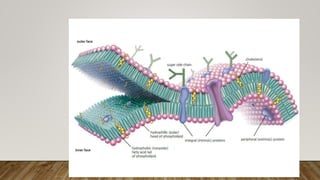
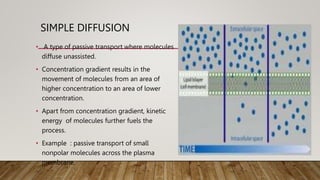
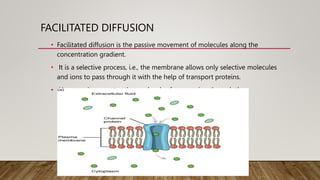
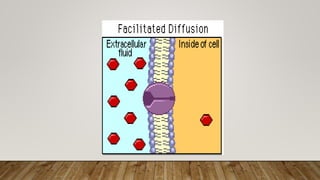
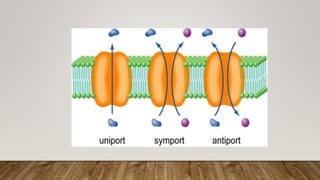
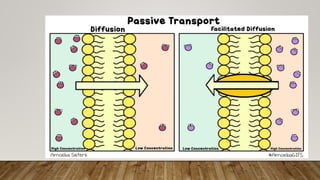
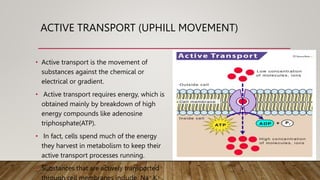
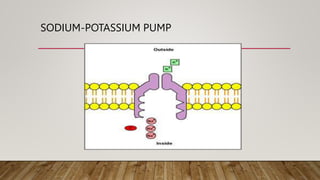
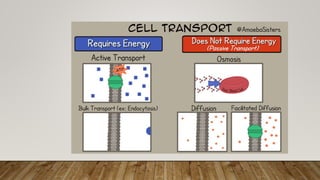
The cell membrane regulates the passage of small molecules via active and passive transport mechanisms, with endocytosis and exocytosis managing macromolecule transport. Passive transport occurs along the concentration gradient without energy, while active transport requires energy to move substances against this gradient. Endocytosis involves the uptake of materials into the cell, and exocytosis pertains to expelling materials from the cell.