Embed presentation
Download to read offline




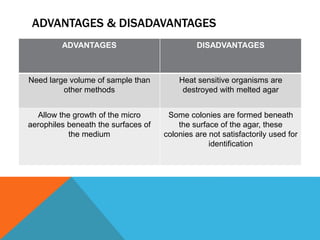

This document outlines a procedure for isolating microorganisms from a sample using the pour plate method. The aims are to isolate and obtain pure cultures of microorganisms. The principle involves diluting the sample and mixing it with warm agar which is then poured into petri dishes to form individual colonies after incubation. Colonies are then transferred to fresh media for identification. The procedure involves preparing and sterilizing media, diluting the sample, pour plating the dilutions, incubating, and recording results to determine the number of viable microorganisms present.






