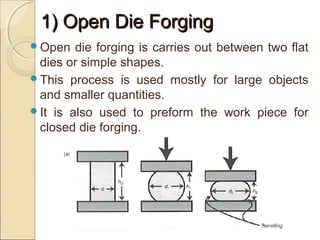
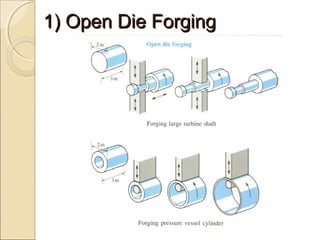
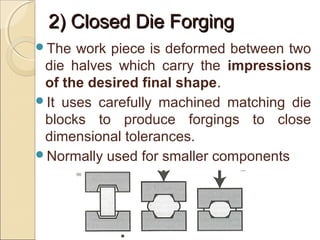
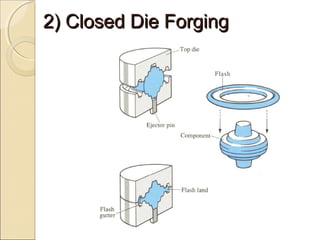
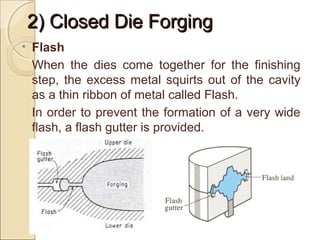
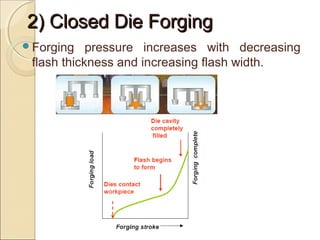
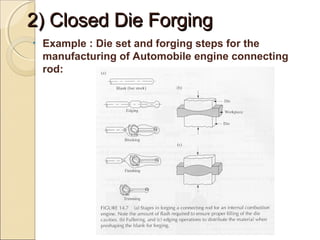
The document discusses two main forging processes: open die forging and closed die forging. Open die forging uses simple flat dies and is used for large or low volume parts. Closed die forging uses carefully machined matching dies to produce parts to close tolerances. The process involves preforming billets, rough forging in blocking dies, finishing in final dies, and trimming flash. Closed die forging produces parts with good dimensions and properties but requires high die costs for small volumes.