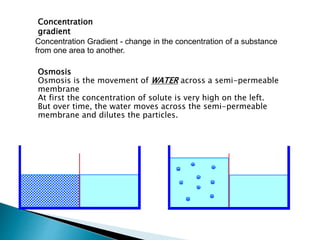
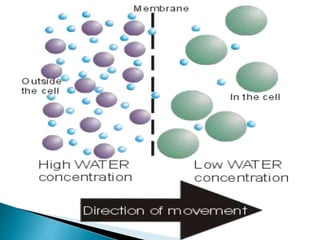
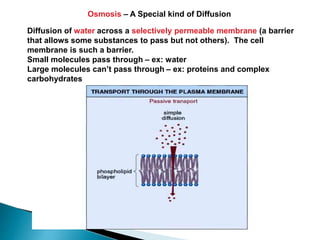
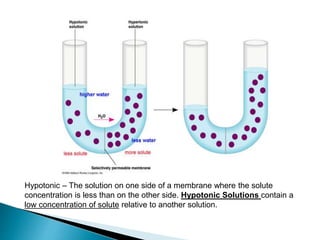
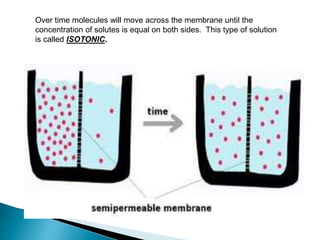
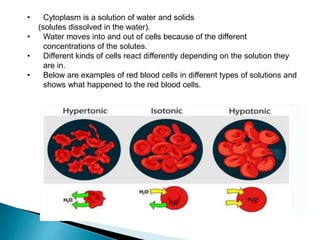
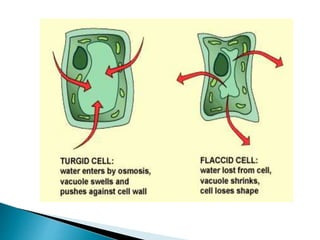
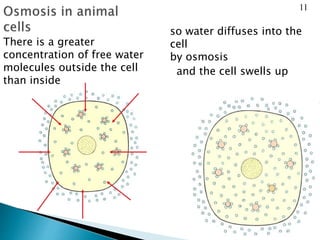
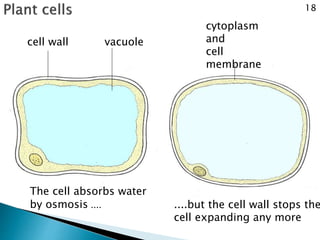
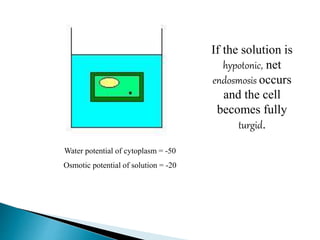
Osmosis is the spontaneous movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to lower water concentration in order to equalize the concentration of water molecules on both sides of the membrane. The movement occurs due to differences in solute concentration between solutions separated by the semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis plays a key role in transporting water into and out of cells and the response of cells to their external environment depends on whether the outside solution is hypo-tonic, iso-tonic, or hyper-tonic compared to the cell cytoplasm.