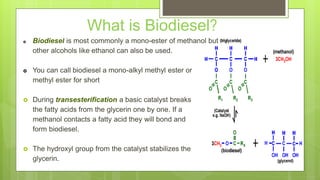
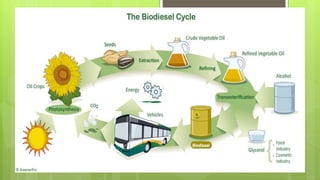
Biodiesel is most commonly a mono-ester of methanol produced through a process called transesterification, where a basic catalyst breaks fatty acids from glycerin and bonds them with methanol to form biodiesel. It has a slightly lower energy density than petrodiesel but offers environmental benefits such as reduced emissions and less reliance on foreign oil imports. Biodiesel production is important as it provides a renewable fuel that can be used directly in unmodified diesel engines, helping energy independence, economic growth, and cleaner air with less global warming.