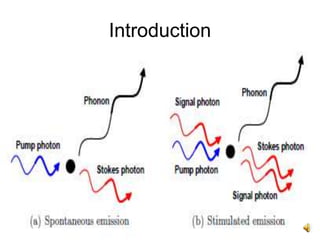
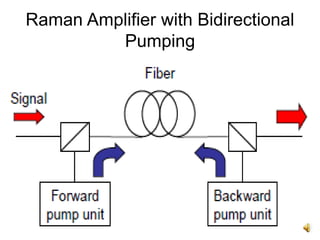
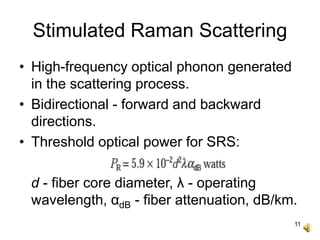
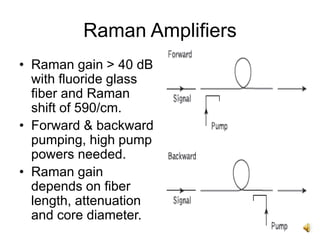
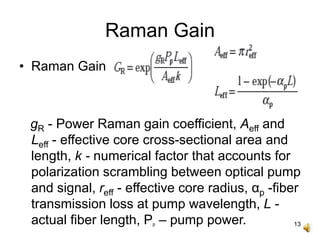
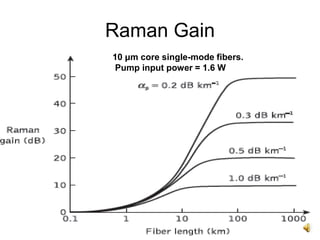
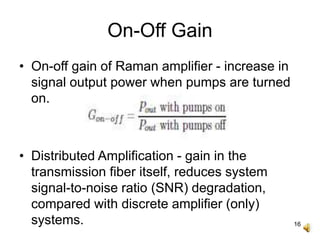
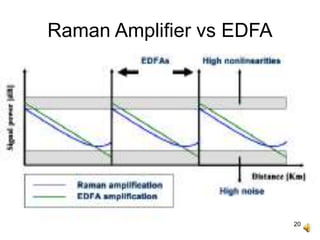
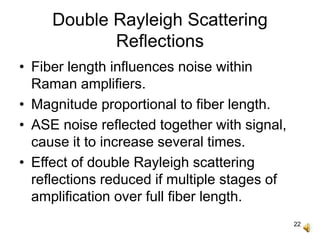
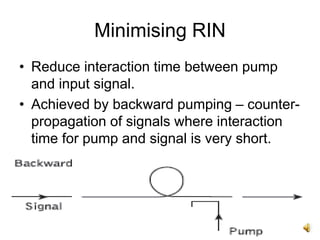
The document covers the principles and technology behind Raman fiber amplifiers, detailing the mechanisms of stimulated Raman scattering and the types of Raman amplifiers, including discrete and distributed models. It discusses key factors influencing Raman gain, noise issues such as amplified spontaneous emission, and deployment challenges, along with various applications in long-distance optical transmission. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of system integration and safety measures in managing high optical powers.