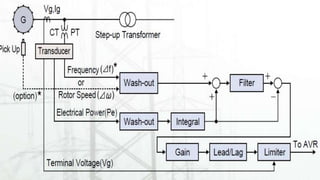
The document discusses power system stability, which is the ability of an electric power system to regain equilibrium after disturbances. It highlights the role of power system stabilizers (PSS) in enhancing damping of rotor oscillations caused by small signal disturbances, elaborating on different types of stabilizers and their functionalities. The advantages and disadvantages of PSS are also mentioned, along with references for further reading.