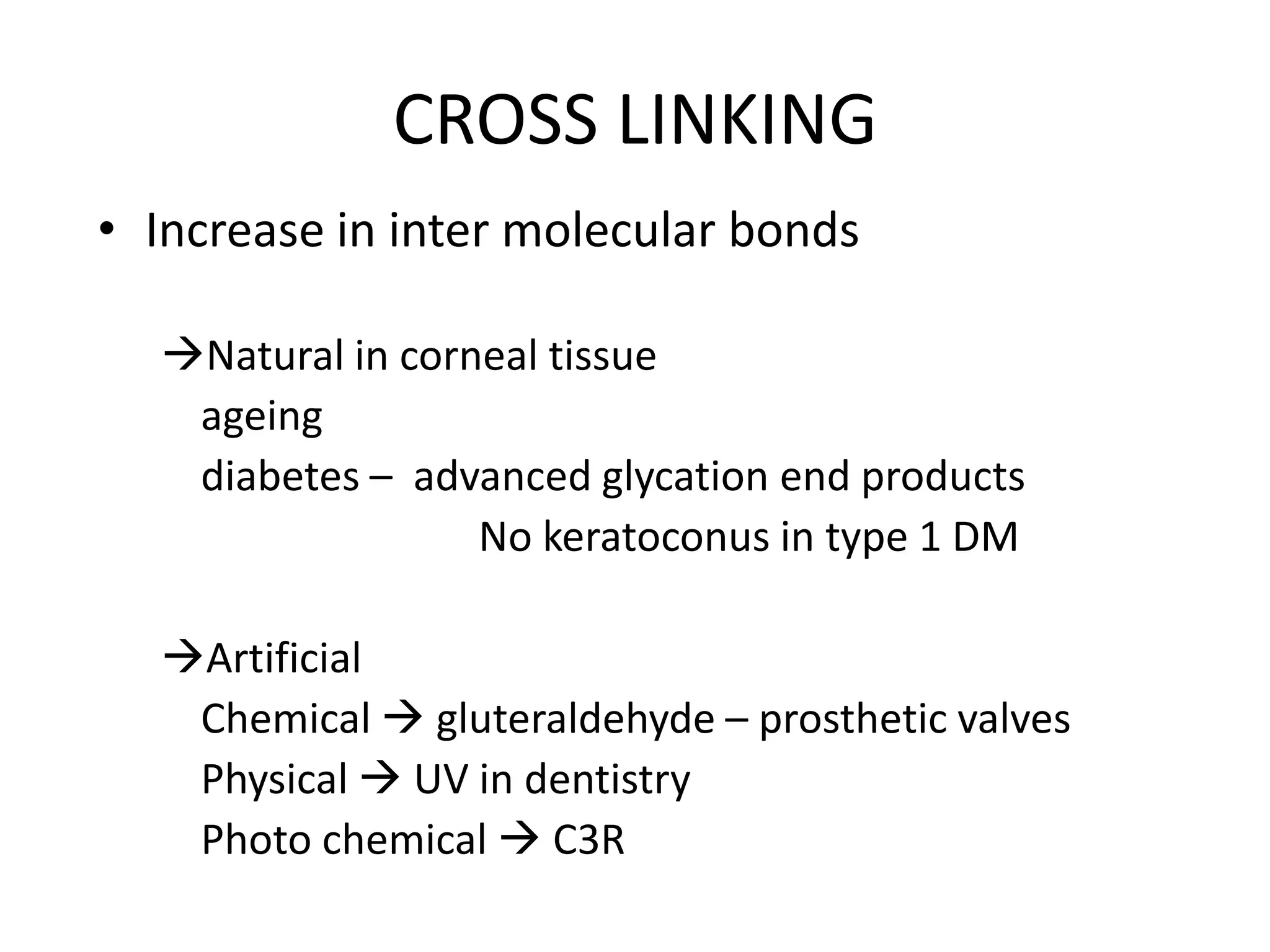
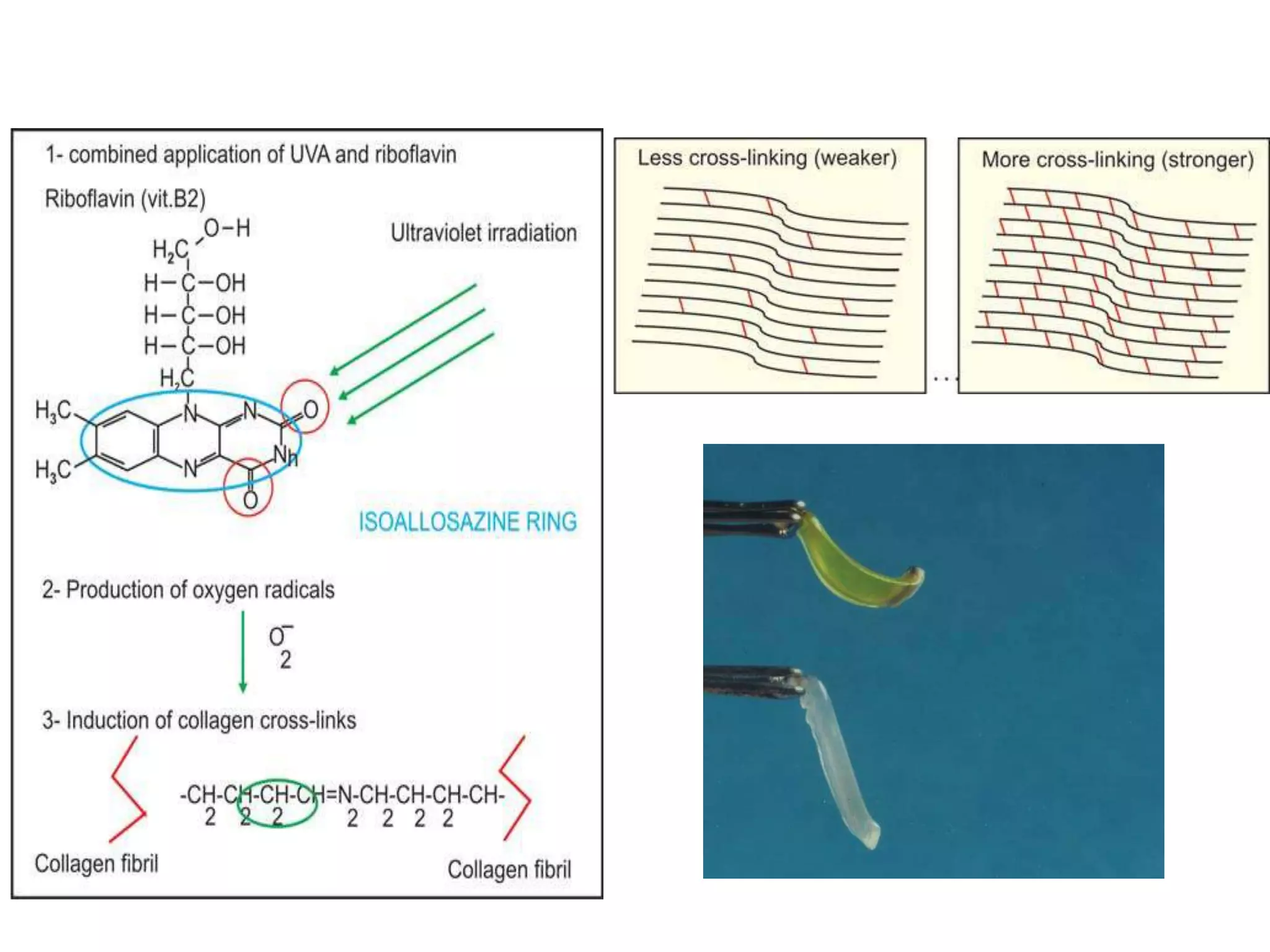
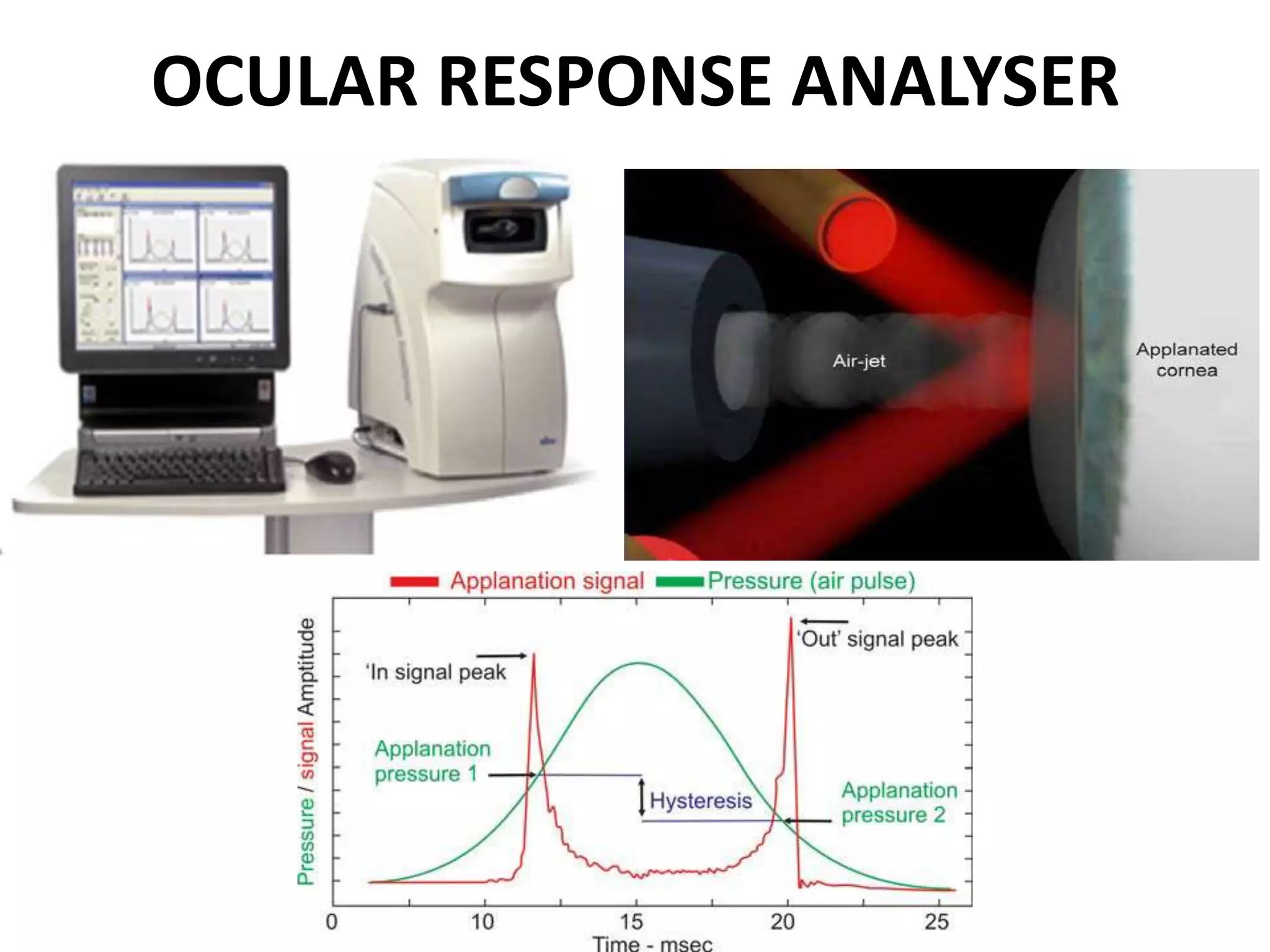
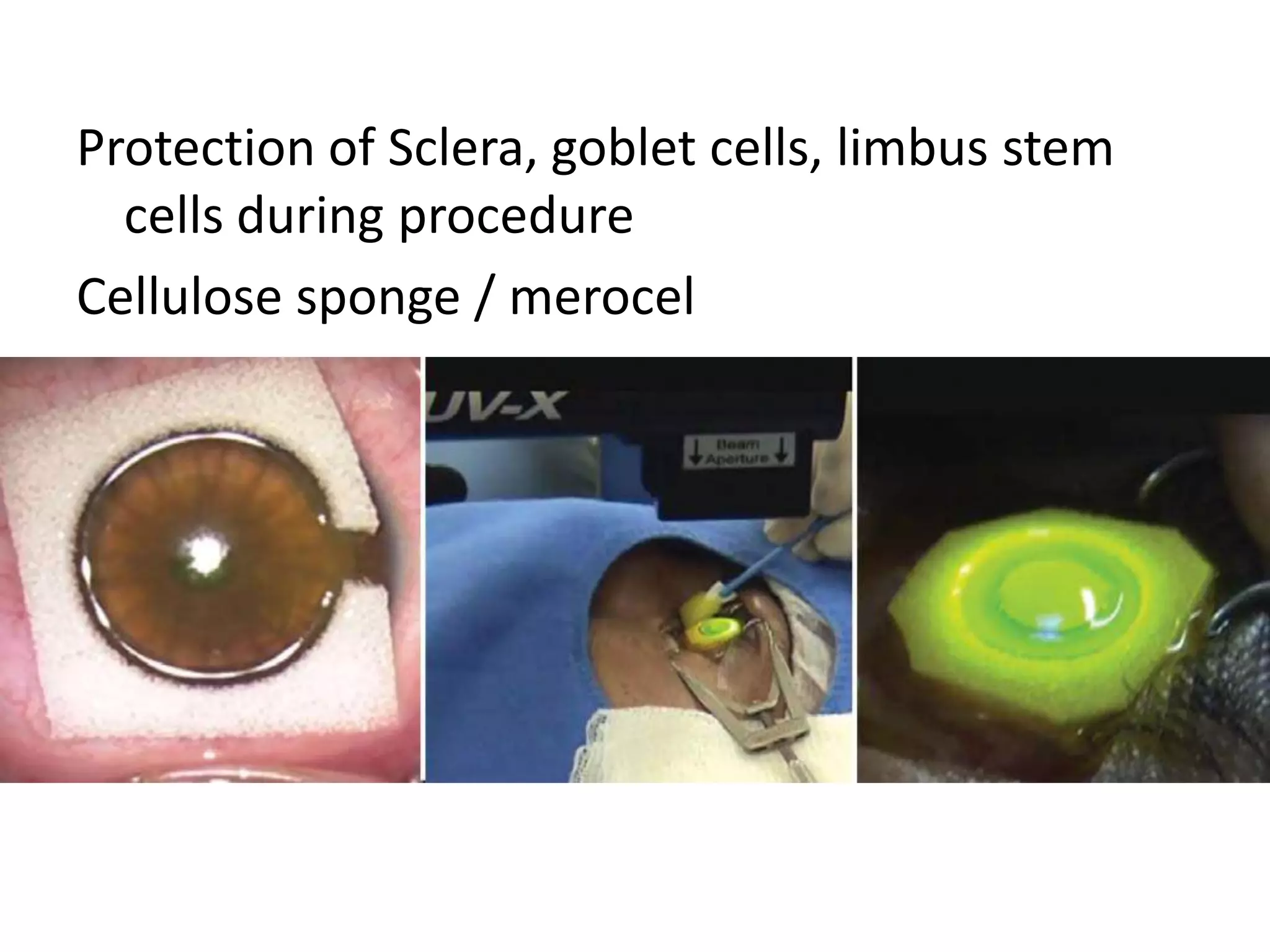
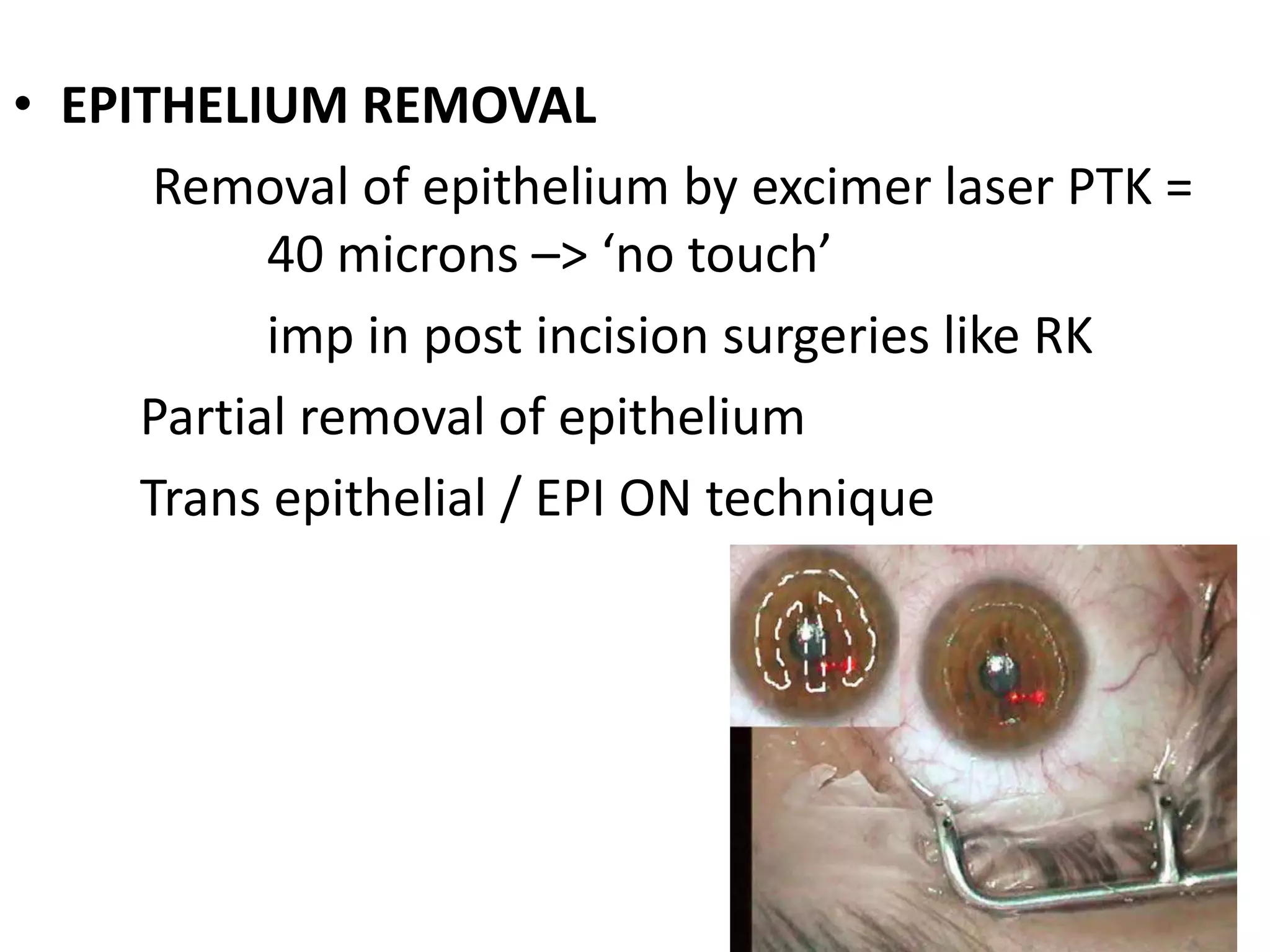
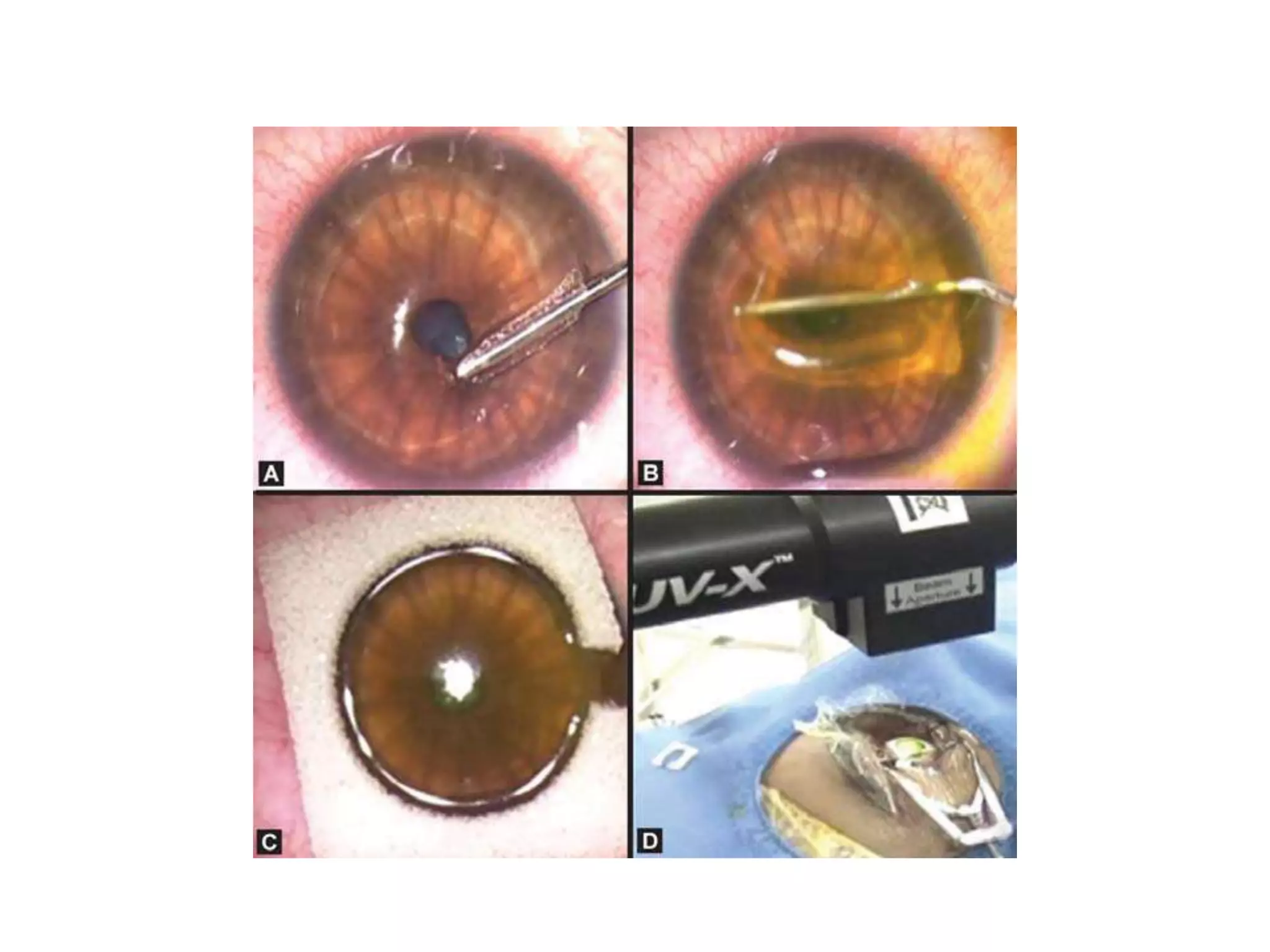
This document discusses corneal collagen cross linking (C3R), a treatment for keratoconus. It begins by describing keratoconus and its symptoms. It then discusses the original C3R protocol developed by Seiler and Spoerl, which involves removing the corneal epithelium, soaking the cornea in riboflavin, and exposing it to UV light. Modifications to the protocol aim to reduce complications by using higher irradiance for less time, different riboflavin delivery methods, and leaving the epithelium intact. Studies show C3R increases corneal collagen bonds and rigidity while halting keratoconus progression in most cases. Contraindications and post-op care are also outlined