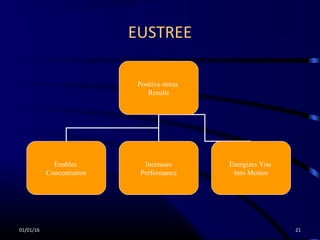
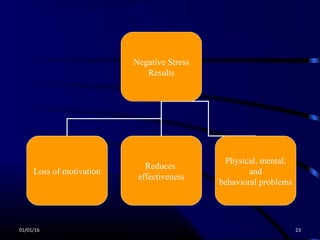
Stress is defined as the "wear and tear" on the body and mind that results from the pressures of life. Stress can come from external stressors like one's environment, social interactions, work, or major life events, as well as internal stressors like lifestyle choices and negative thinking patterns. The body has an alarm response to stress that prepares it for "fight or flight," but too much distress can lead to physical, mental, behavioral, and emotional symptoms. To manage stress, one can use the ABC strategy - becoming aware of stress triggers, maintaining a balance between positive and negative stress, and using various control techniques like changing one's thinking, behaviors, and lifestyle habits. Control techniques include stress management methods like relaxation,