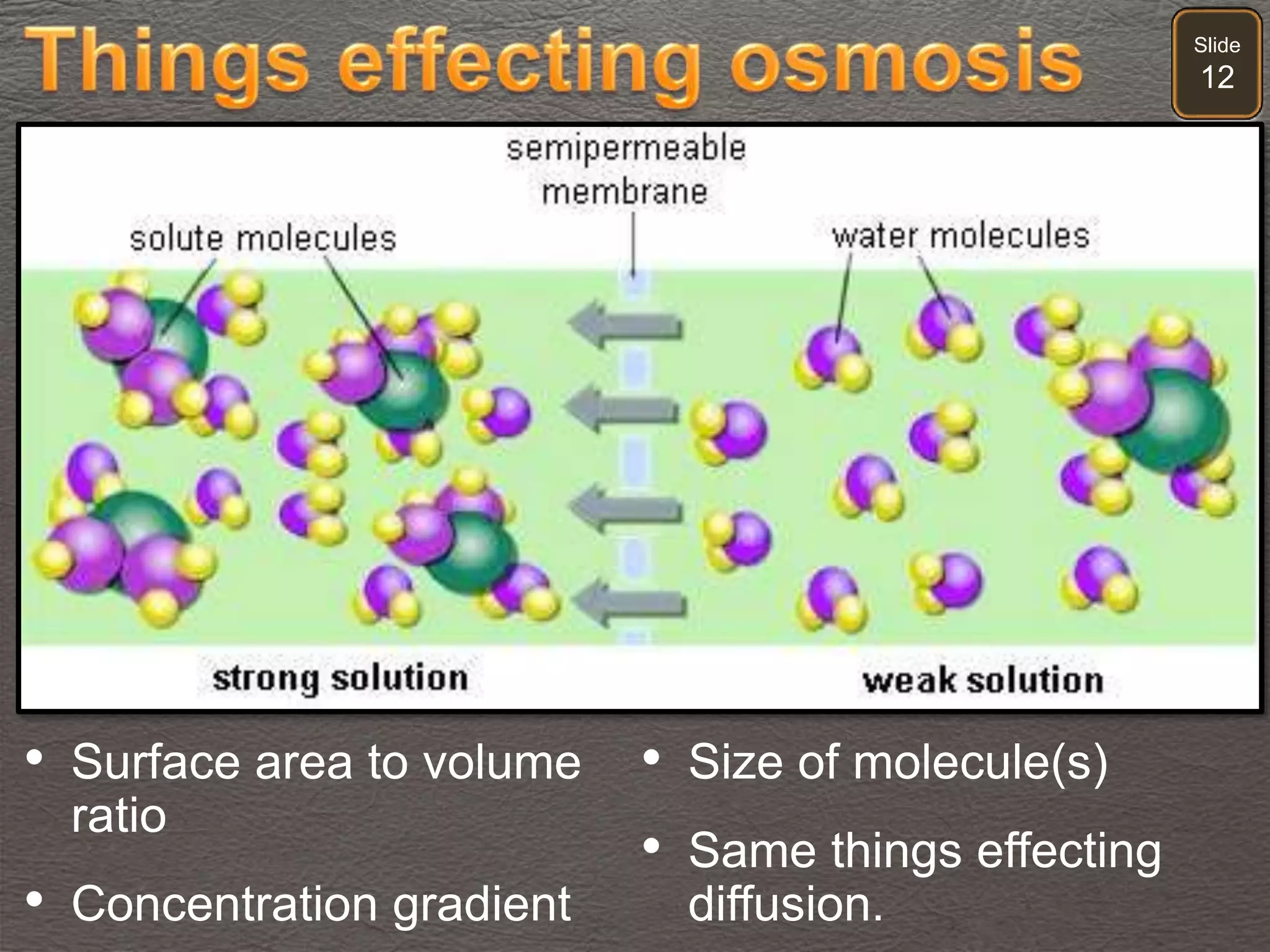
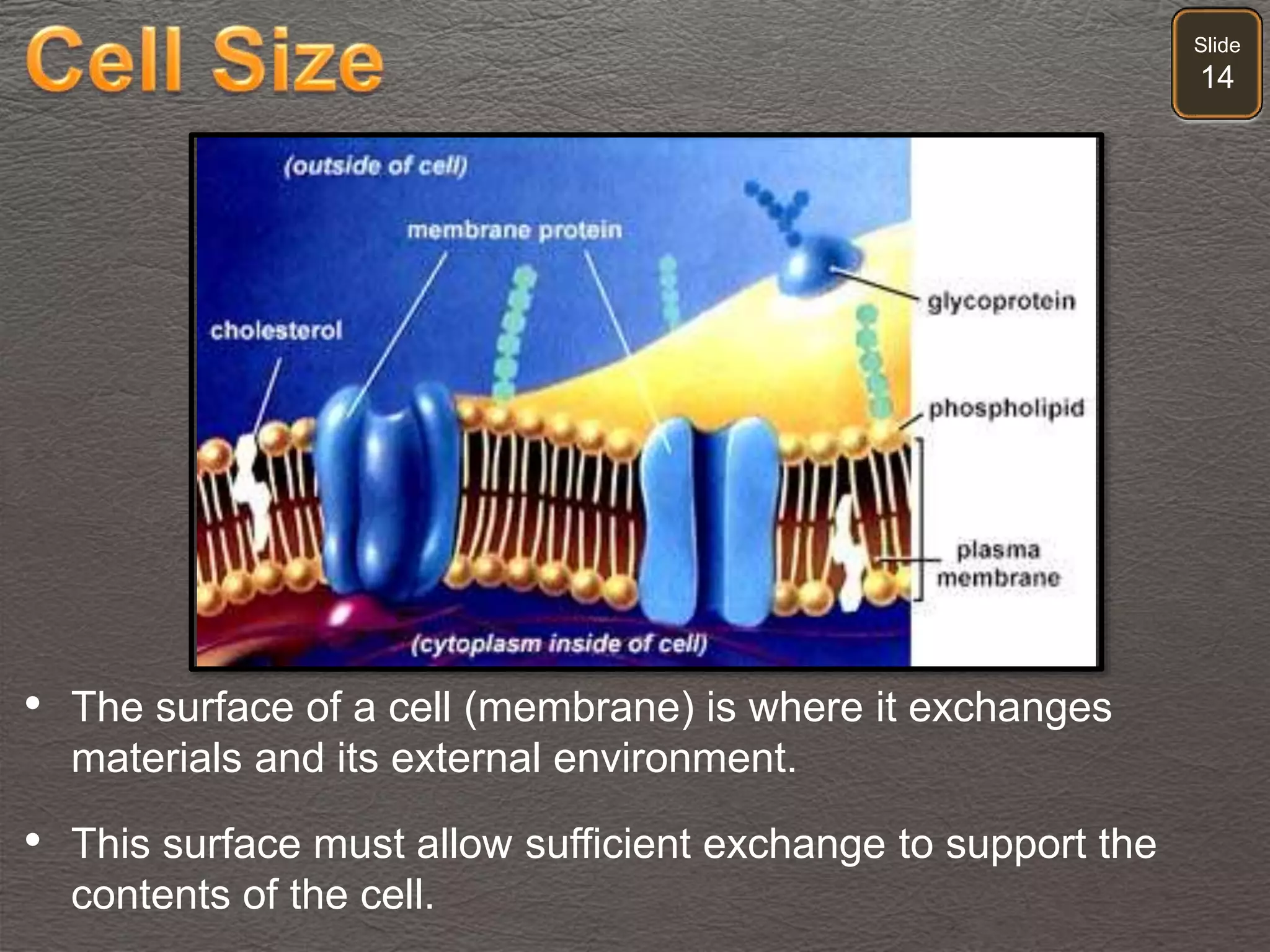
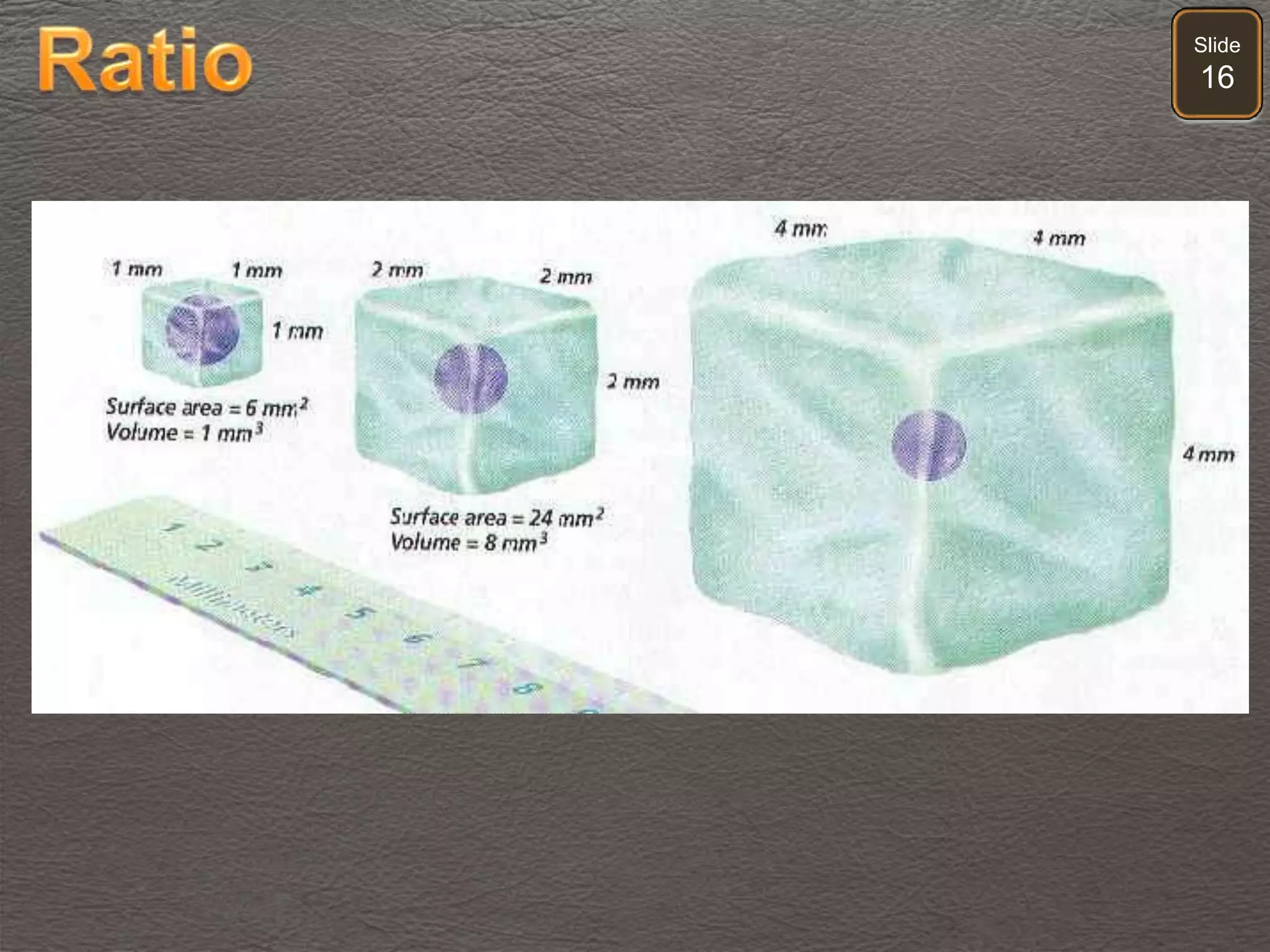
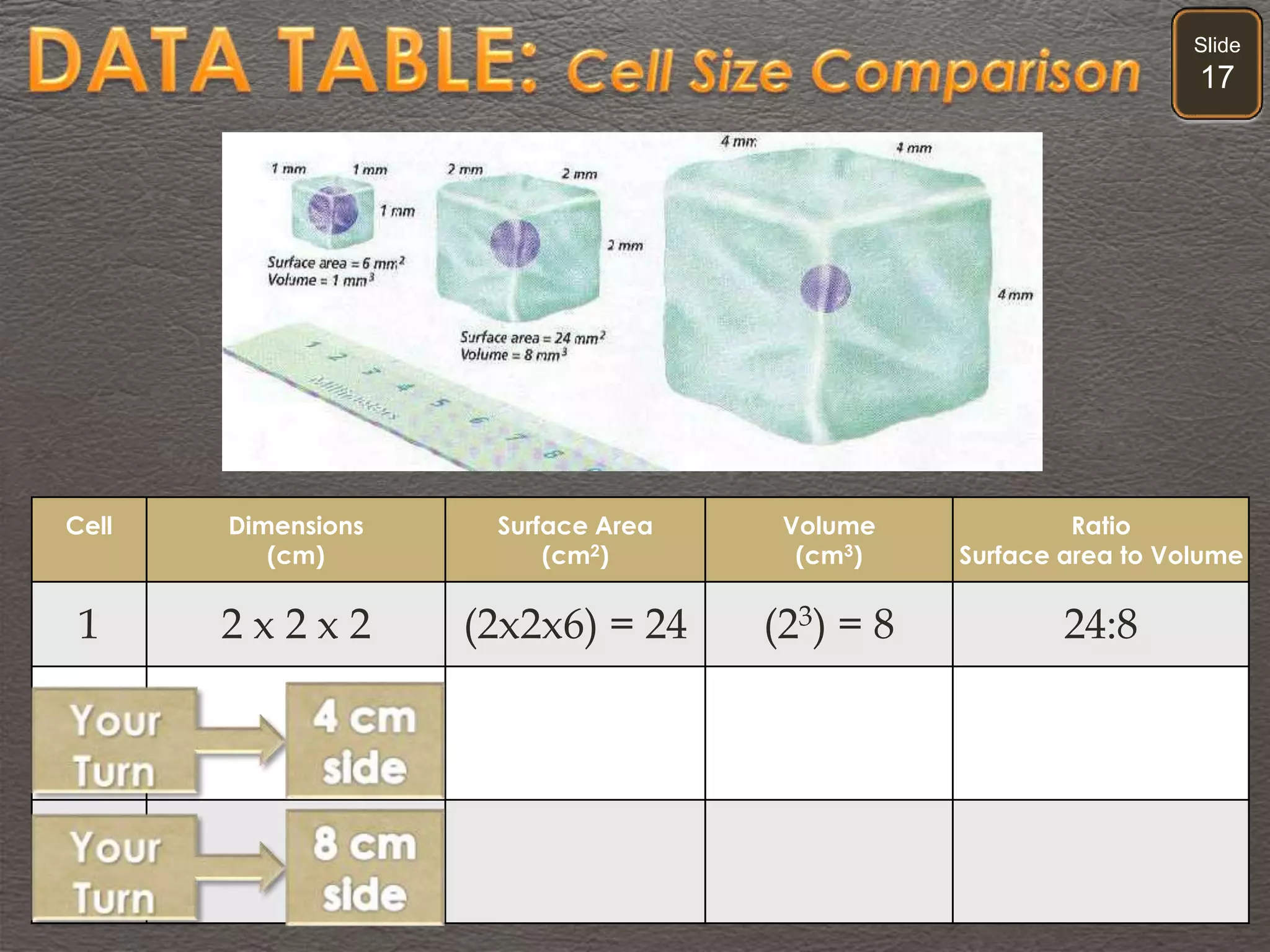
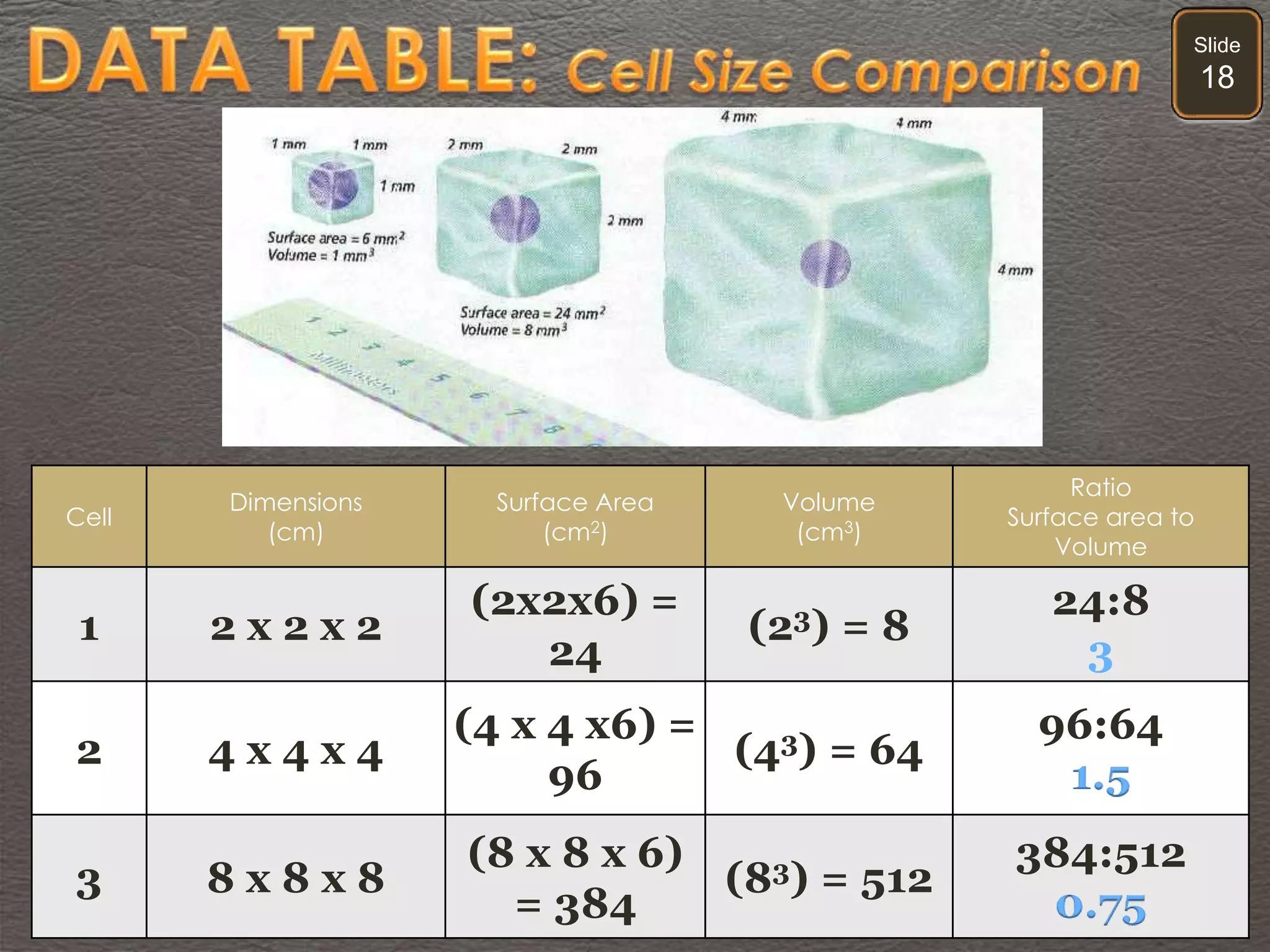
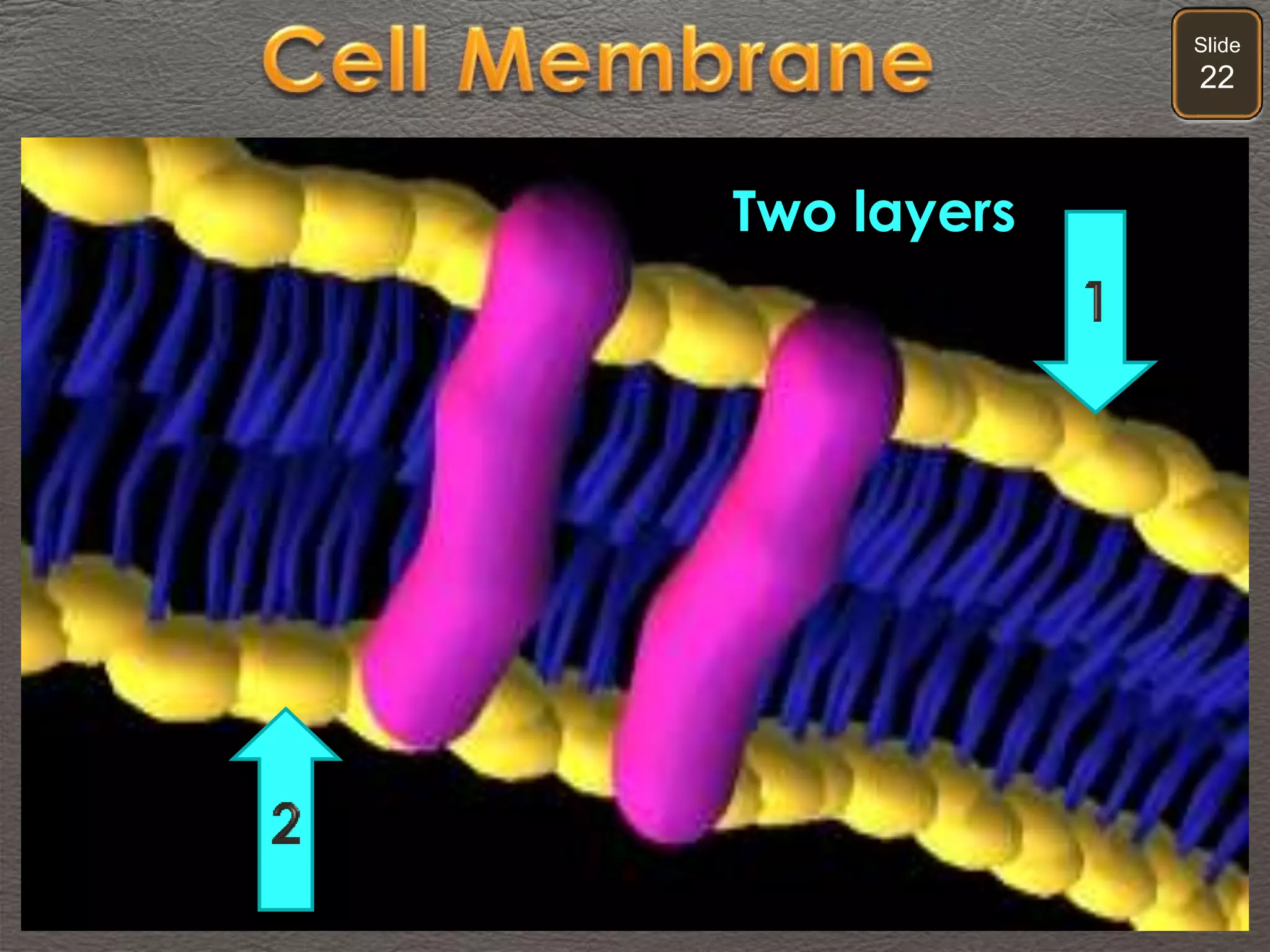
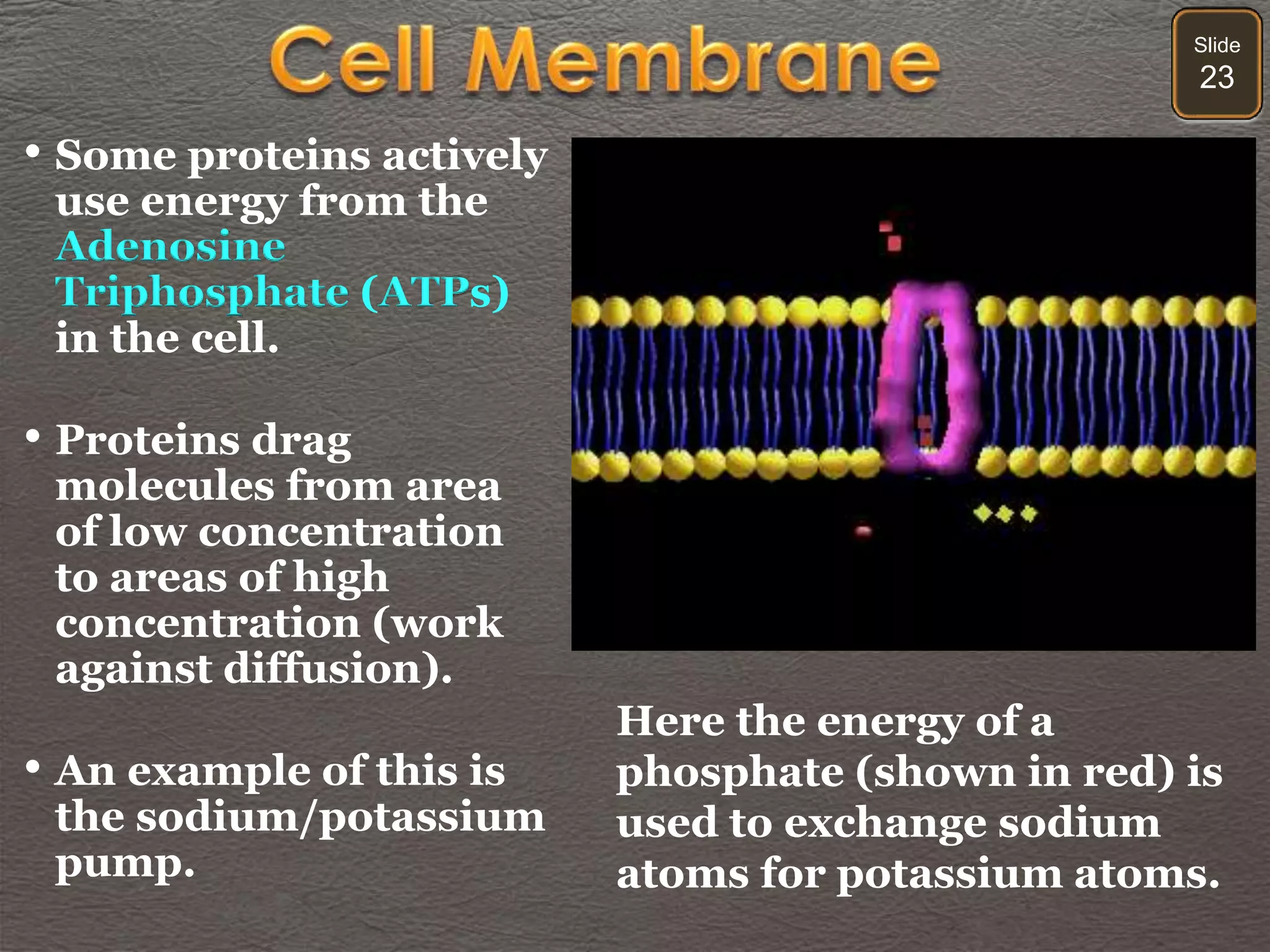
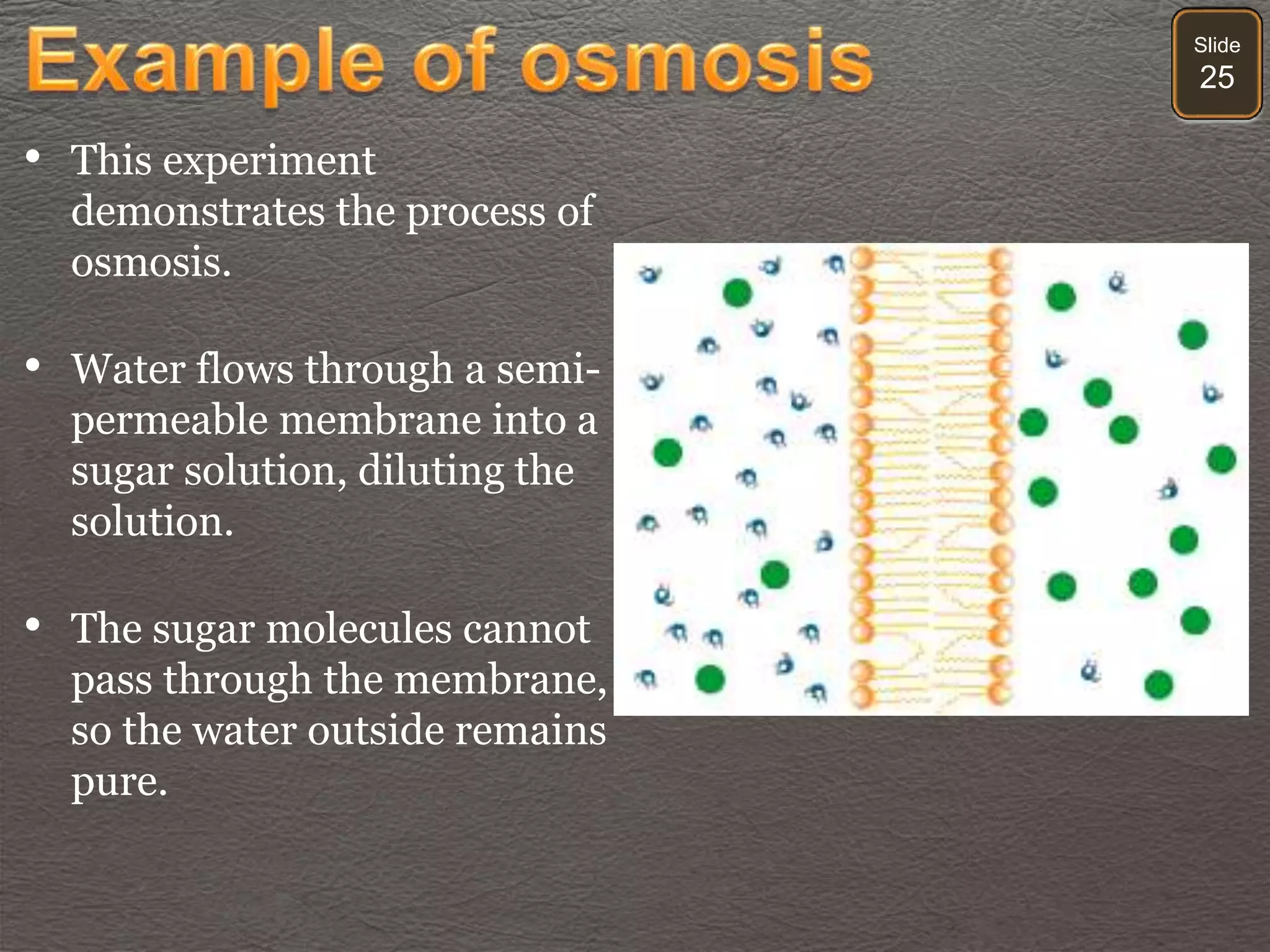
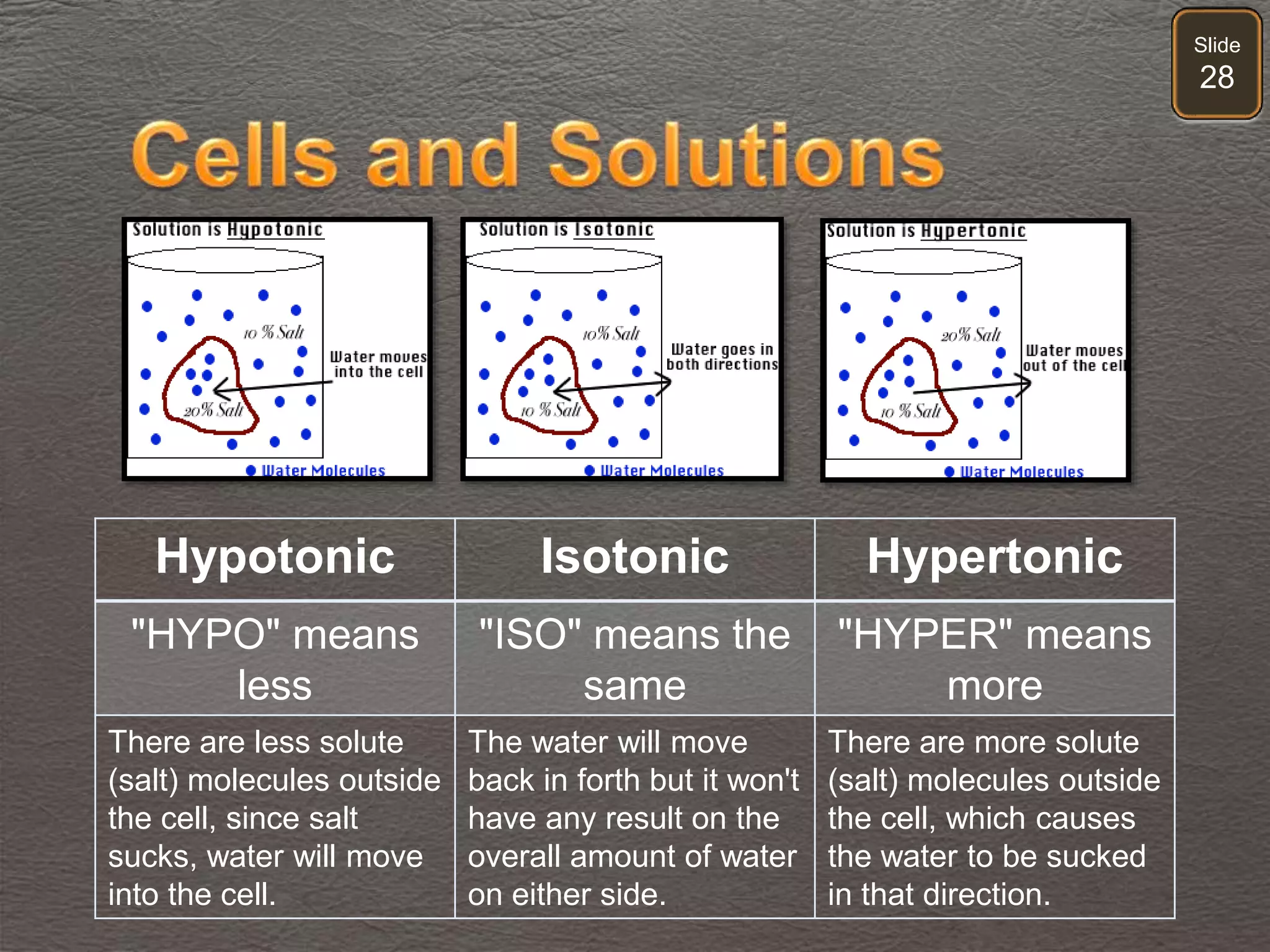
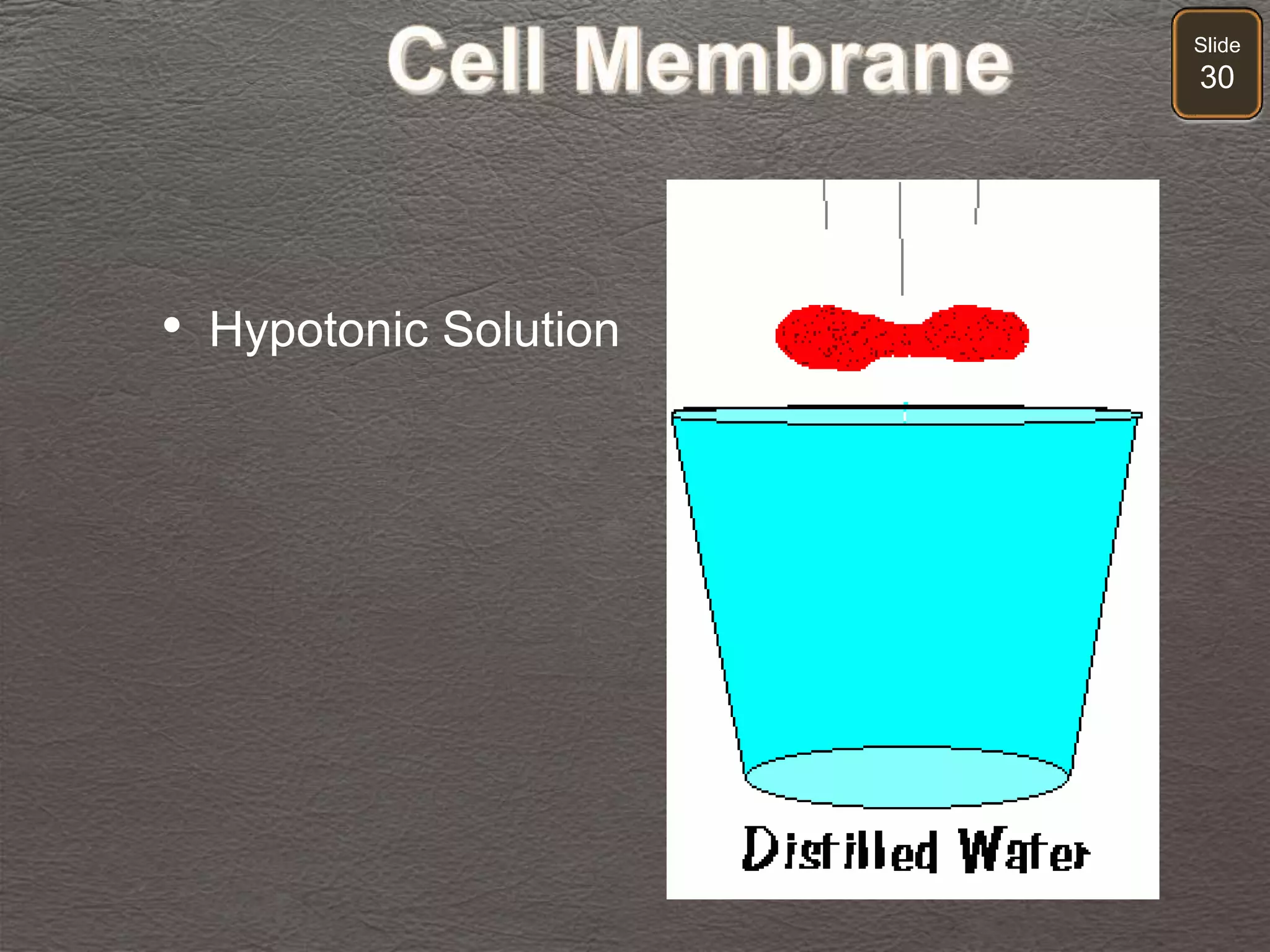
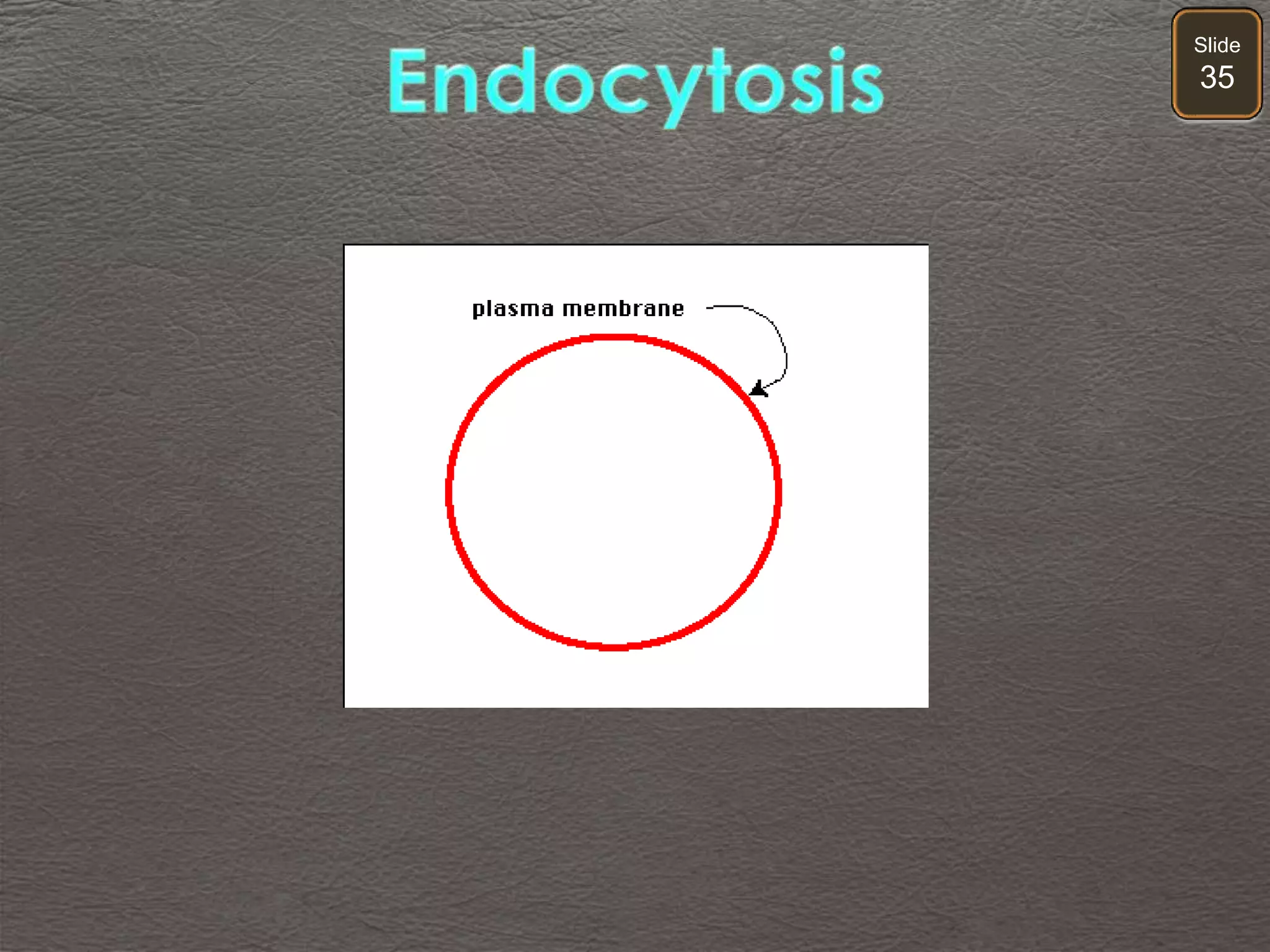
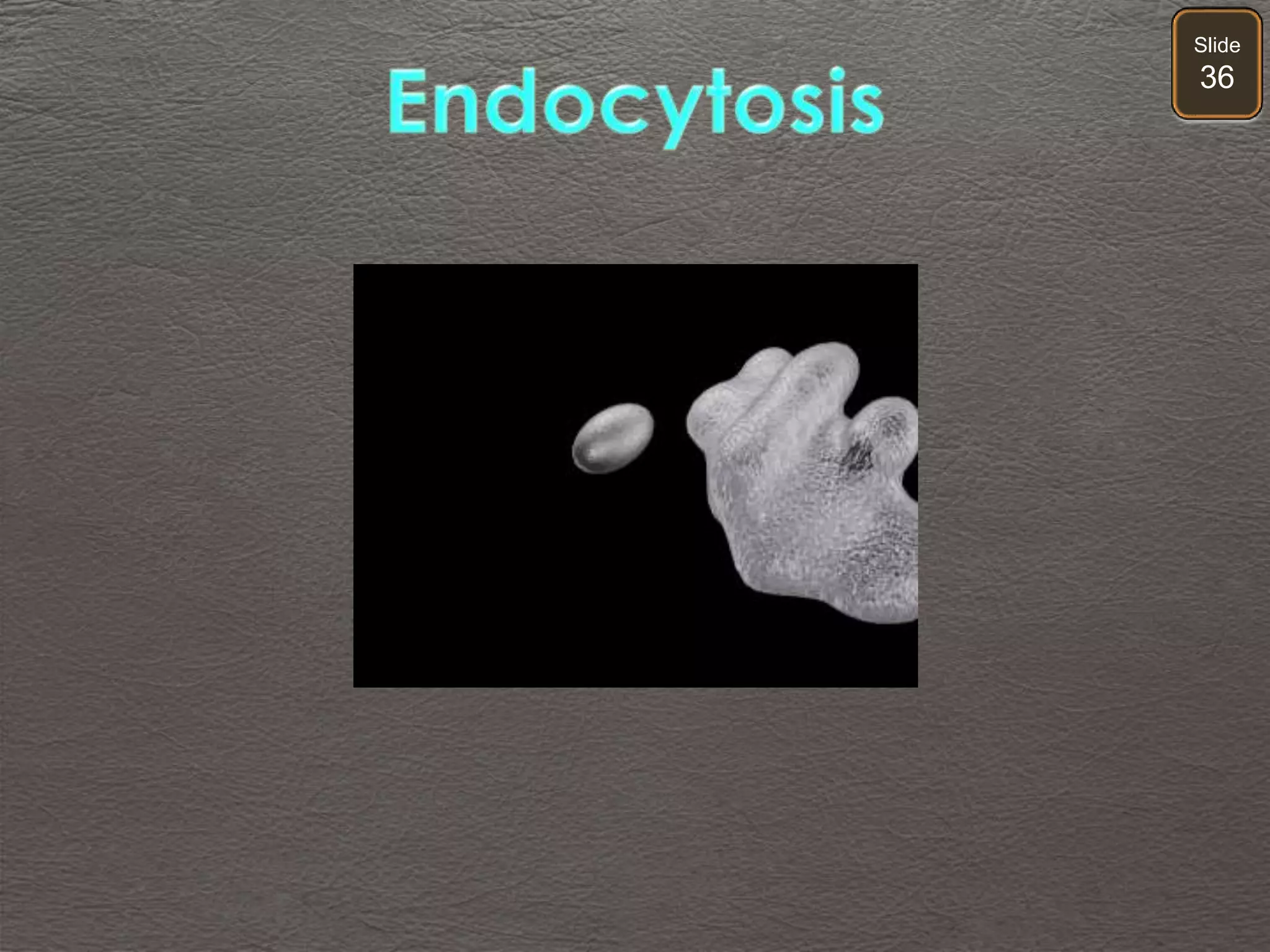
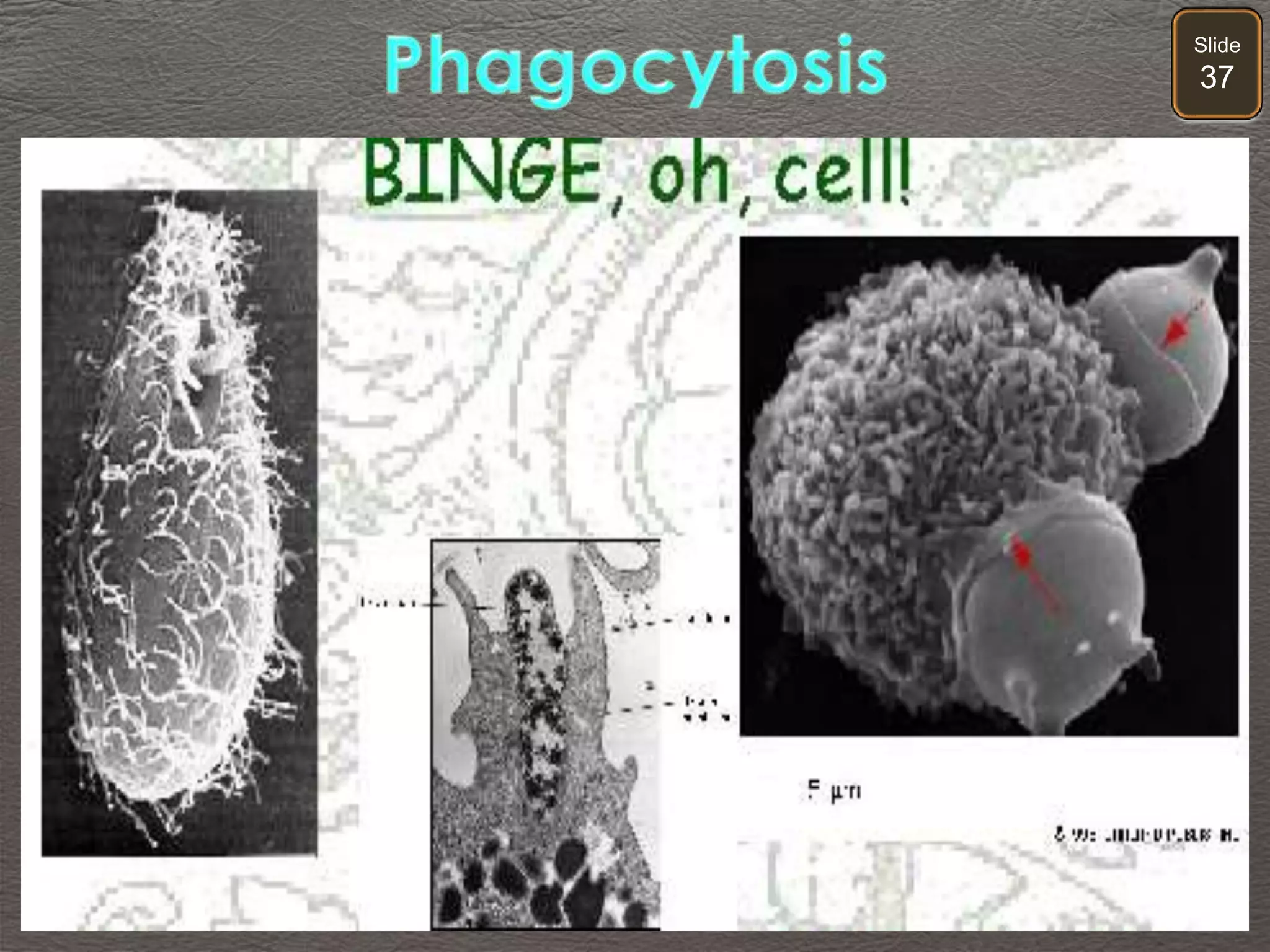
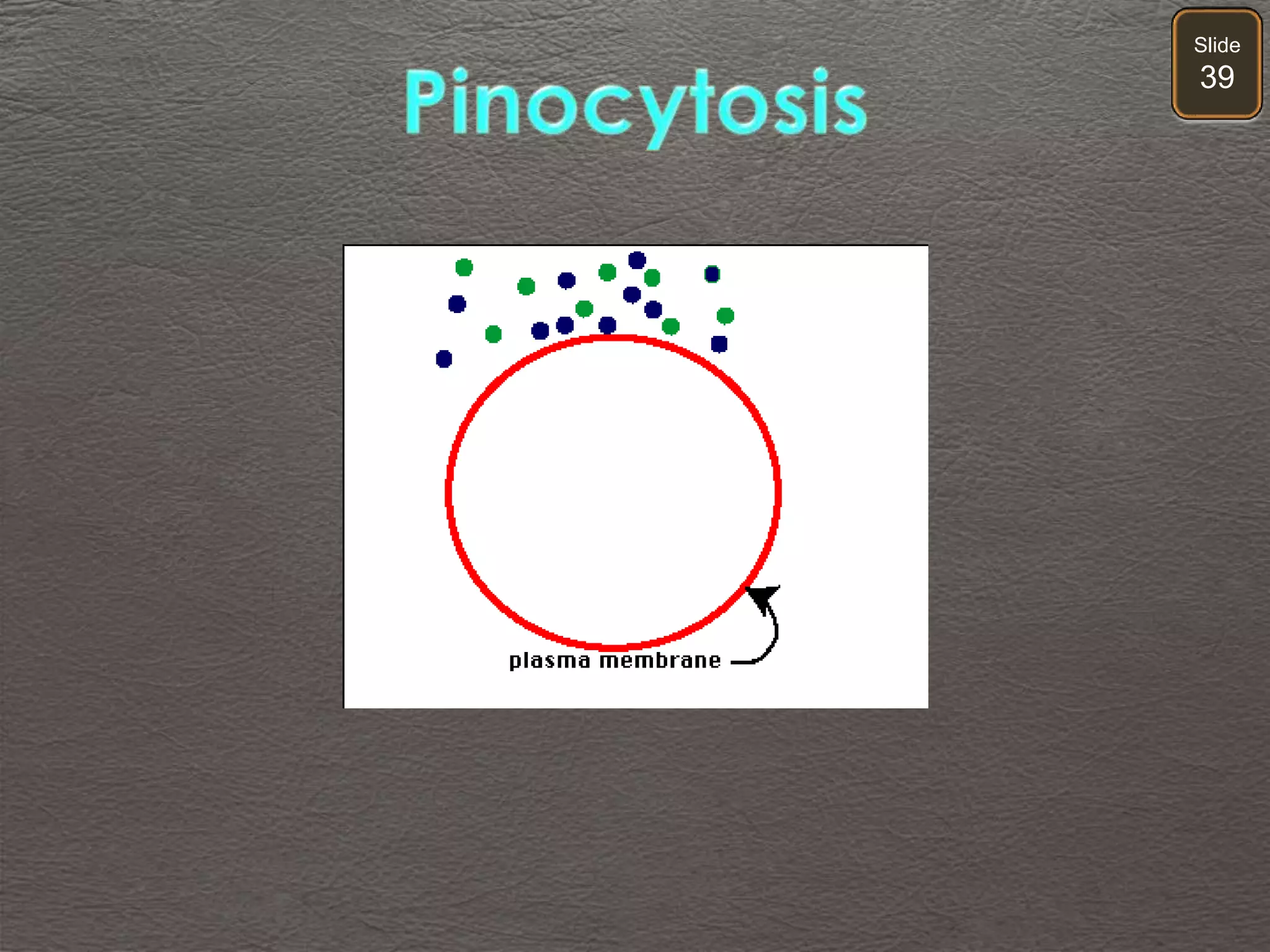
The document discusses cellular transport mechanisms, including passive processes like diffusion and osmosis, and active processes such as endocytosis and exocytosis. It explains essential concepts like concentration gradients, cell size limitations related to surface area to volume ratios, and how cell membranes regulate material passage. Diagrams and experiments illustrate these transport processes and their implications for cell function.