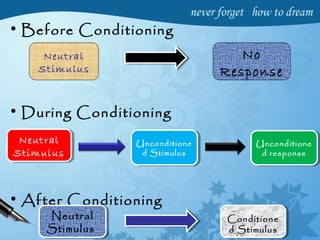
The presentation covers the concept of learning, its nature, and factors that influence it, such as motivation, practice, environment, and social groups. It introduces various theories of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning, and cognitive learning, each explaining different mechanisms of behavior acquisition. Ultimately, the document emphasizes that learning leads to permanent changes in behavior driven by both direct and indirect experiences.