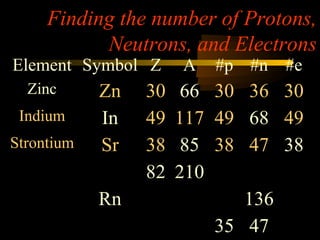
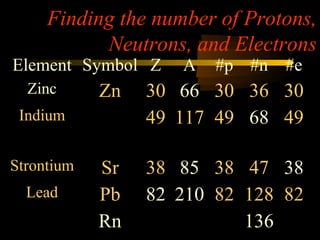
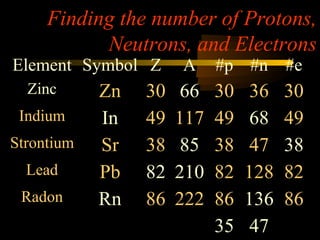
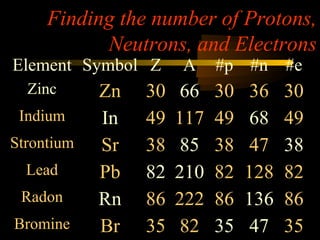
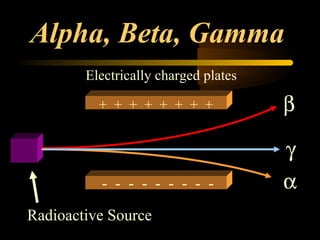
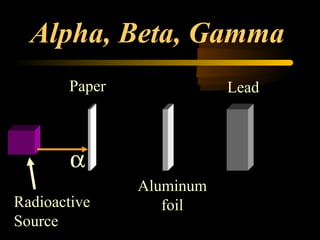
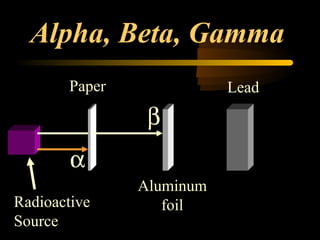
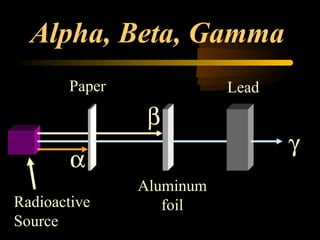
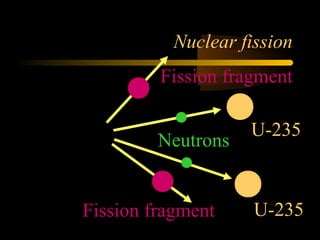
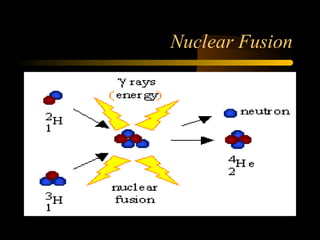
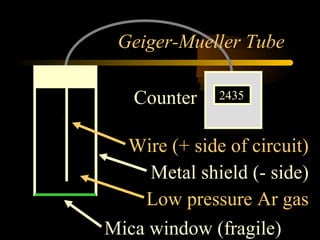
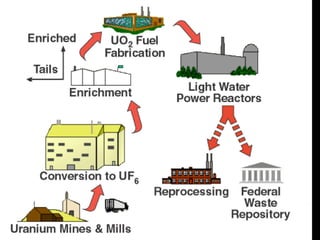
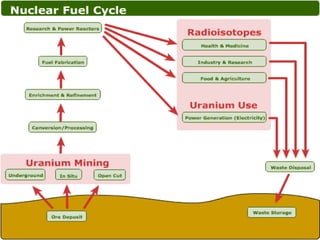
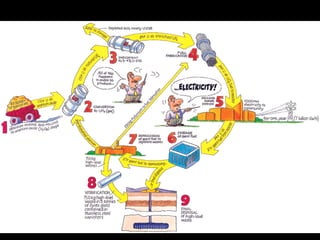
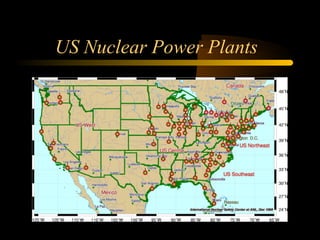
Here are the steps to solve a half-life problem:
1. Pick a starting mass (e.g. 30 g)
2. Choose a half-life (e.g. 5 years)
3. Plot the mass after each half-life on a graph with mass on the y-axis and time/half-lives on the x-axis
4. The graph will be exponential decay
5. Mass never reaches exactly zero
6. Radioactivity is no longer a problem after about 5-7 half-lives as the mass becomes very small
7. Exponential decay is described by the equation: M = M0 * (1/2)^(t/t1/2)