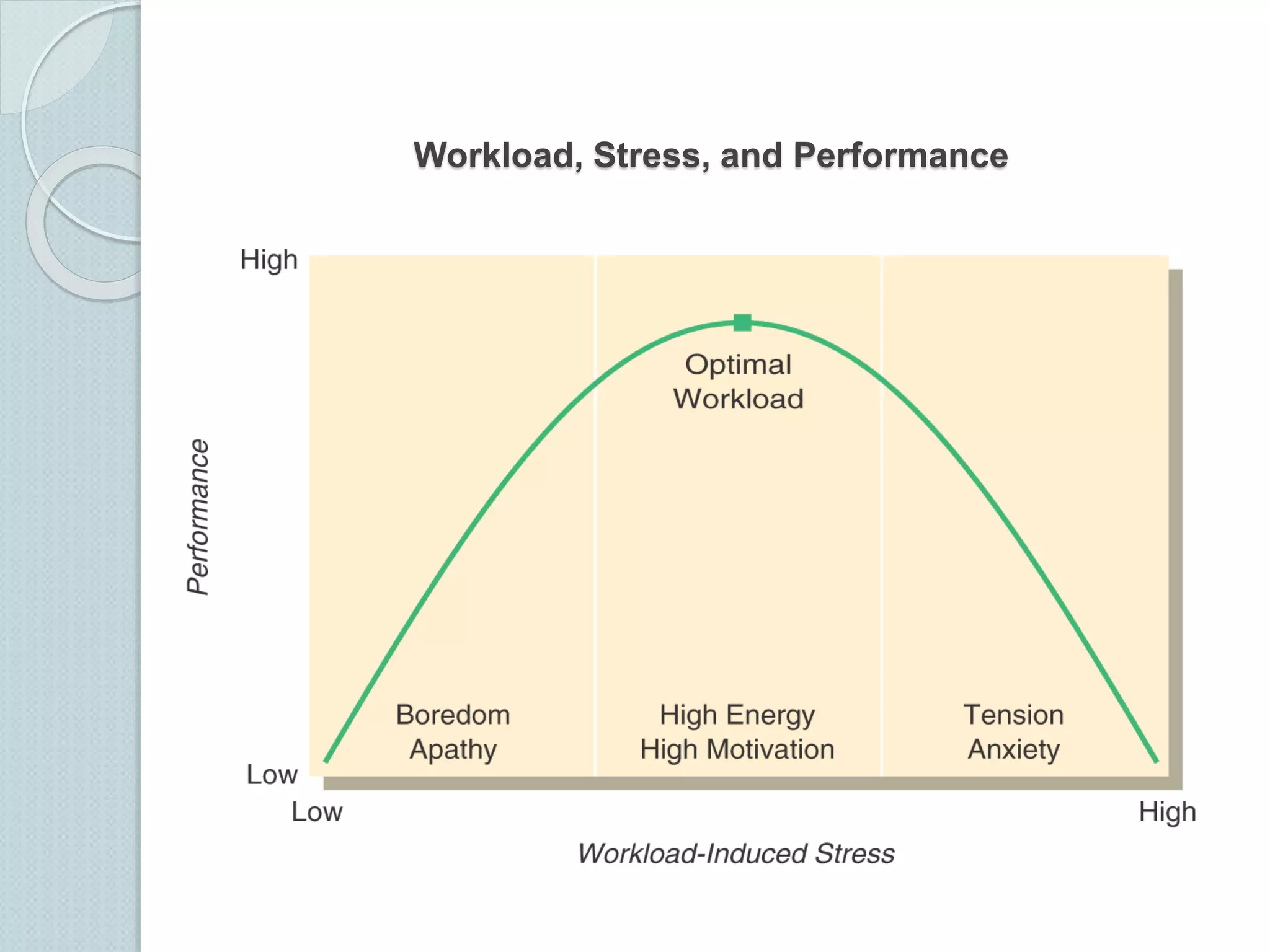
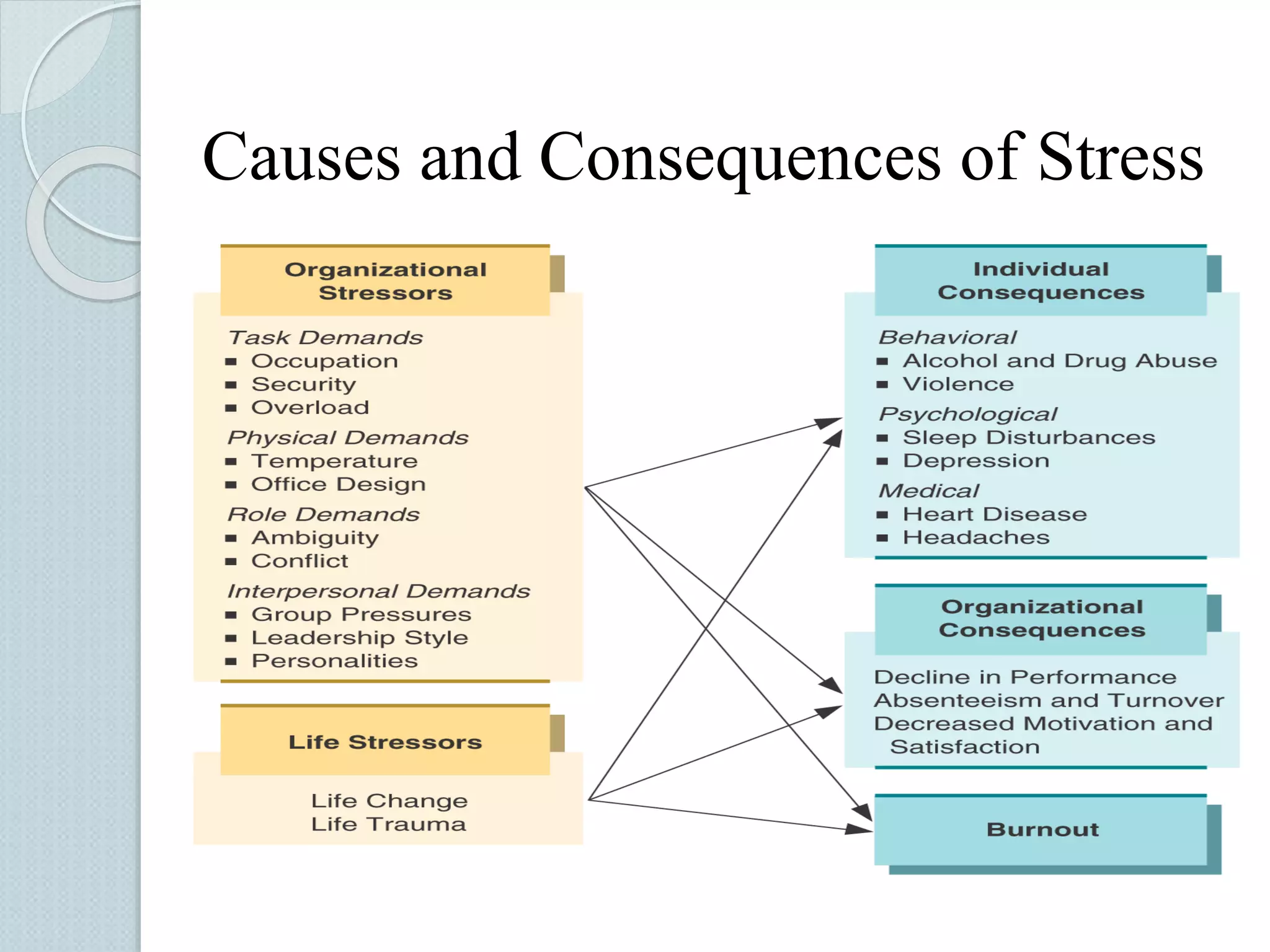
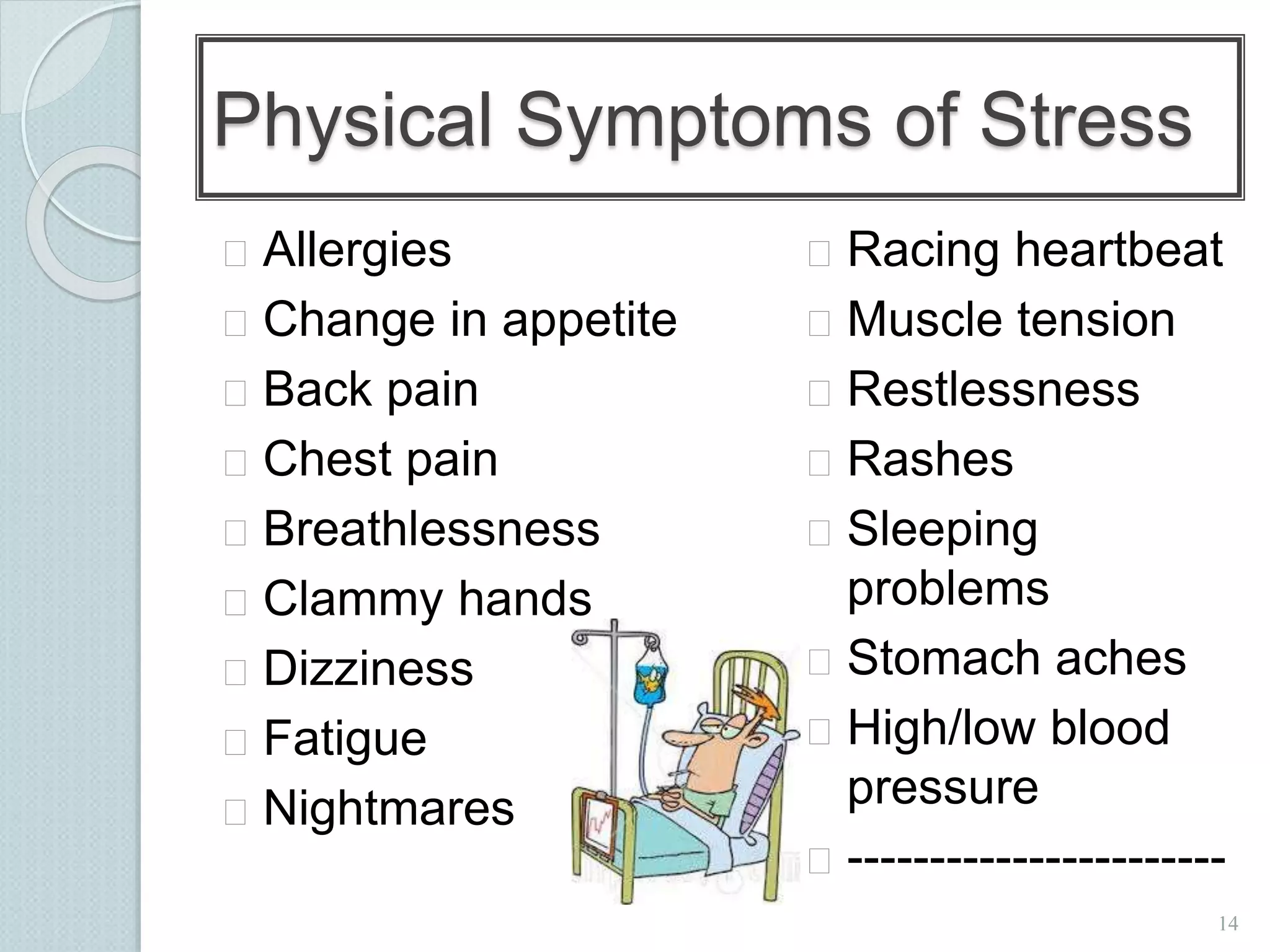
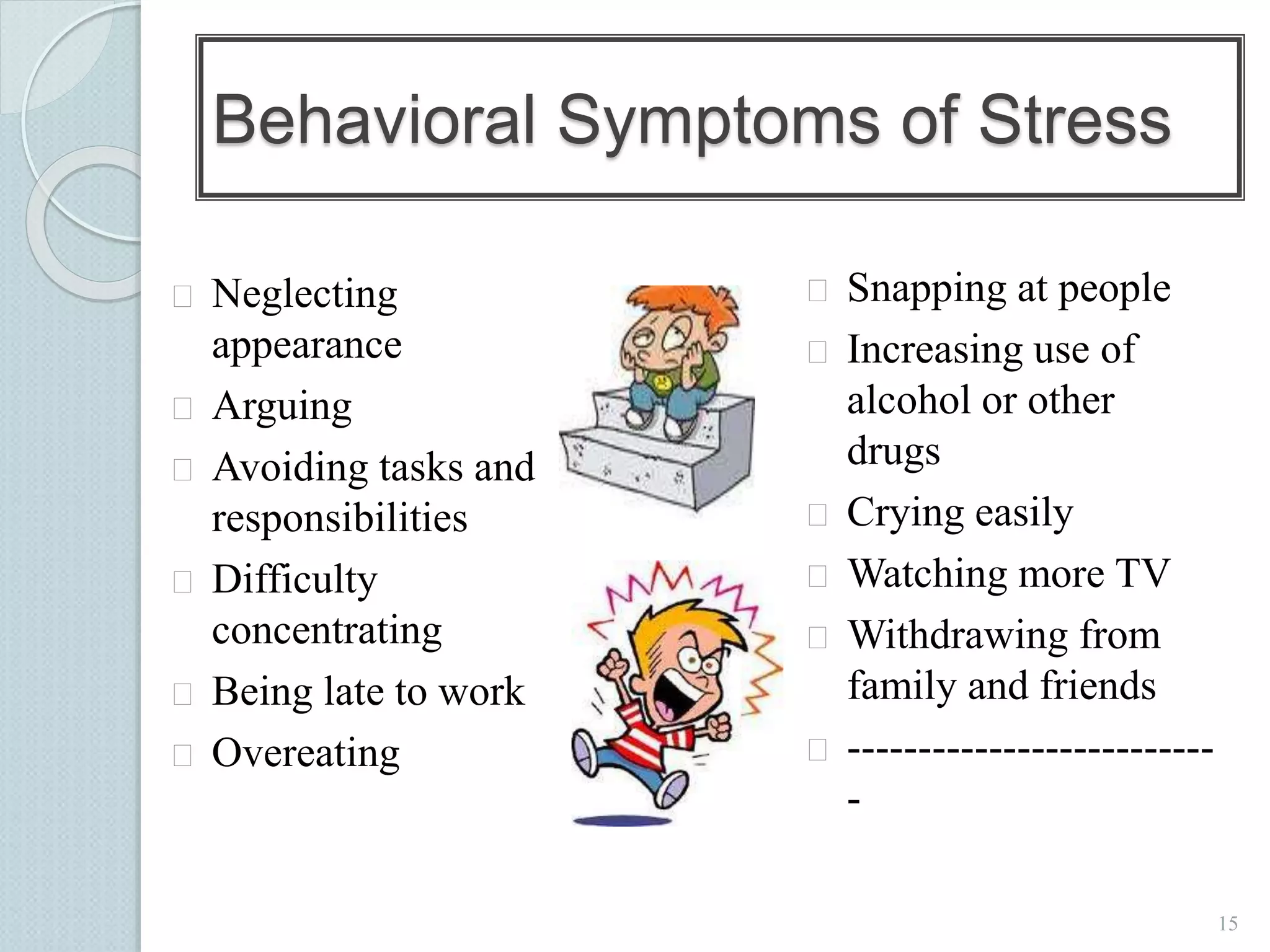
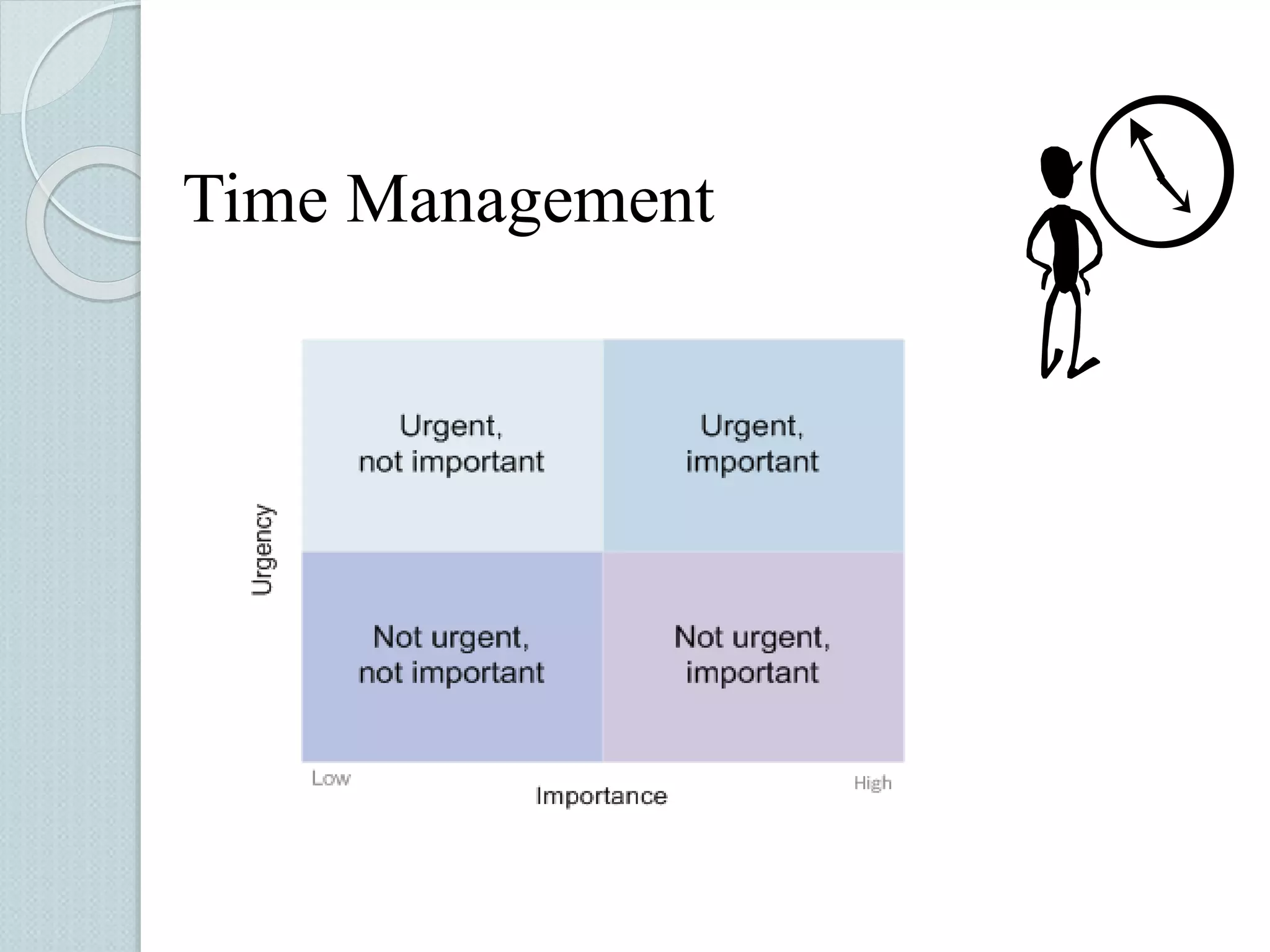
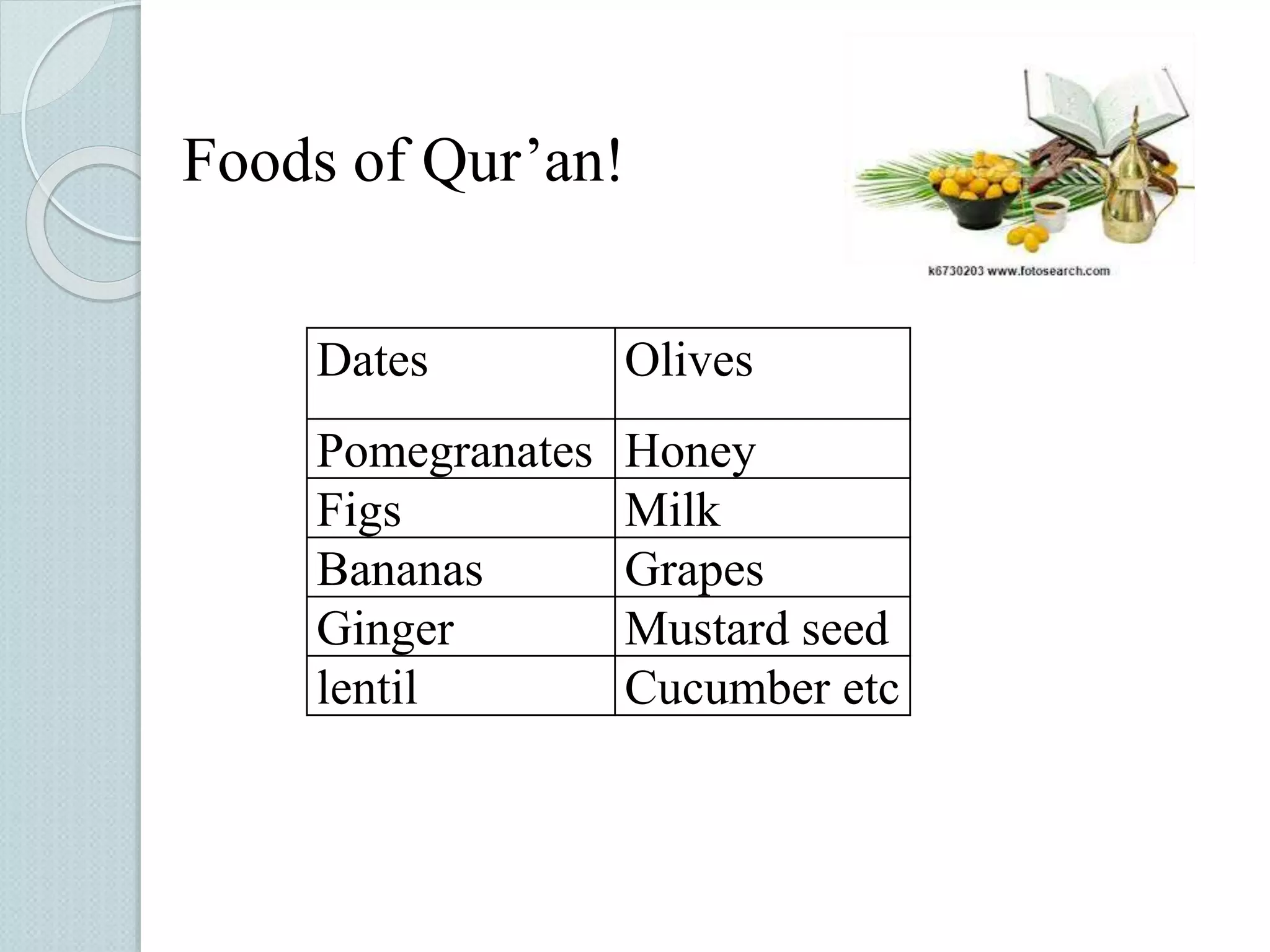
The document discusses techniques for managing stress and nervousness. It begins by defining stress and nervousness, and describes the different types of stress. It then discusses the physical, behavioral, and emotional symptoms of stress. Various causes of stress are outlined, including life events, daily hassles, jobs, and personality types. The document provides many techniques for managing stress, such as time management, exercise, relaxation, spirituality, and seeking social support. It concludes by discussing how stress management relates to Islamic teachings like patience, prayer, gratitude, and having faith in Allah.