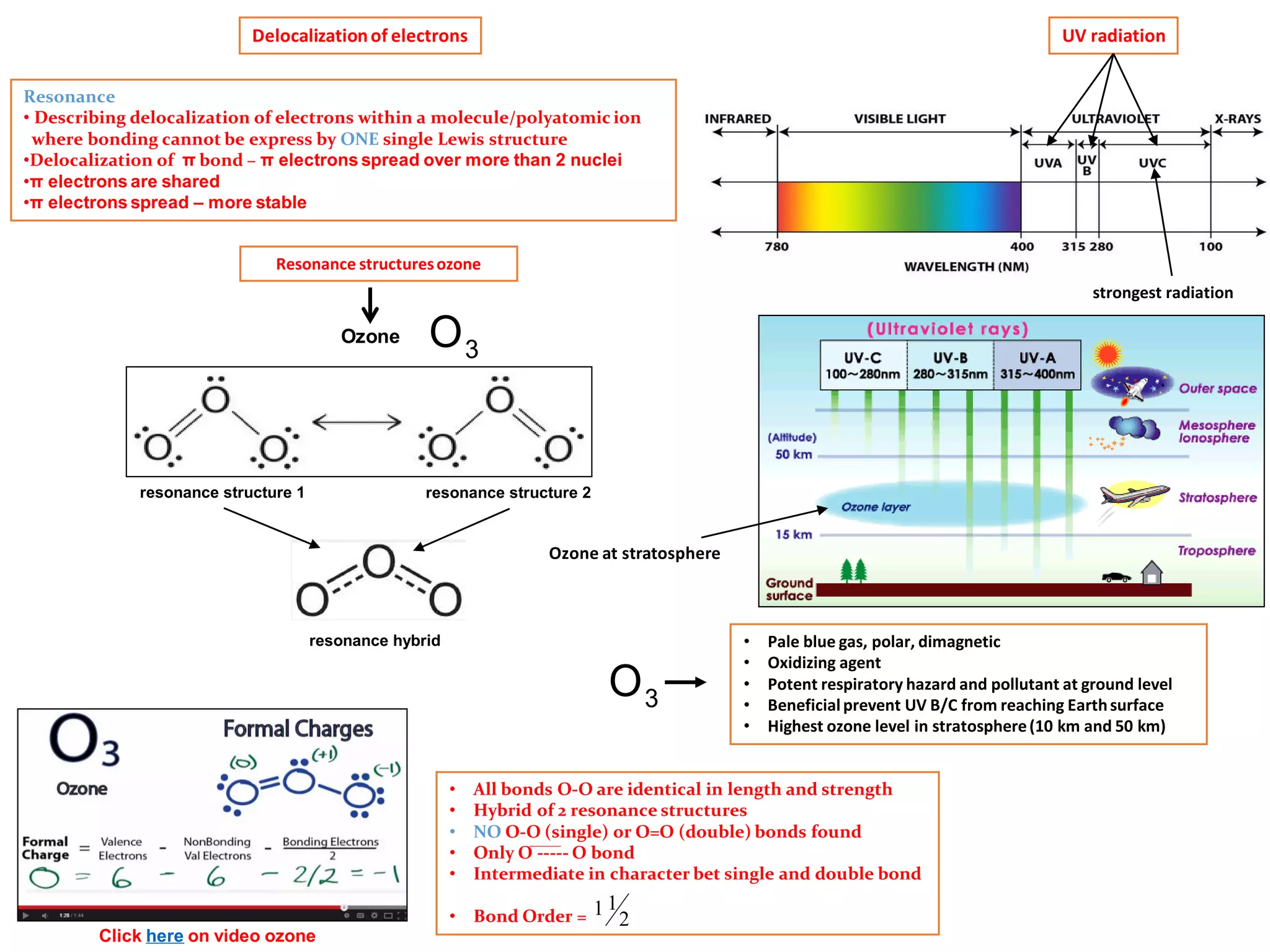
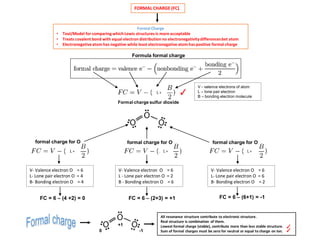
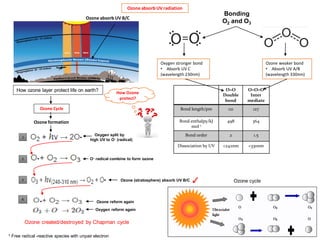
- Ozone (O3) has a delocalized structure where the electrons are shared between all three oxygen atoms, giving each O-O bond an intermediate bond order of 1.5.
- This resonance hybrid structure is more stable than any single Lewis structure and explains why the O-O bonds are identical in length and strength.
- Ozone absorbs ultraviolet radiation below 330nm, protecting life on Earth from high-energy UV rays.