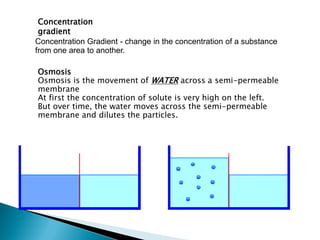
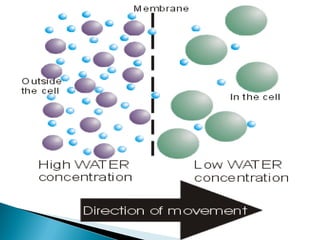
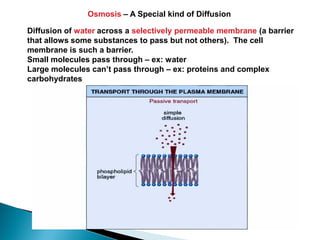
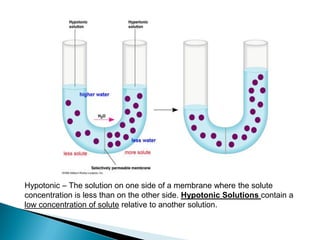
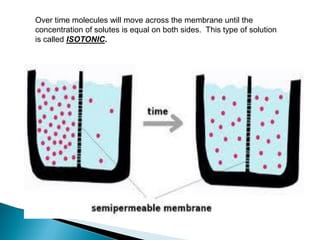
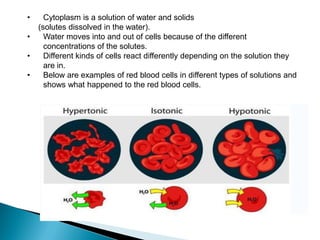
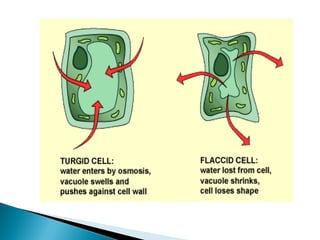
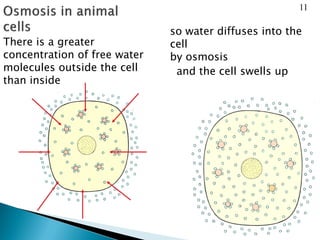
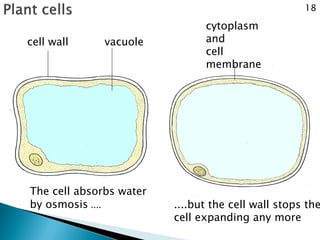
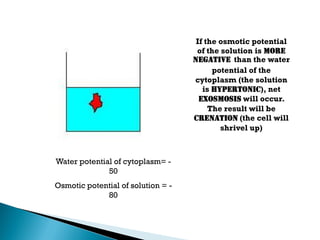
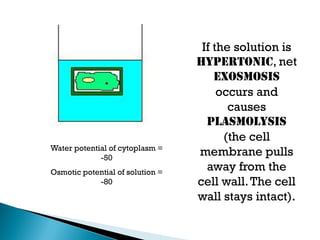
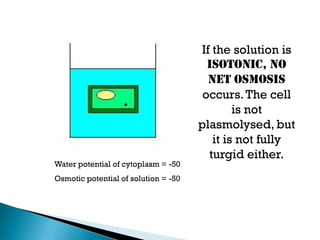
Osmosis is the spontaneous movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration in order to equalize the concentrations. It provides the means for water transport into and out of cells. The direction of osmosis depends on the solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane - if one side has a higher concentration than the other, water will diffuse into the lower concentration side. This movement of water allows cells to remain turgid and control their volume under different osmotic conditions by taking in or releasing water through osmosis.