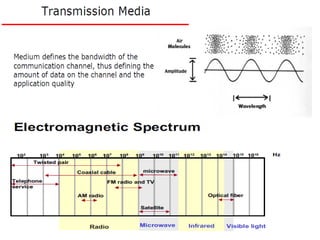
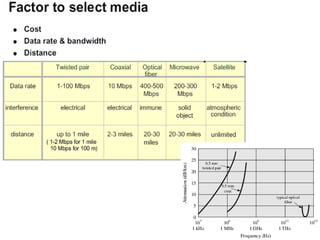
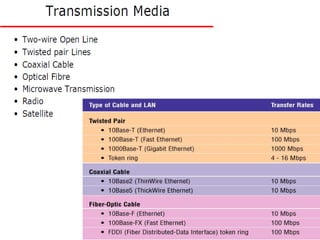
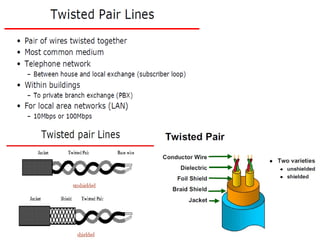
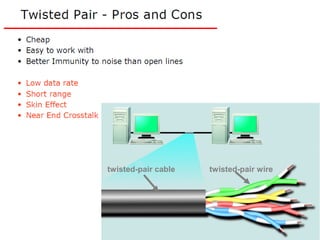
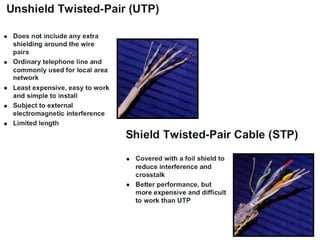
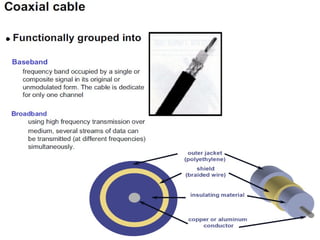
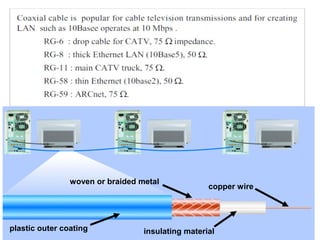
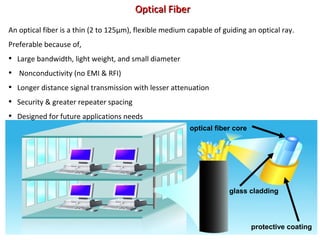
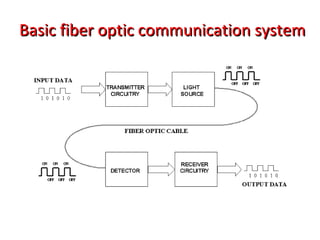
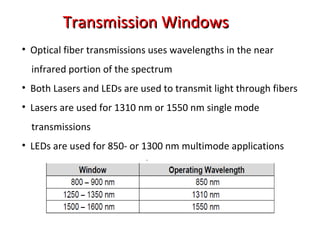
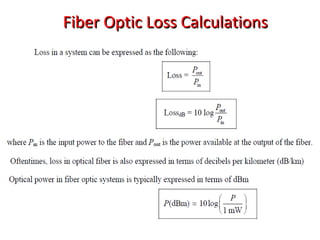
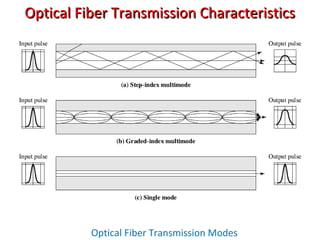
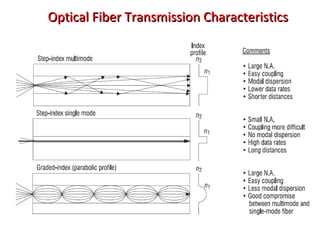
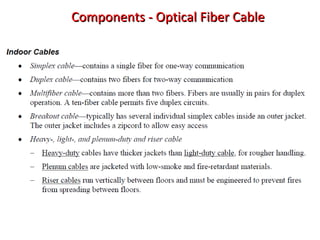
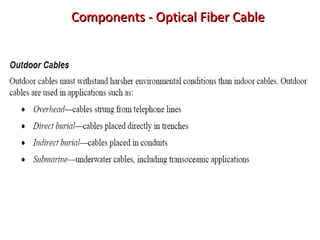
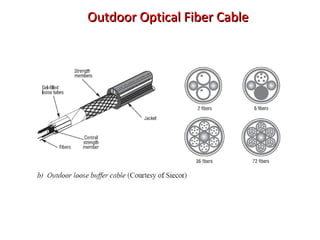
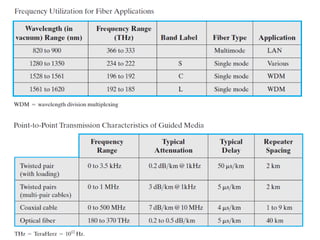
This document provides information about optical fibers, including their core components, types, transmission characteristics, and applications. It discusses the basic structure of an optical fiber, which consists of a glass core surrounded by a cladding layer and protective coating. The document outlines the three main types of optical fibers - step-index multimode, graded-index multimode, and single mode - and their uses in different communication systems. It also covers optical fiber transmission windows, loss calculations, and system components.