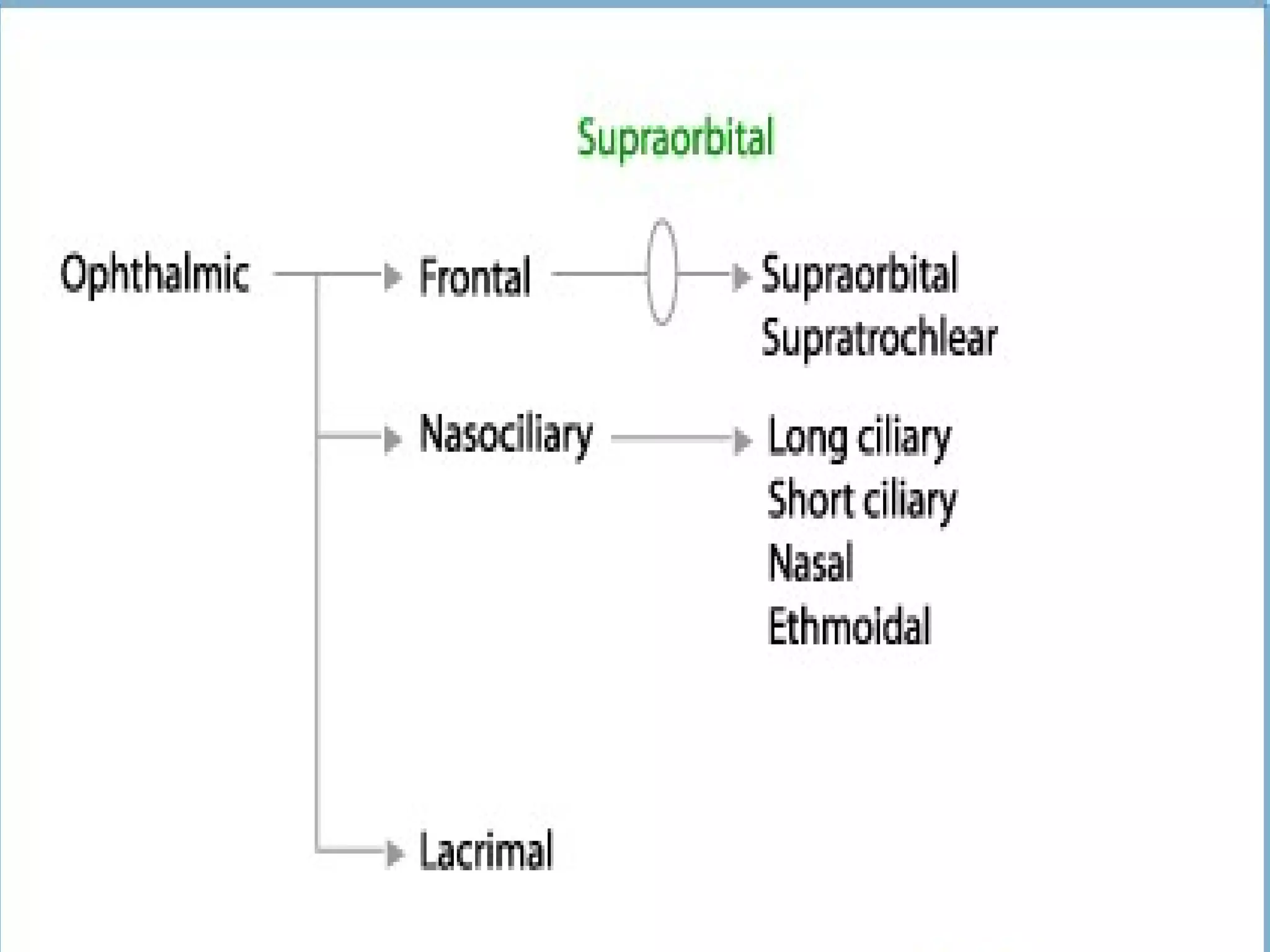
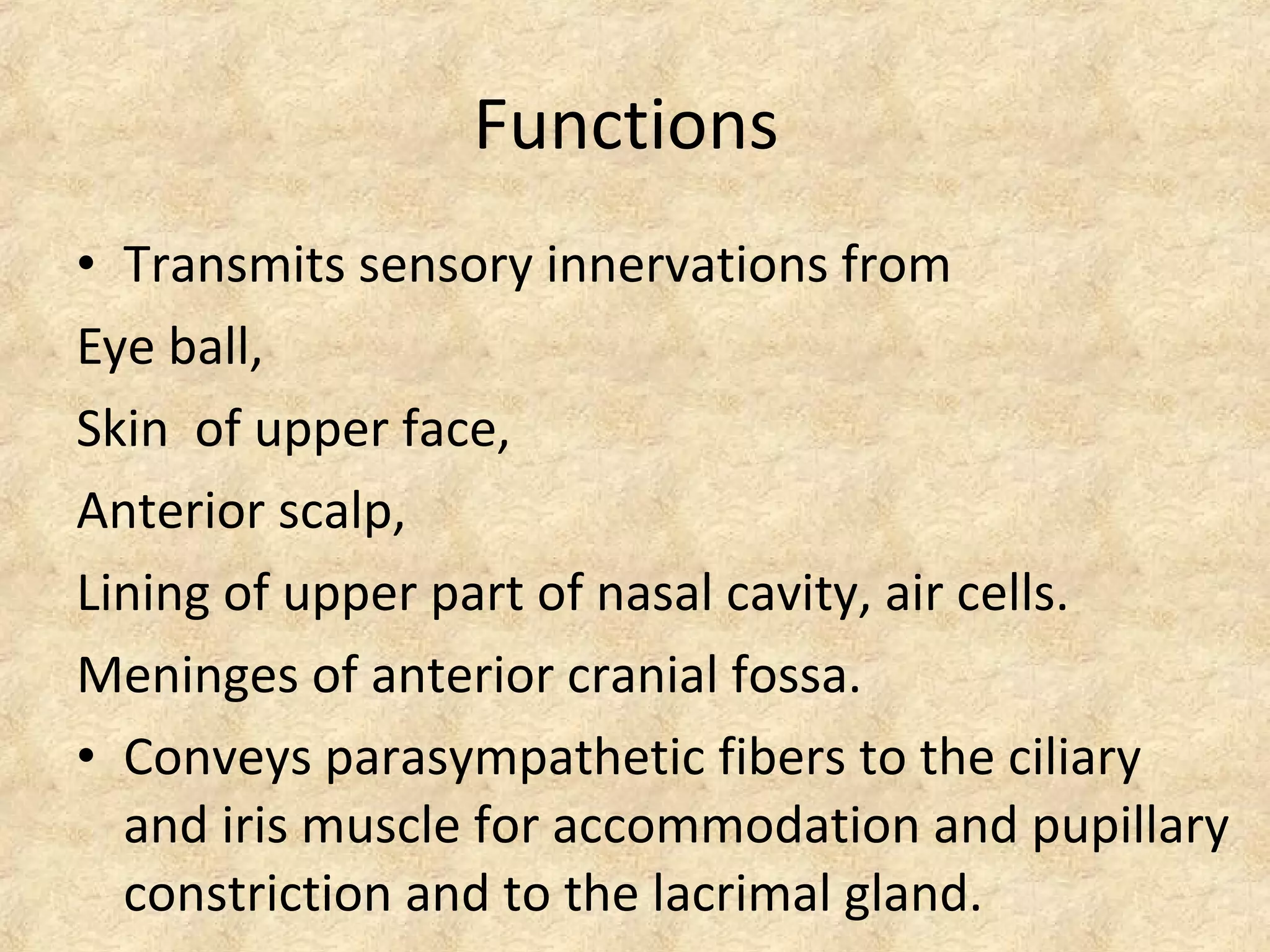
The ophthalmic nerve is the smallest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve. It arises from the upper part of the semi lunar ganglion and passes forward along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus before dividing into three branches - the lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary nerves. These branches innervate sensory structures of the eye, upper face, and nasal cavity. The ophthalmic nerve also transmits parasympathetic fibers that control functions of the iris, ciliary muscle, and lacrimal gland.