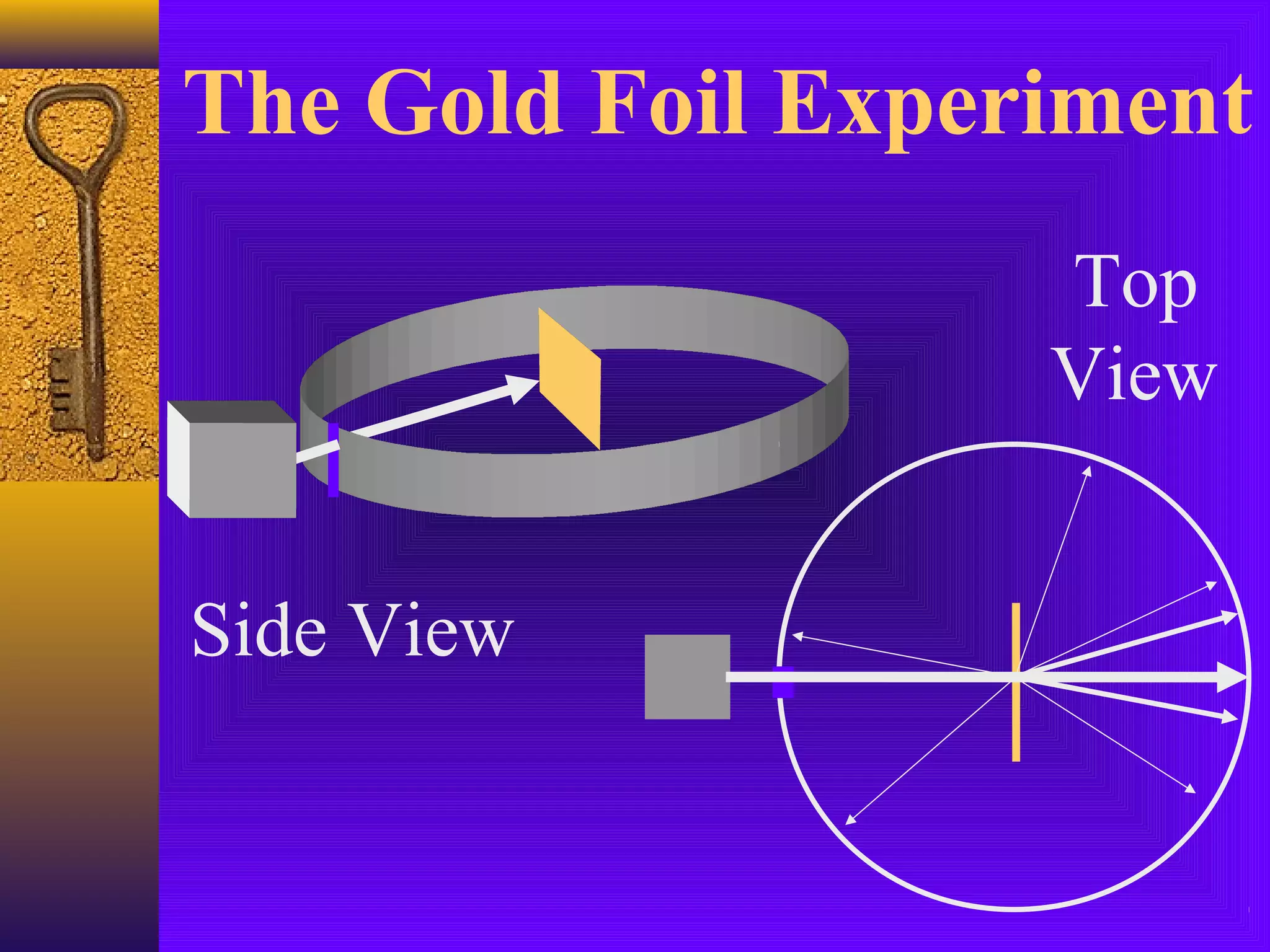
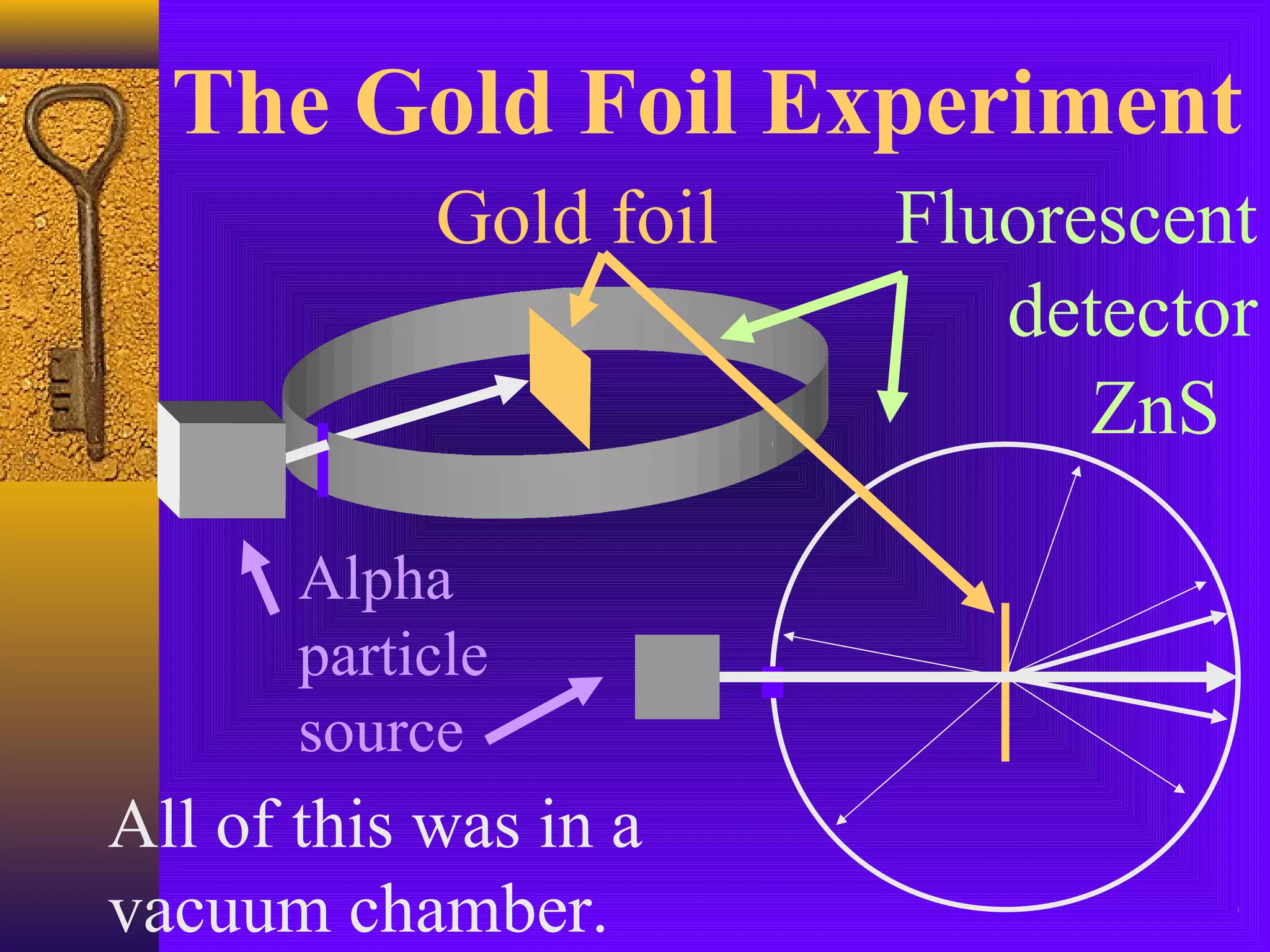
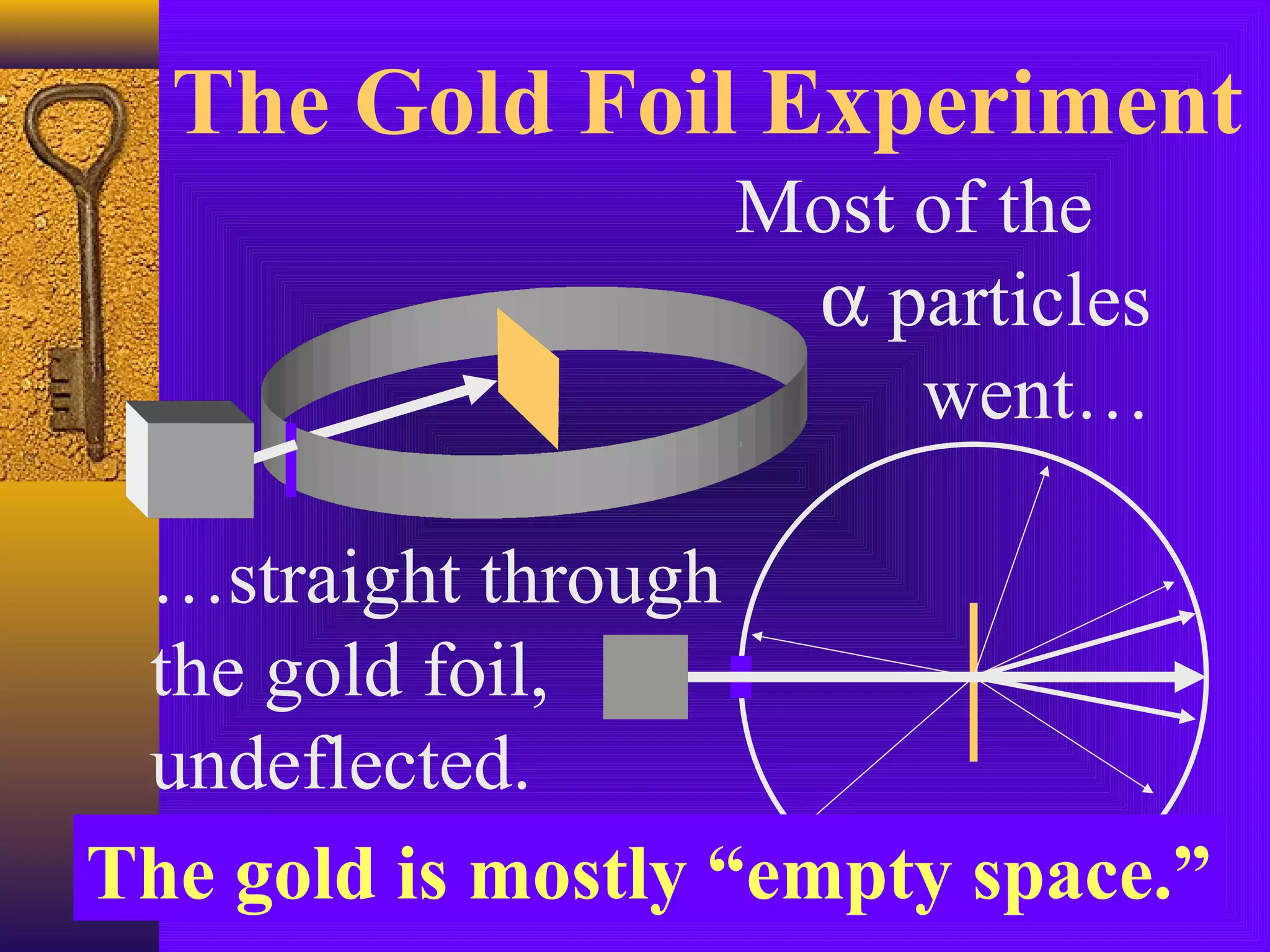
1) Early Greek philosopher Democritus proposed that all matter is made of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
2) In the early 1800s, English scientist John Dalton developed the first serious atomic theory, proposing that elements are made of atoms and atoms of the same element have the same properties.
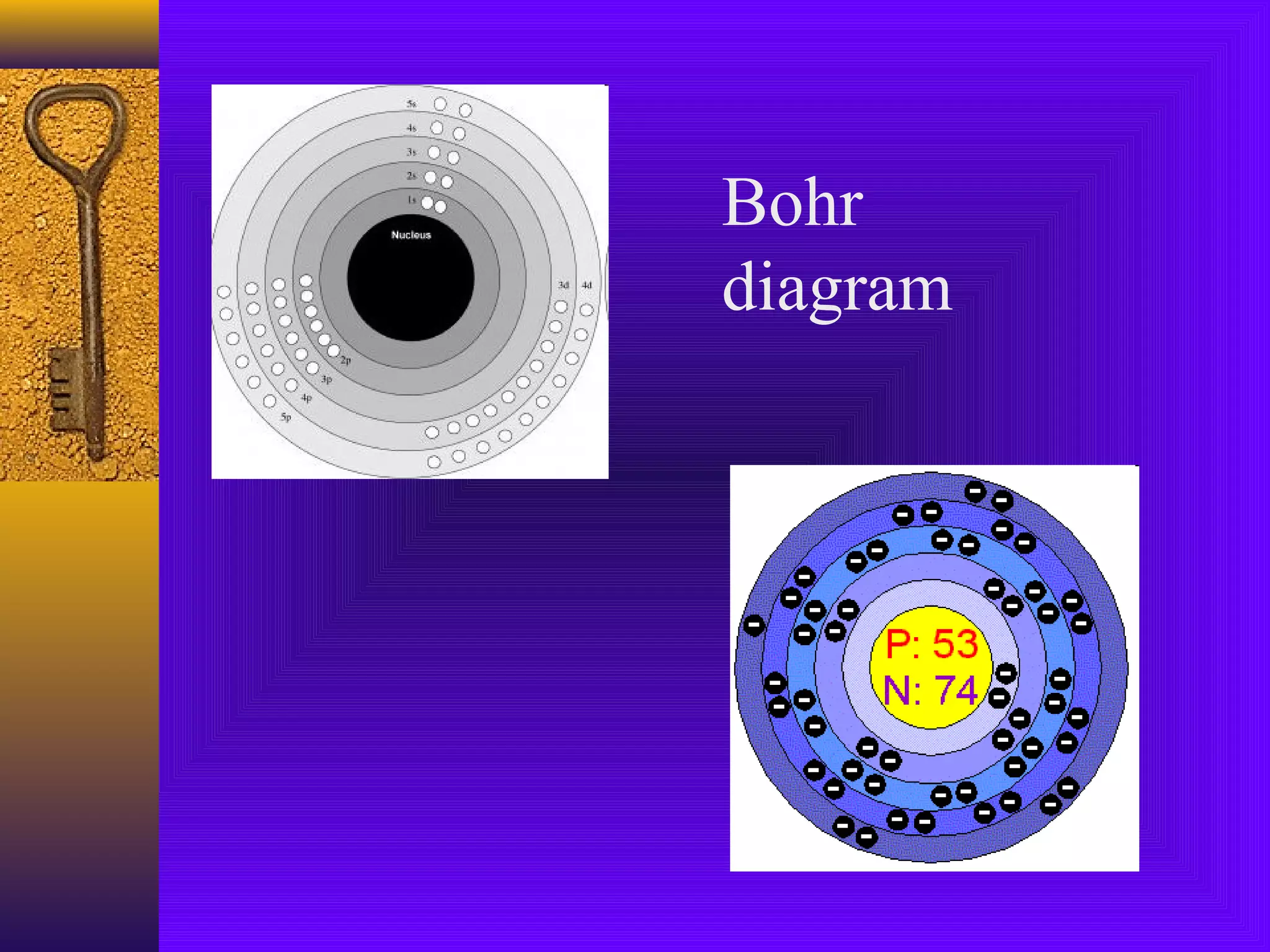
3) J.J. Thomson's discovery of the electron in 1897 showed that atoms contain smaller subatomic particles, challenging the idea that atoms are indivisible.