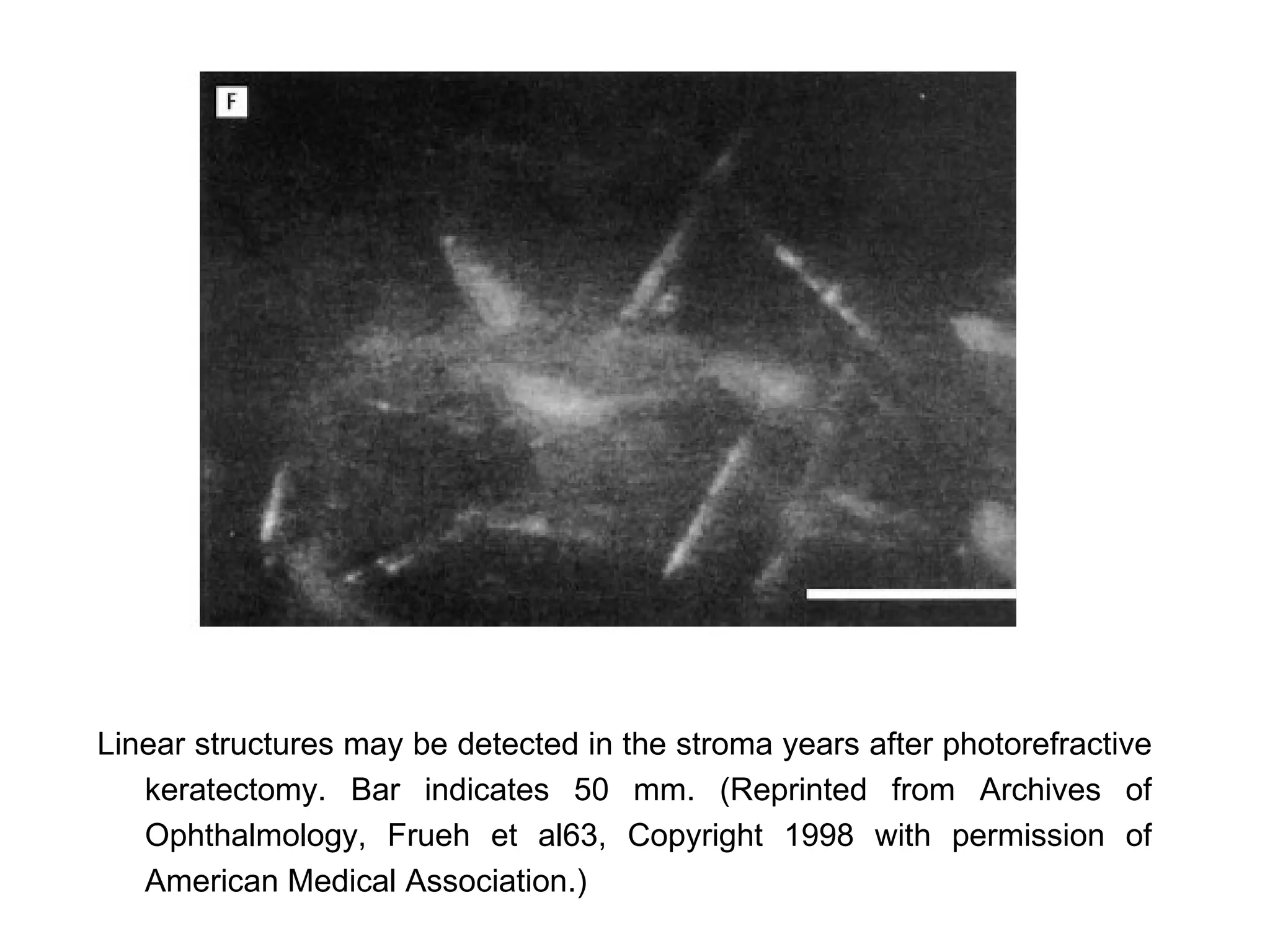
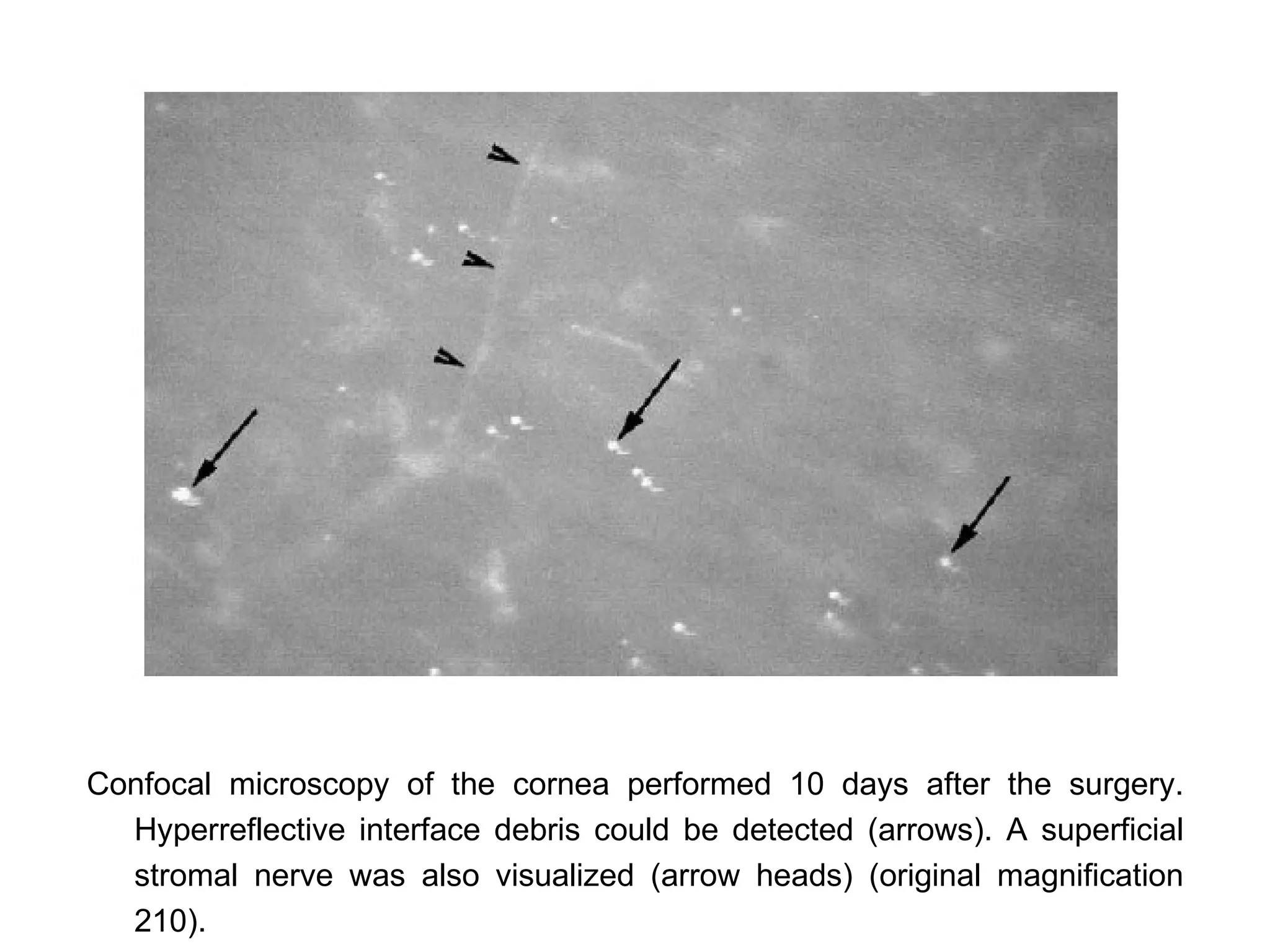
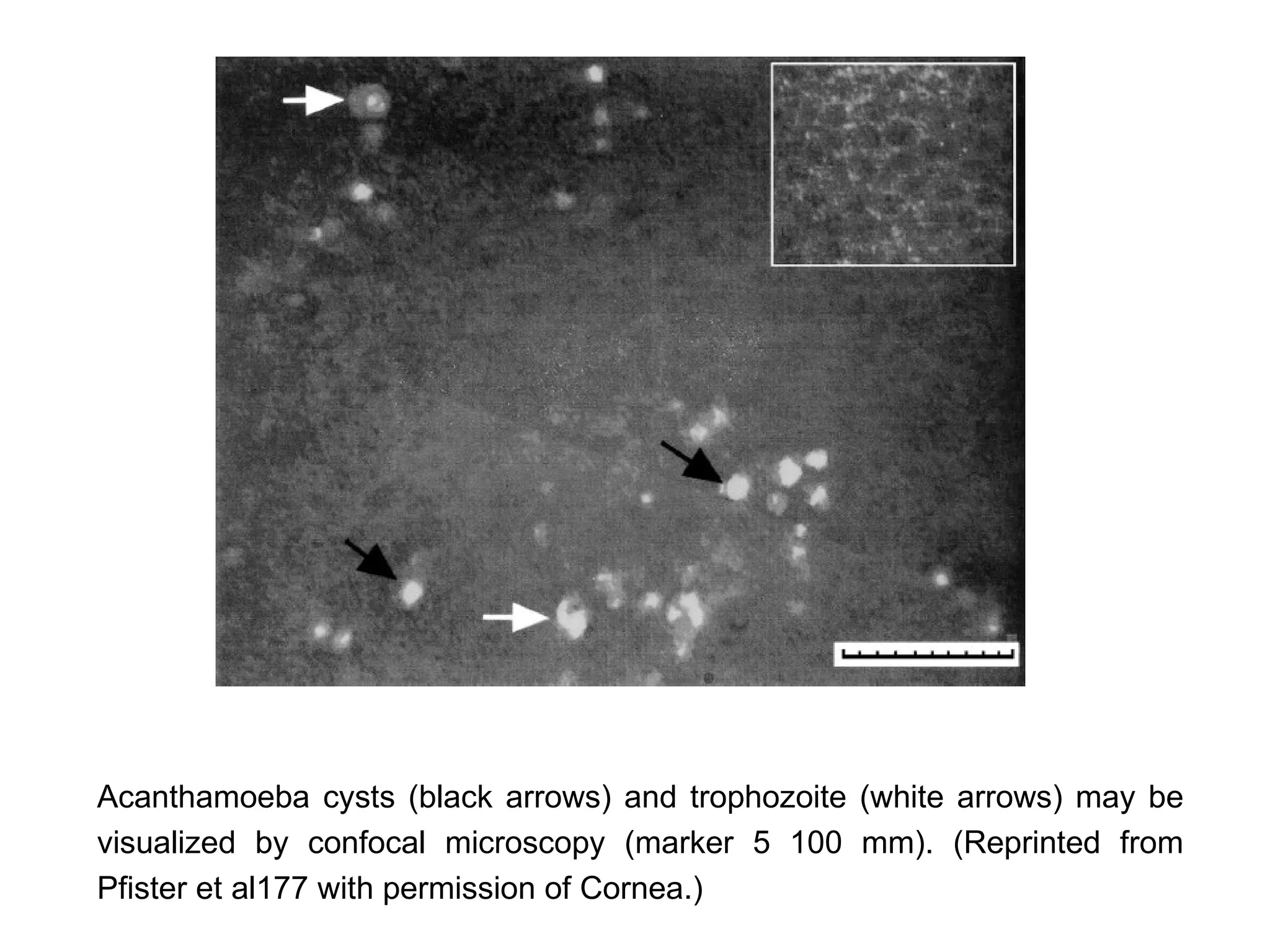
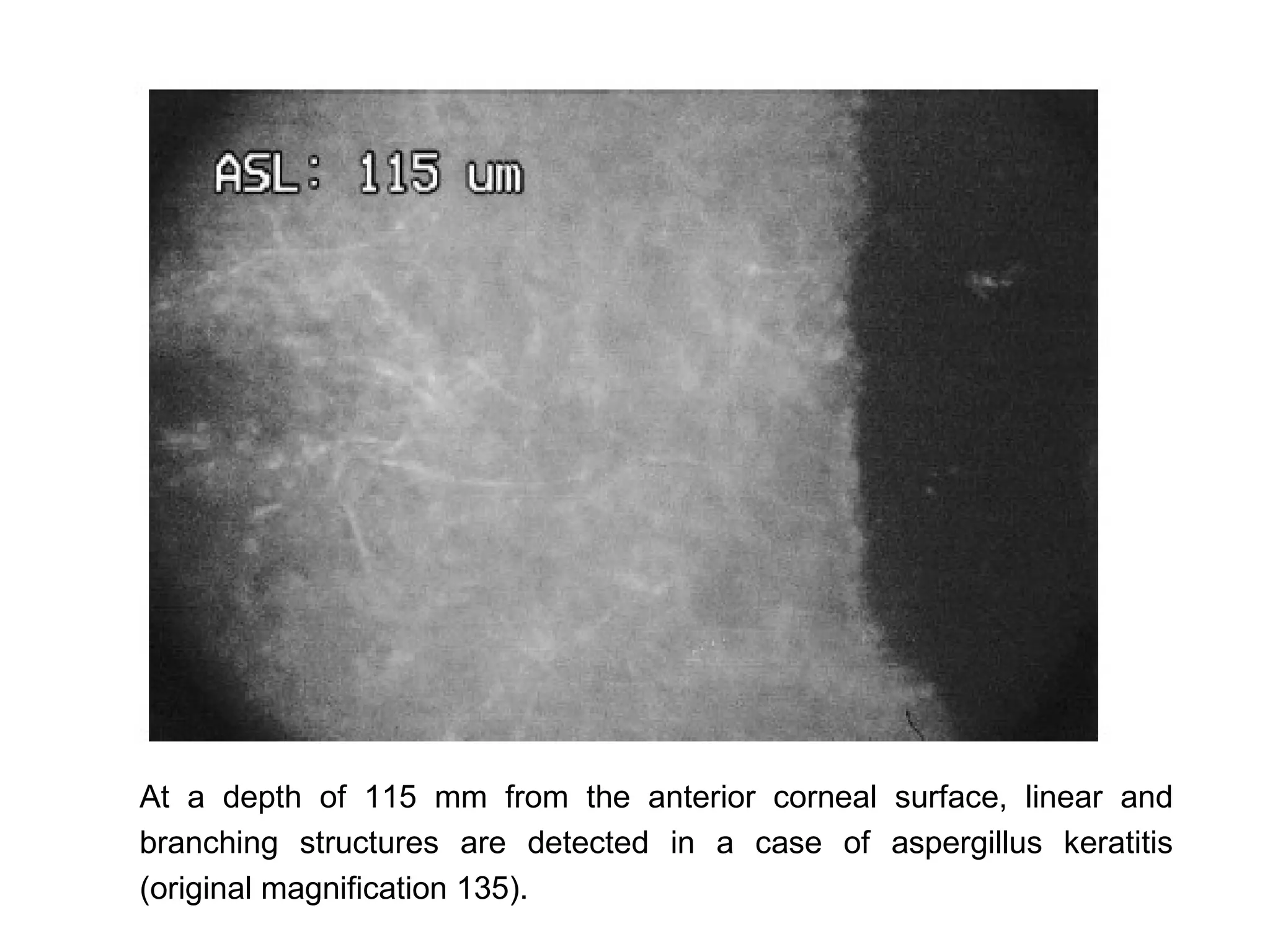
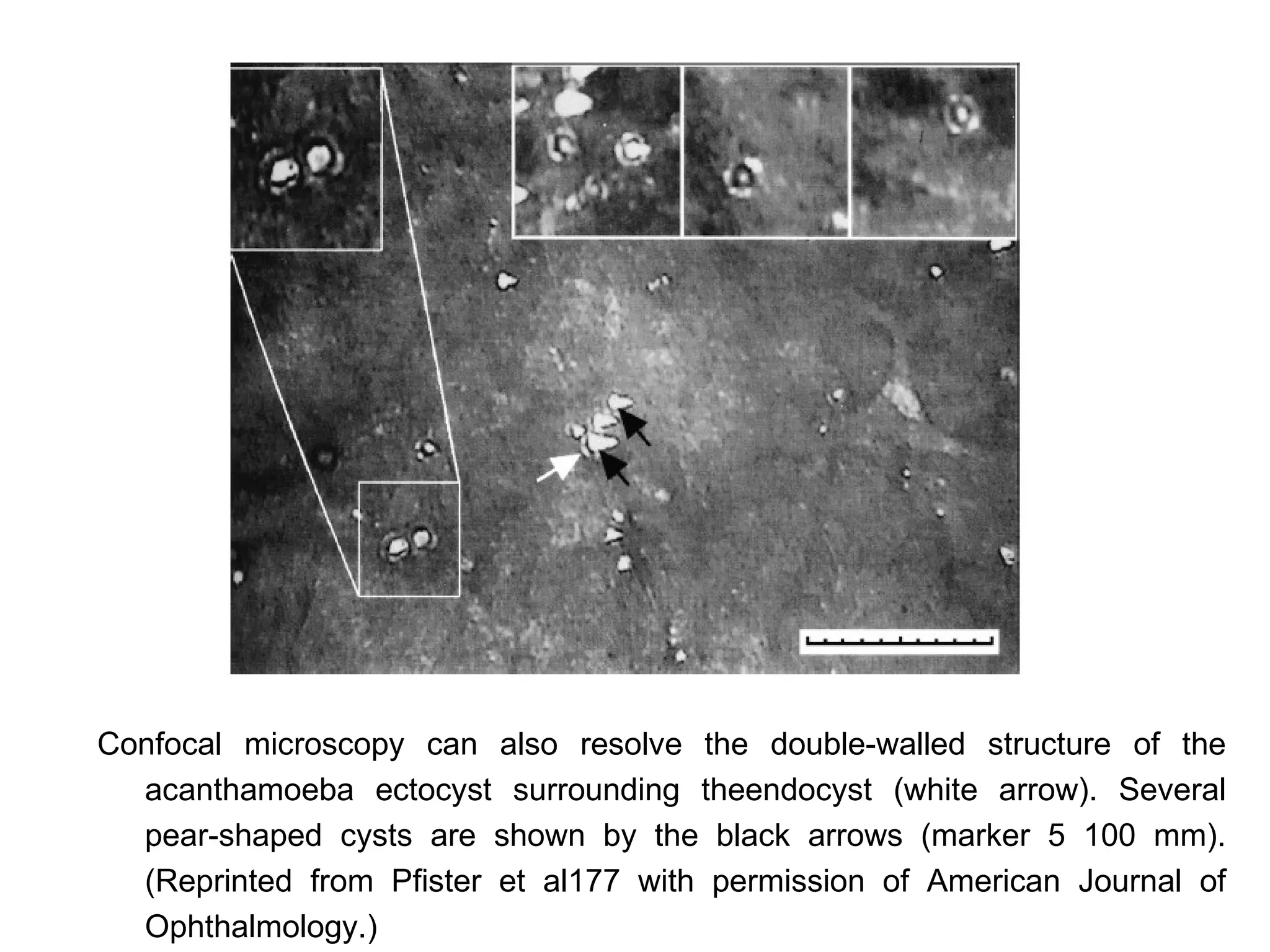
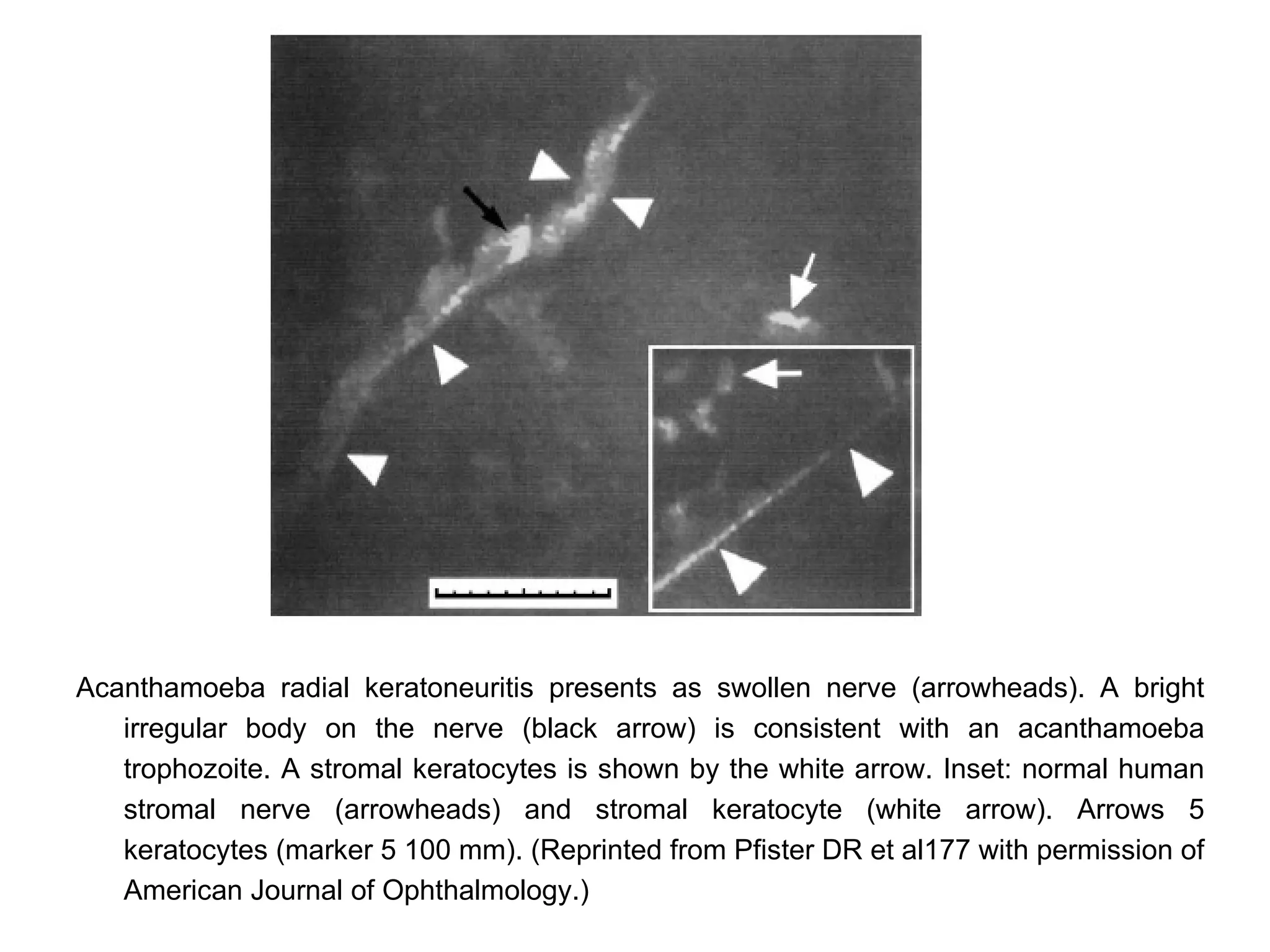
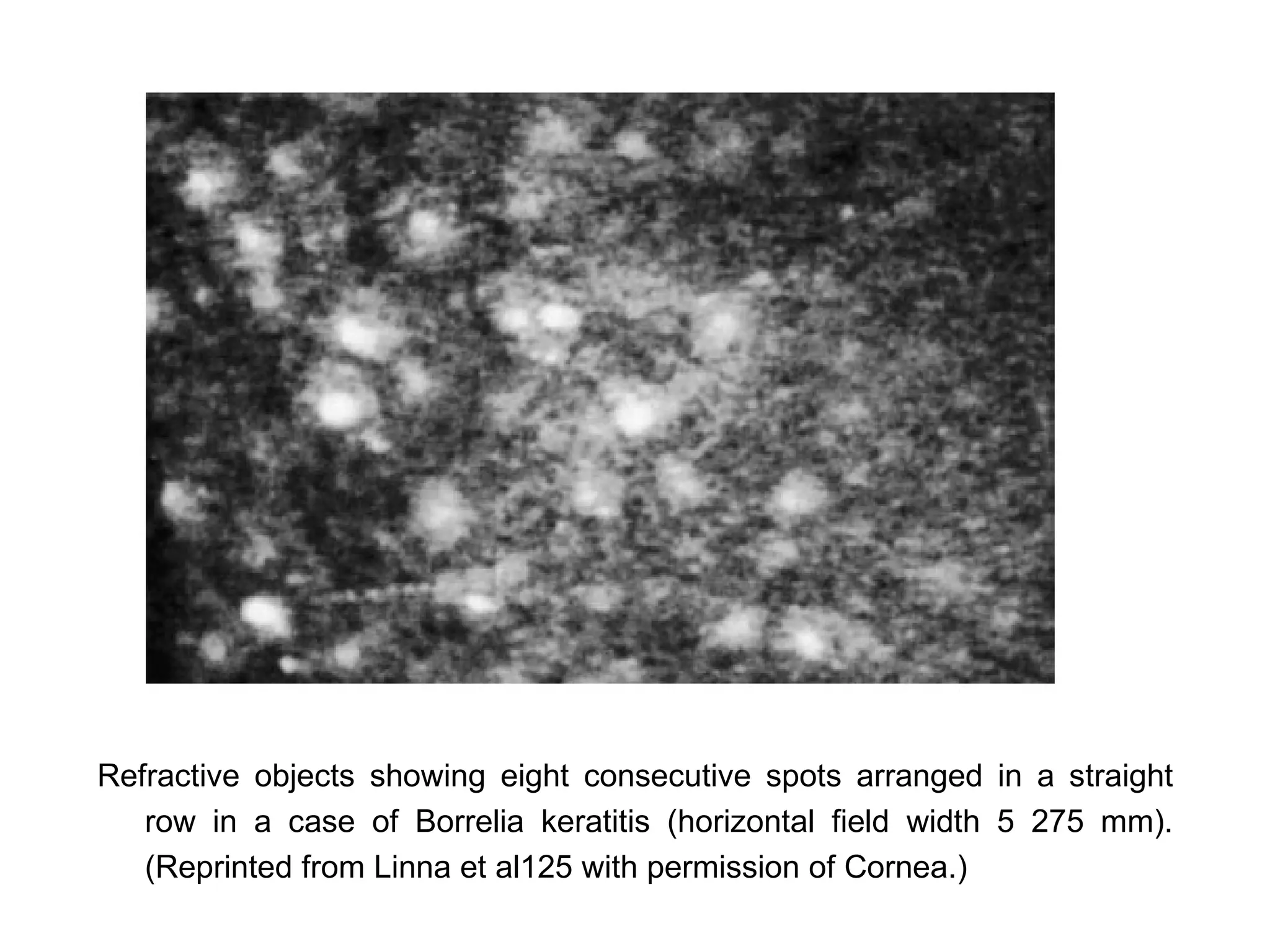
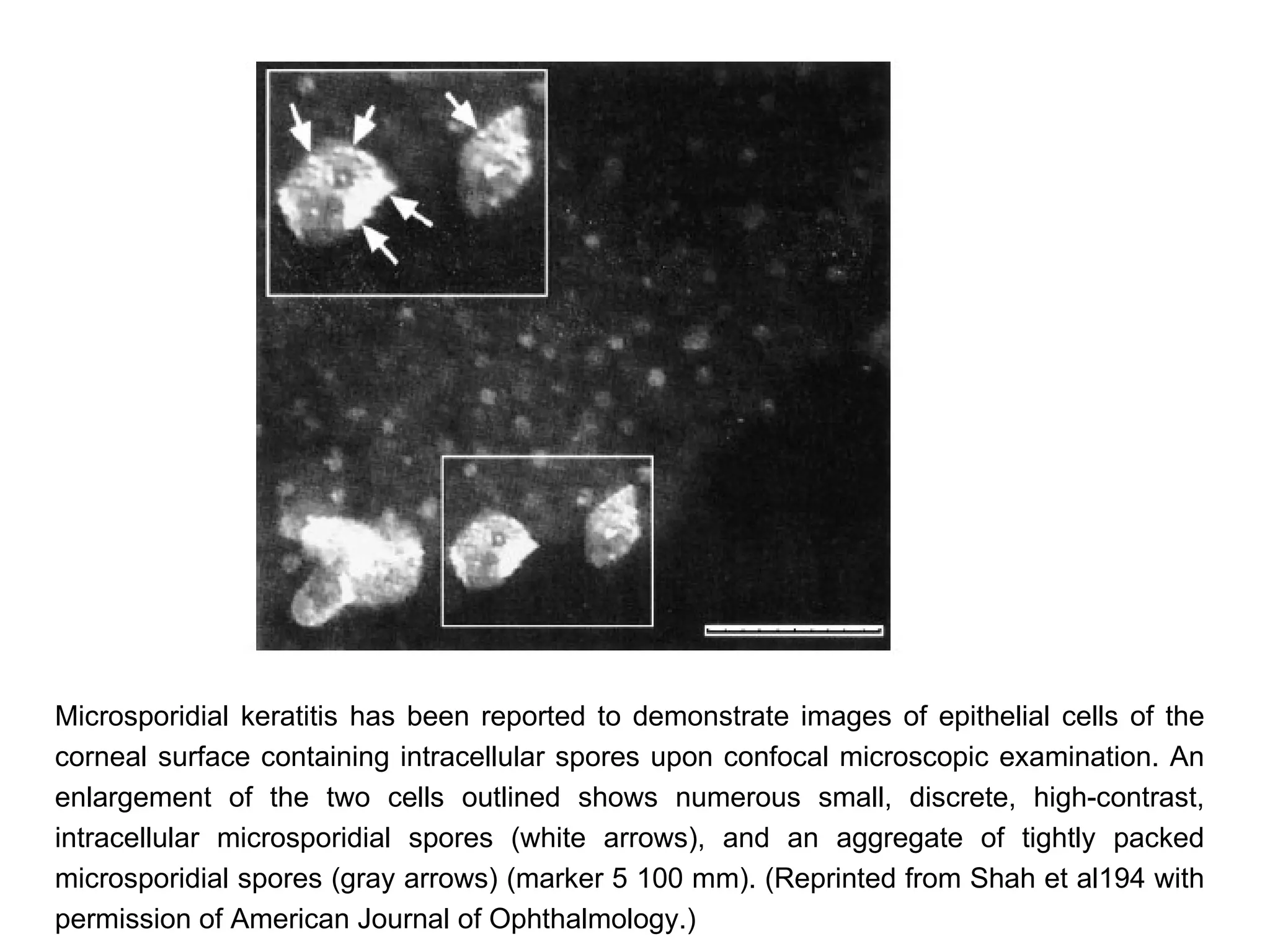
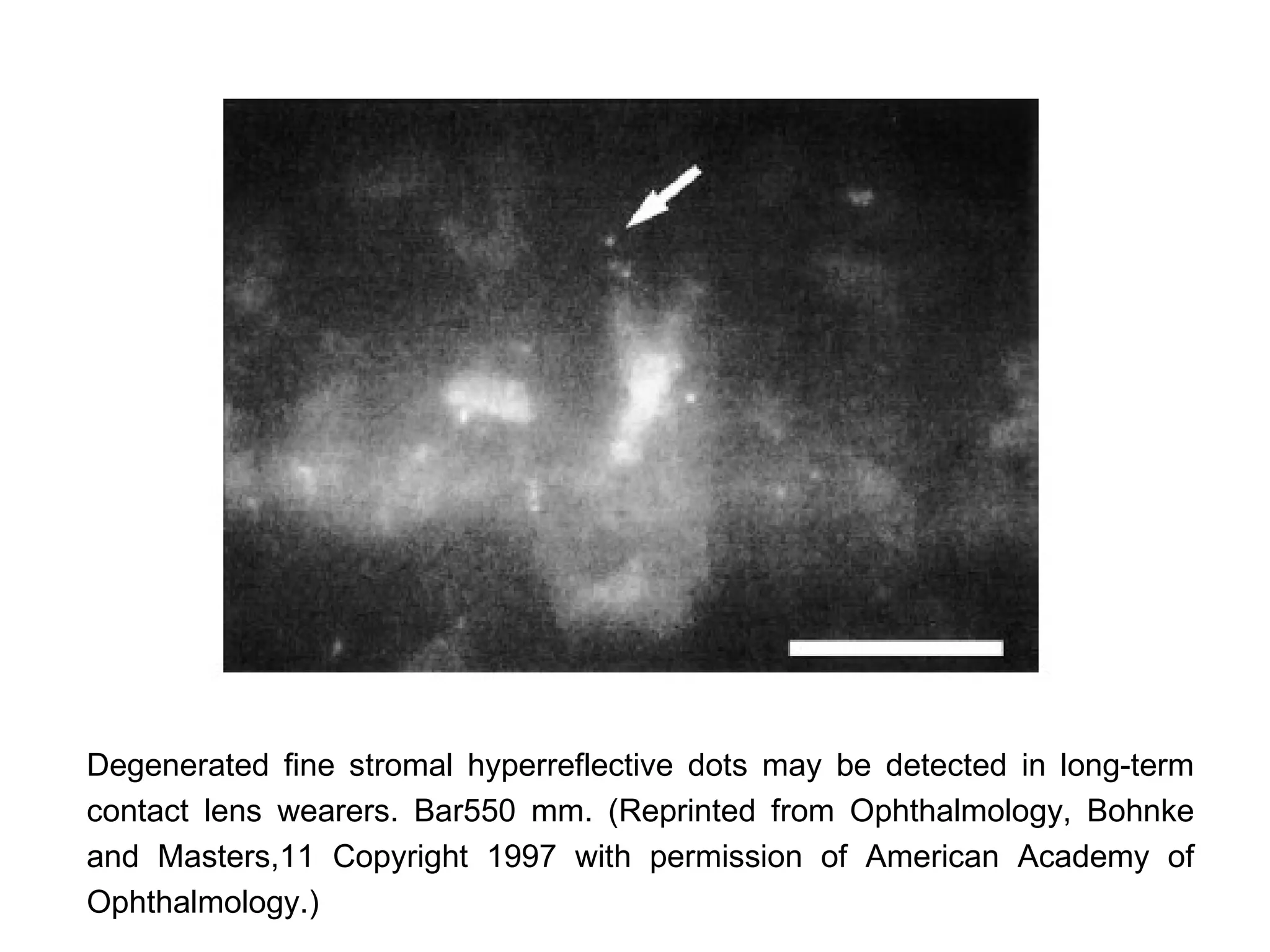
This document discusses techniques for measuring corneal thickness and examining the cornea using confocal microscopy. It describes pachymetry methods including optical, ultrasonic, and specular microscopy pachymetry. Ultrasonic pachymetry is now the preferred method due to its ease of use, precision and ability to measure thickness eccentrically. Confocal microscopy allows high magnification examination of the living cornea and measurement of thickness for each layer.