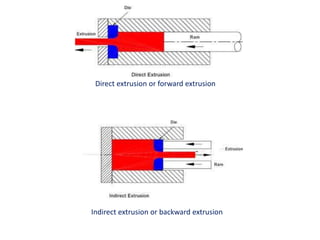
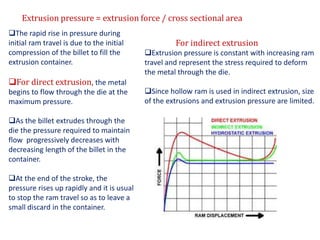
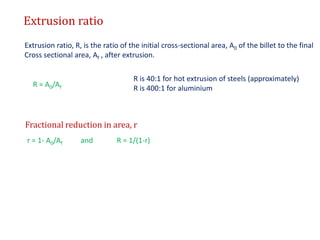
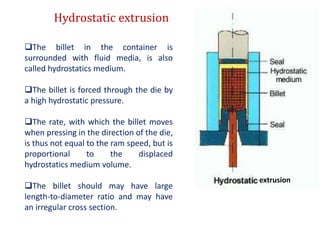
This document provides an overview of the extrusion process. It defines extrusion as forcing a block of metal through a die under high pressure to reduce its cross-section. Extrusion can be hot or cold, direct or indirect. It discusses extrusion equipment, pressures, ratios, defects, and features like its cost-effectiveness and ability to produce complex cross-sections. Hydrostatic extrusion is also introduced, where the billet is surrounded by a fluid and forced through the die.