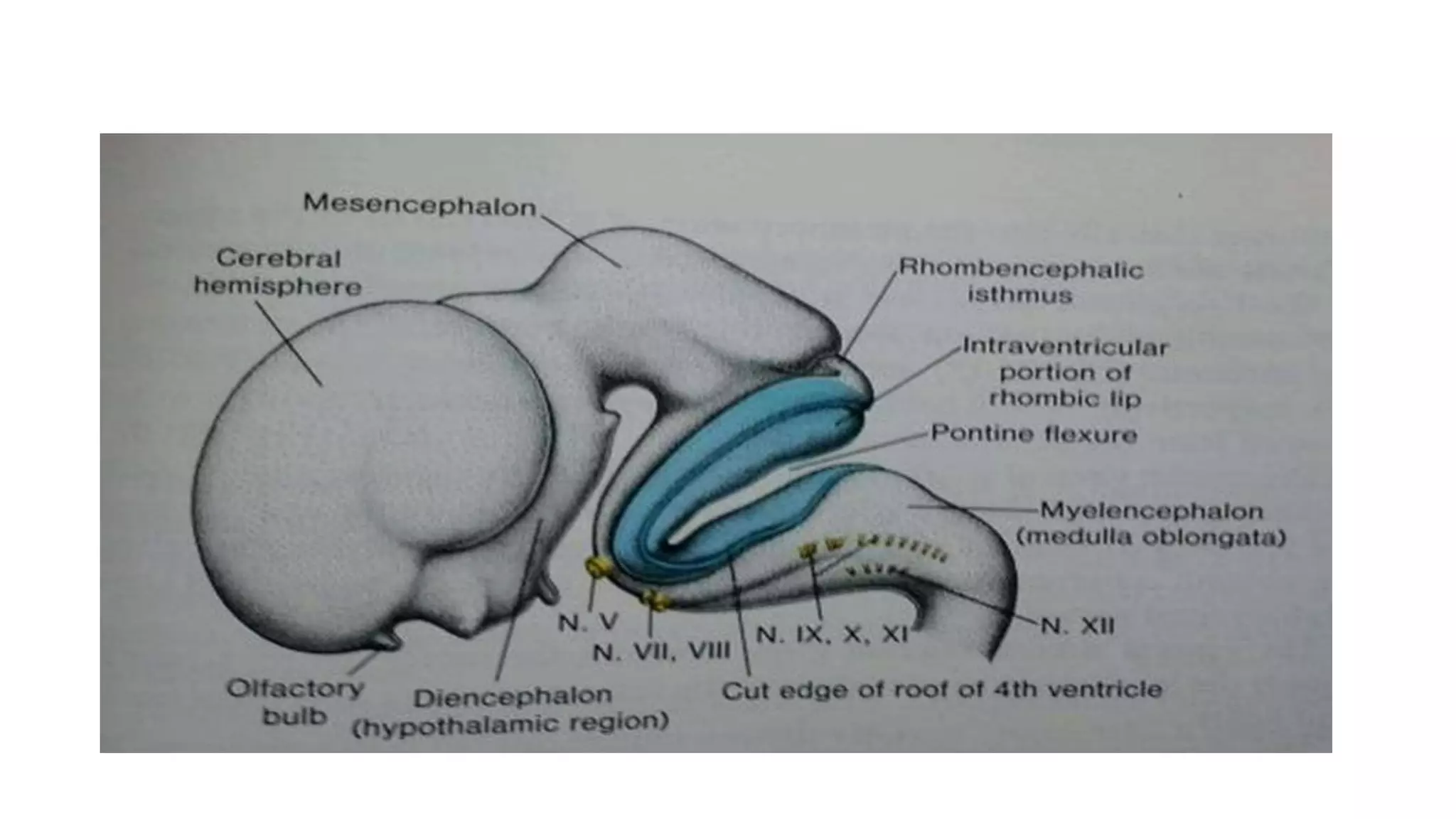
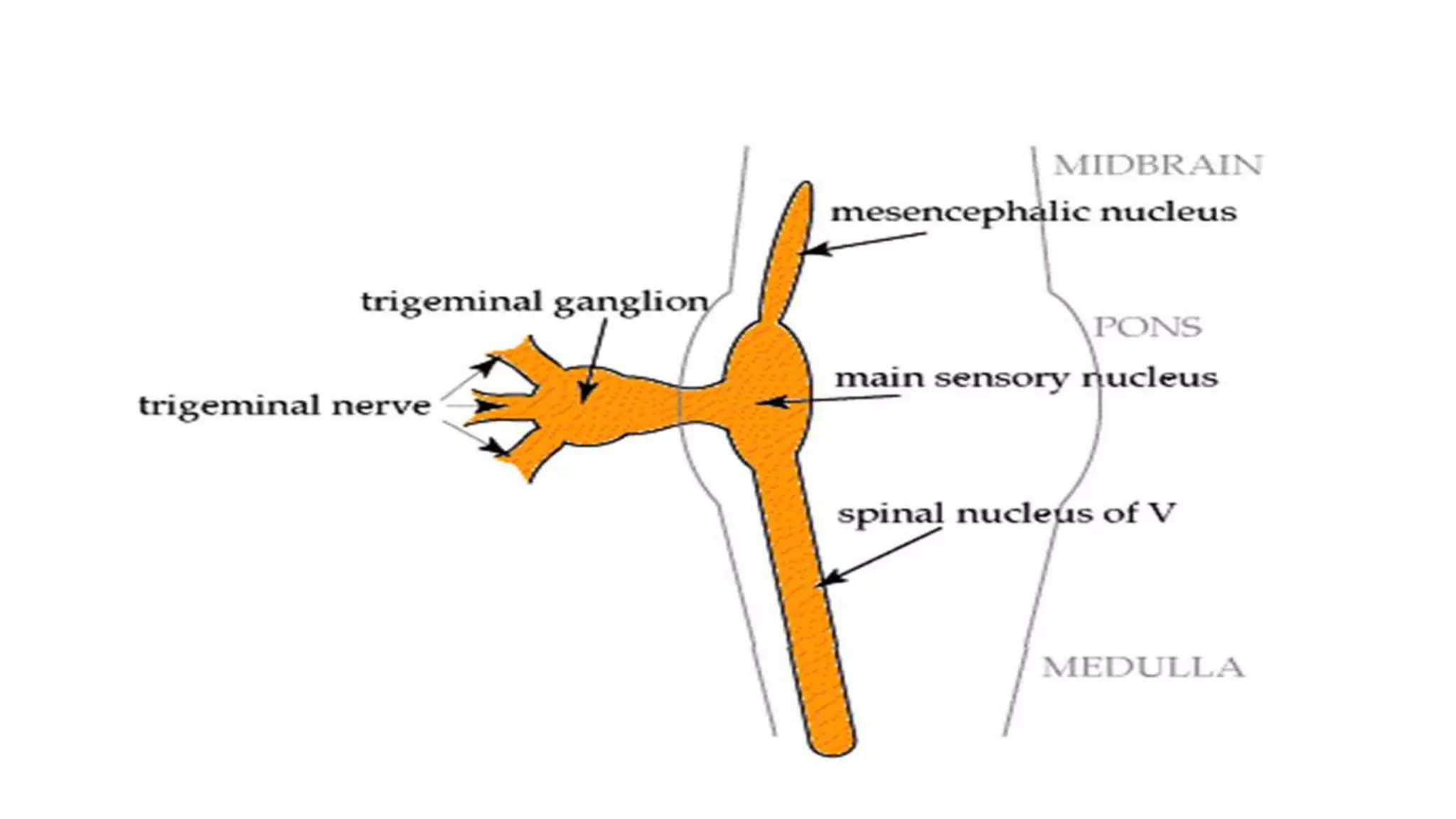
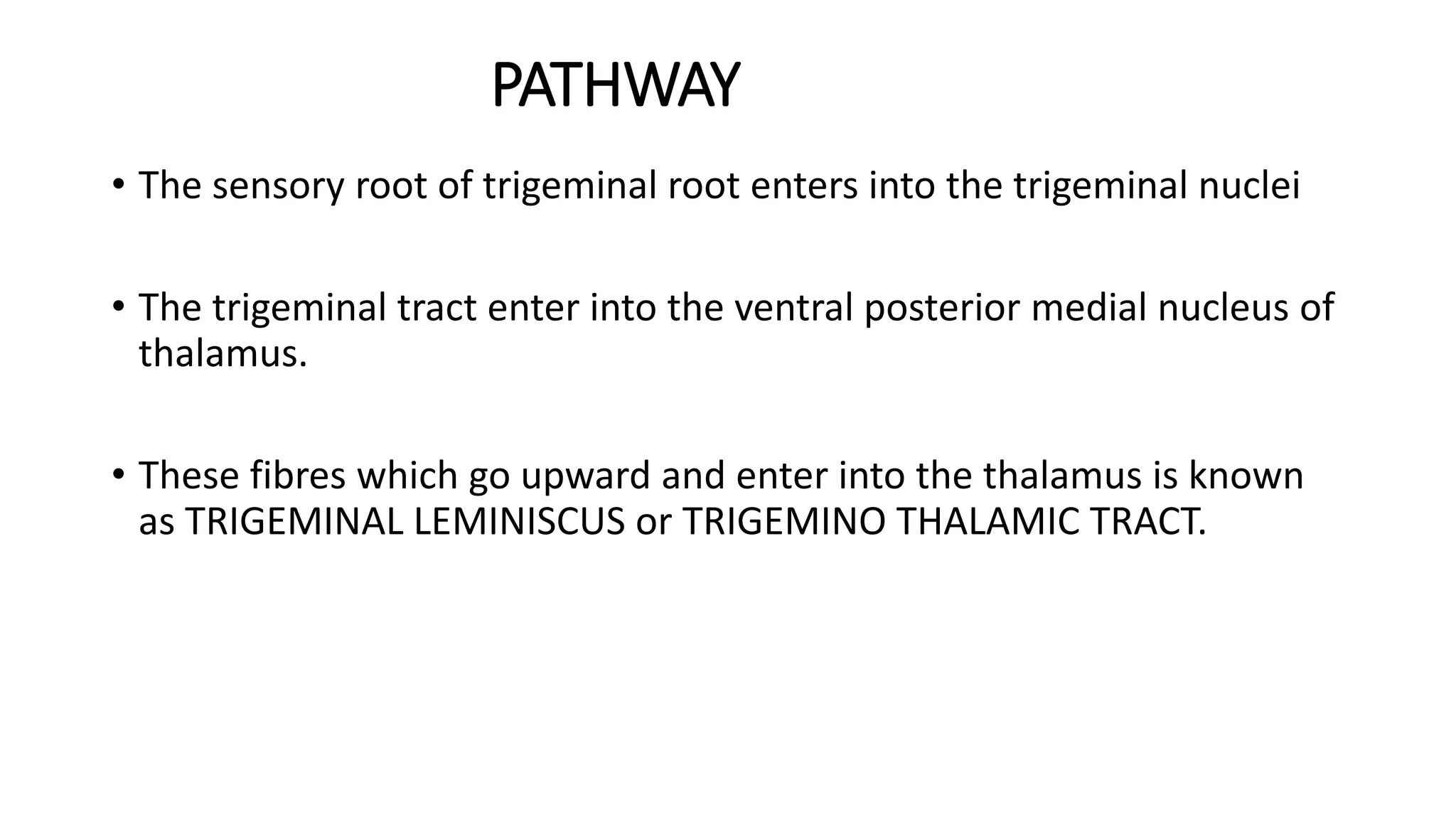
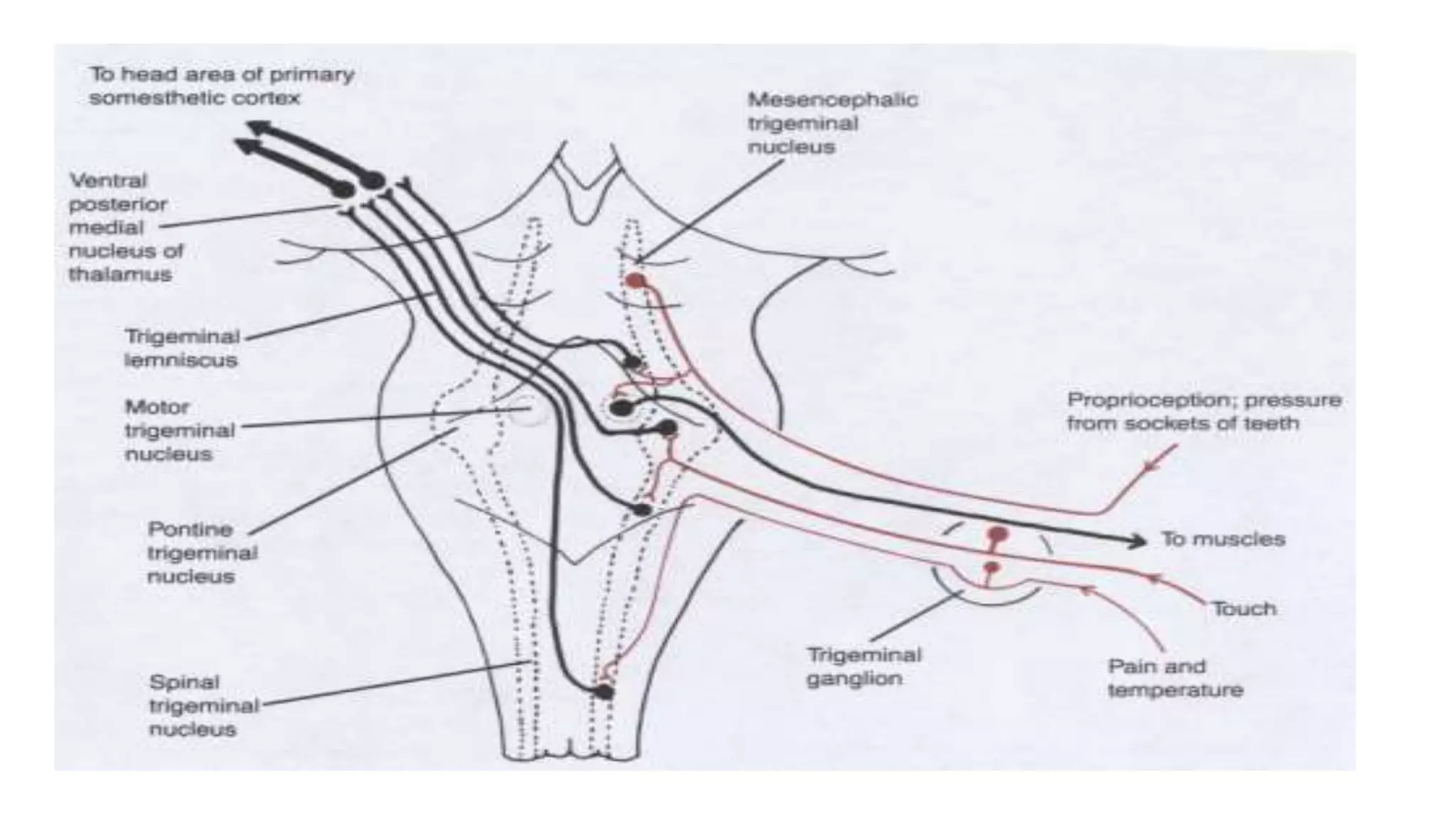
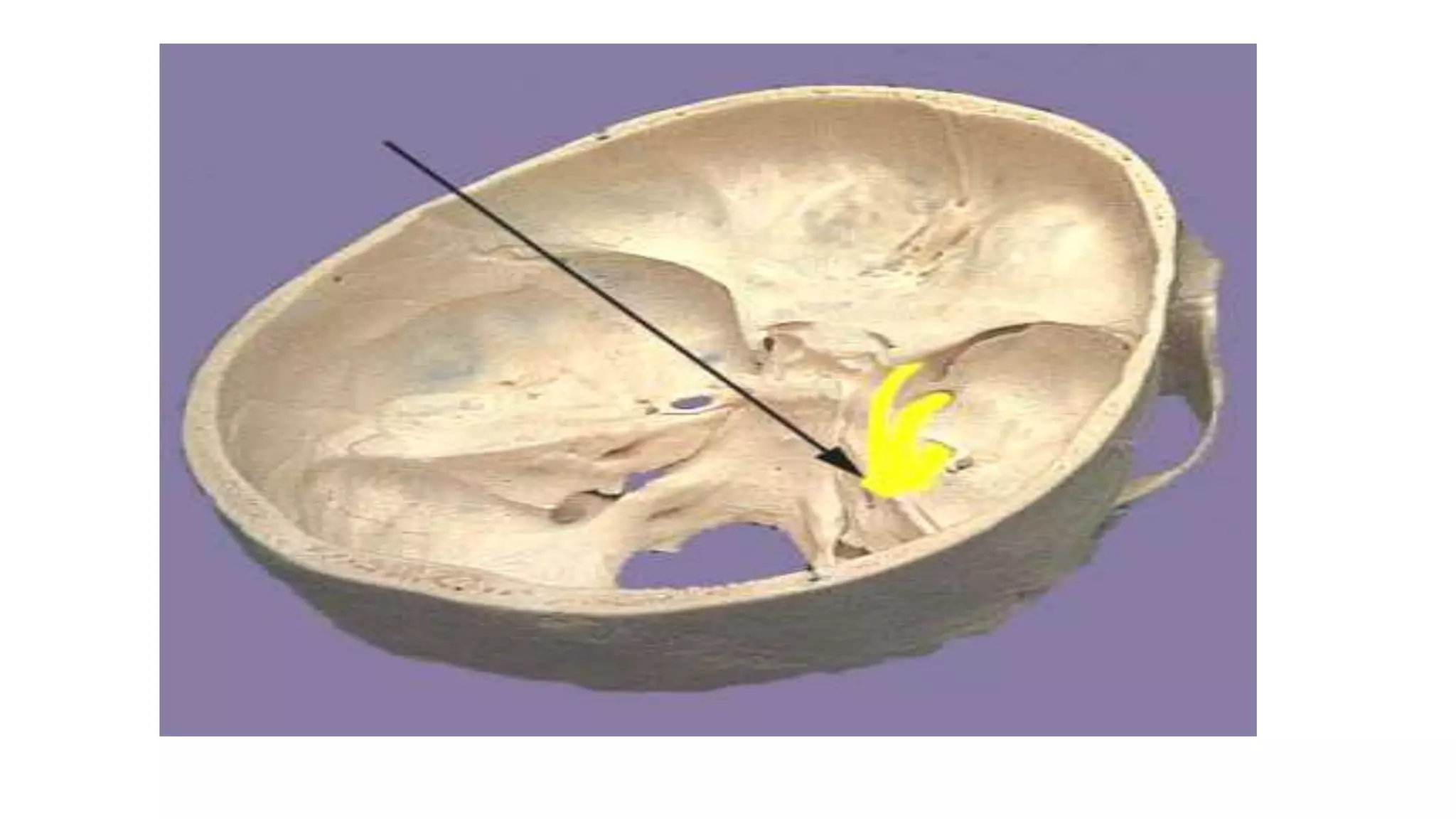
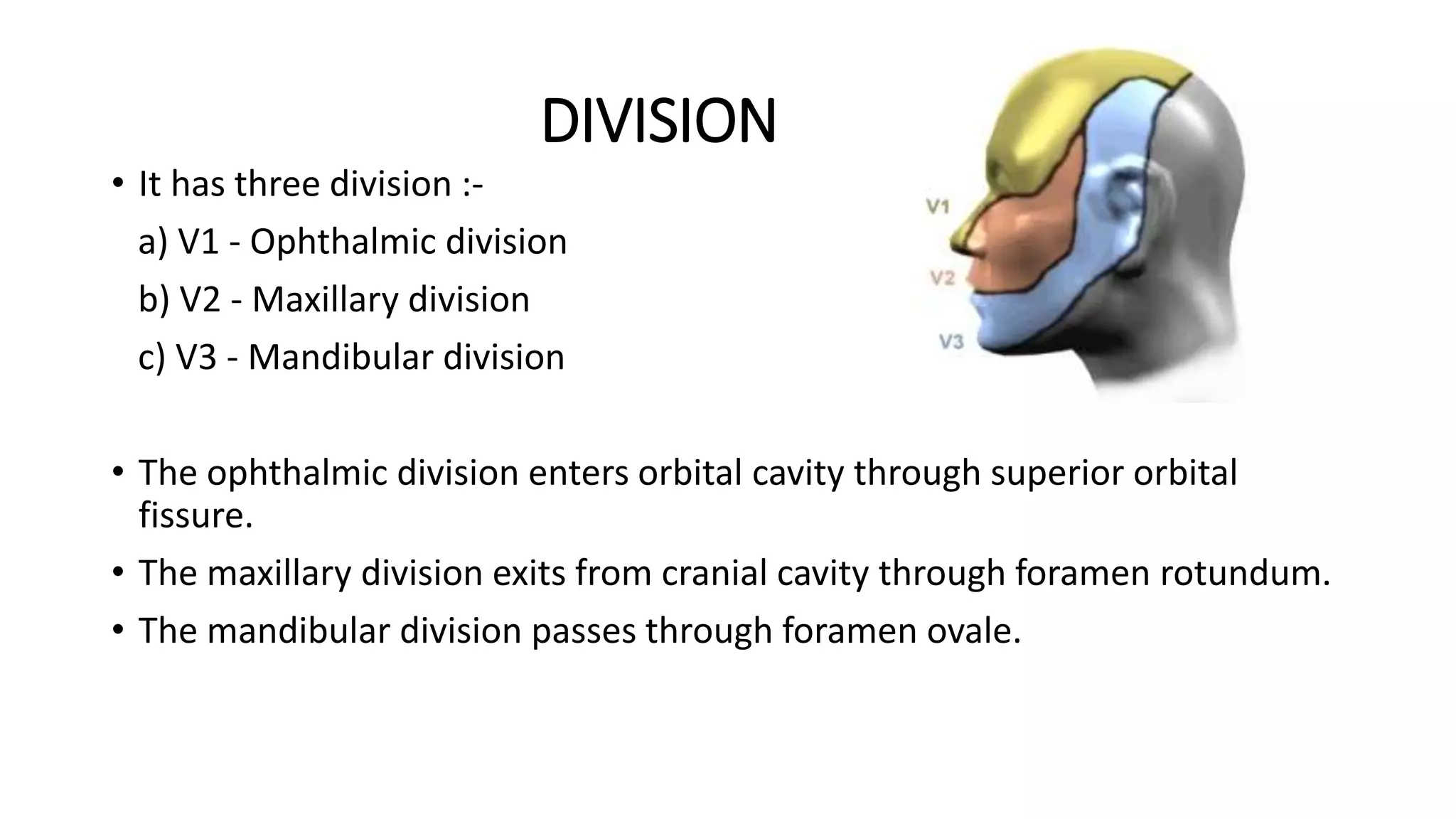
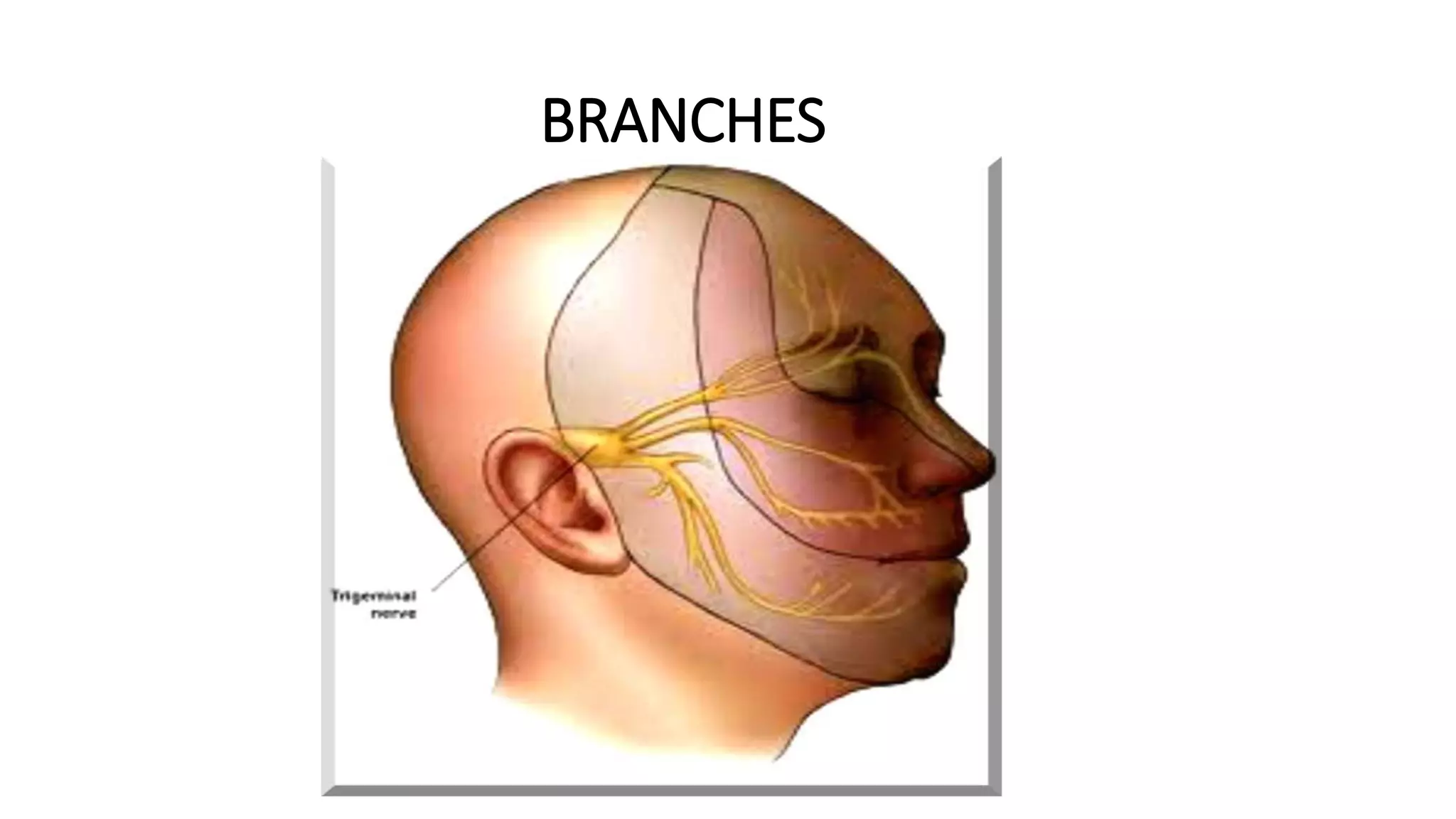
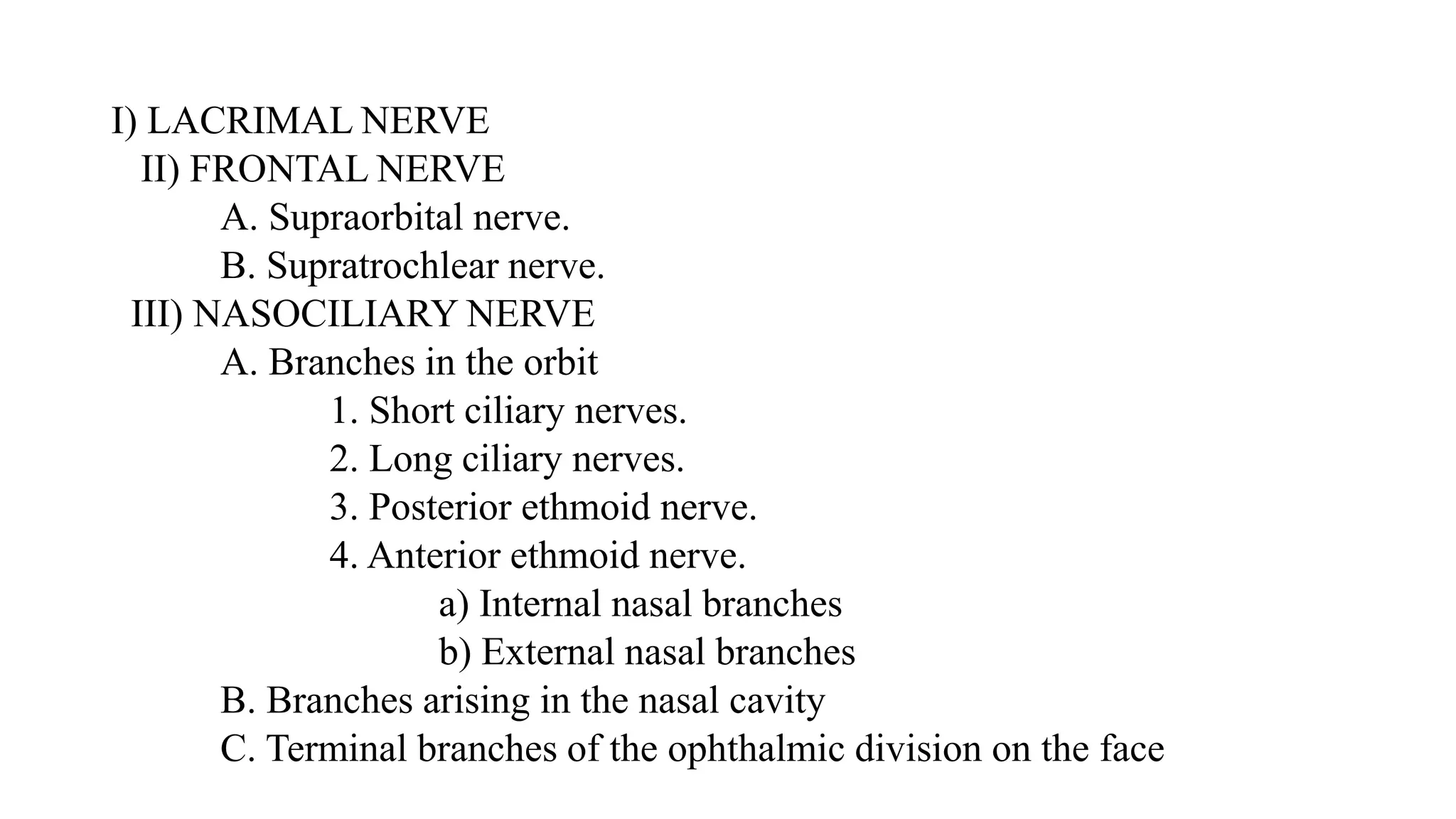
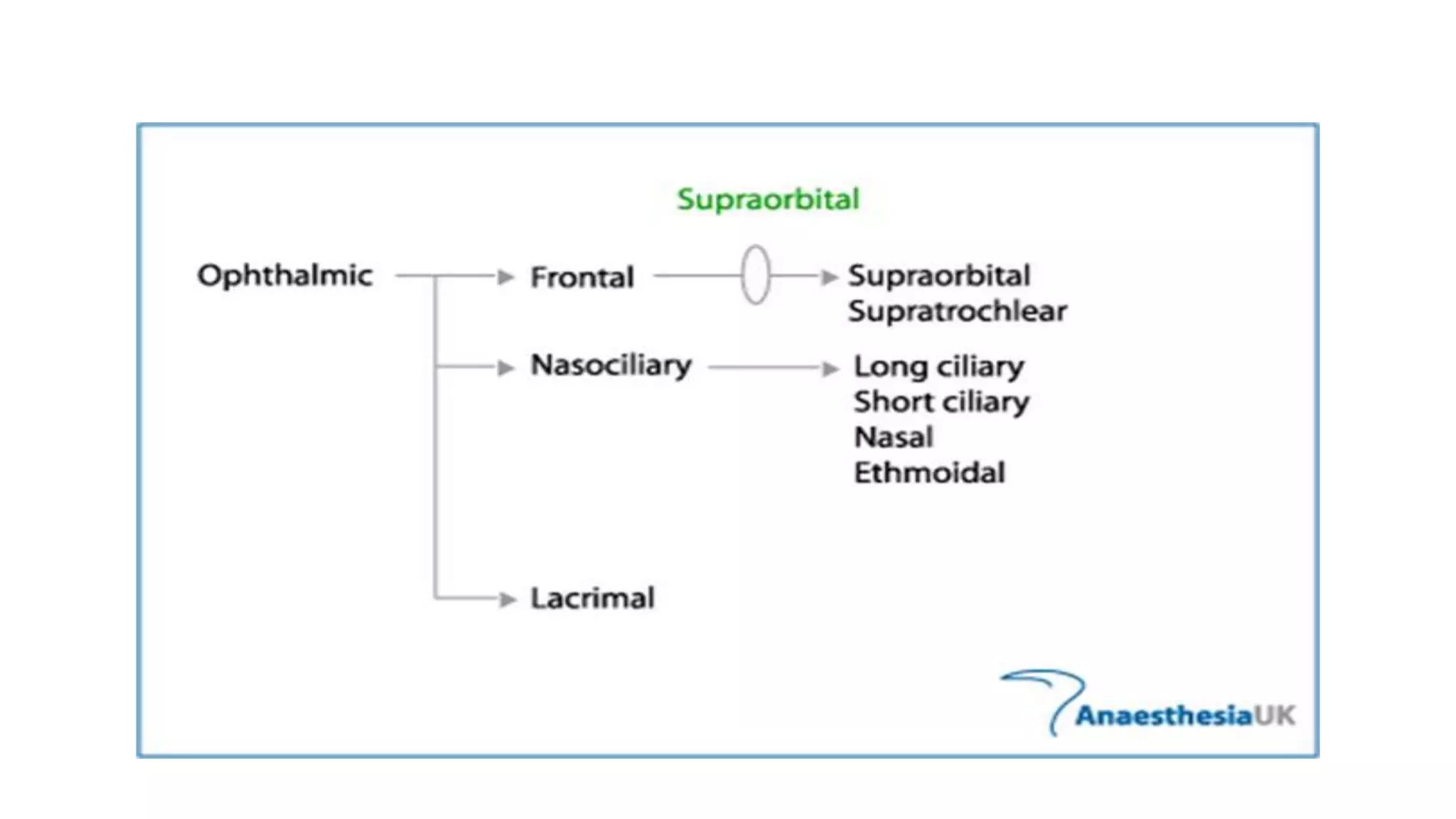
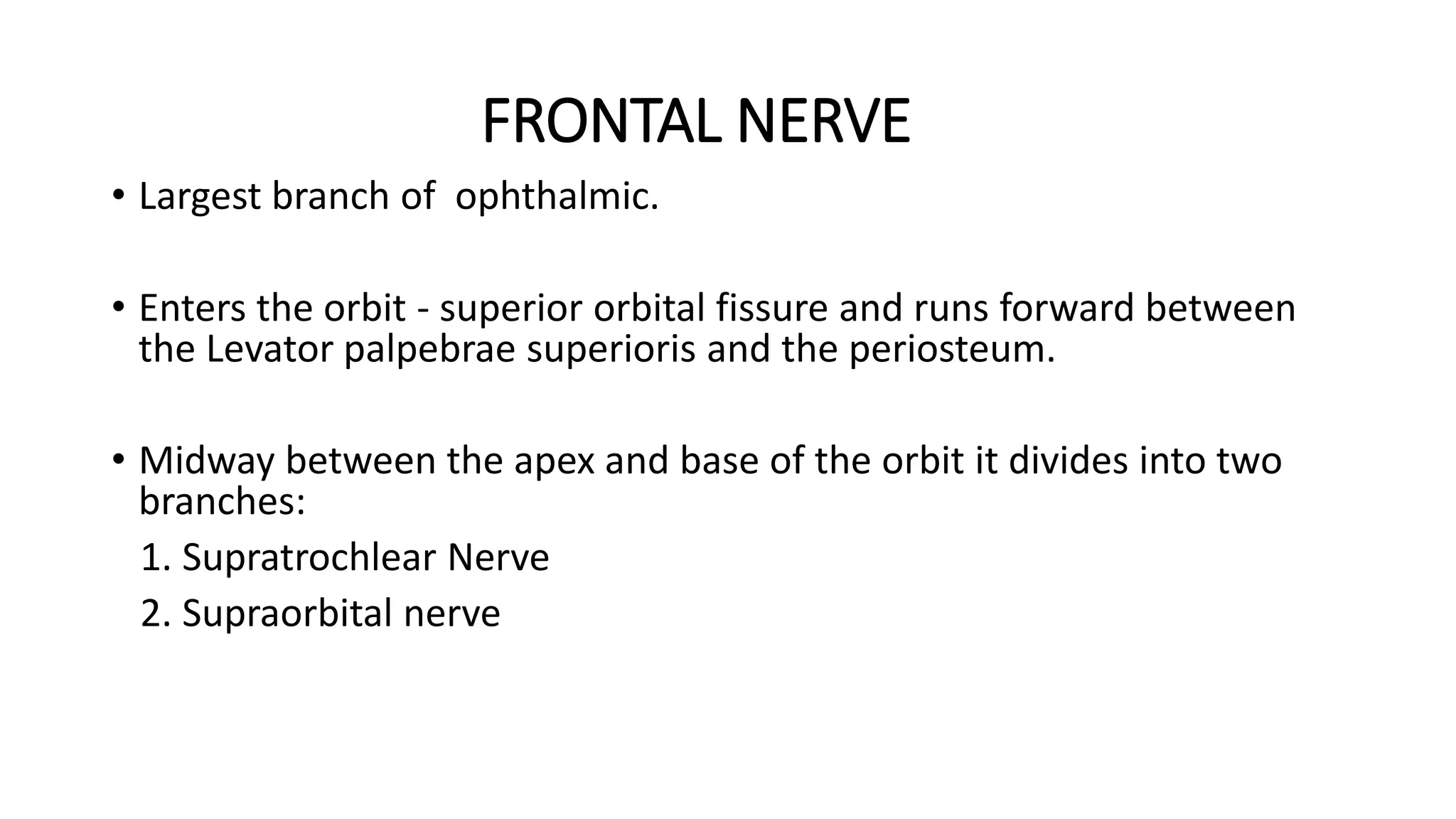
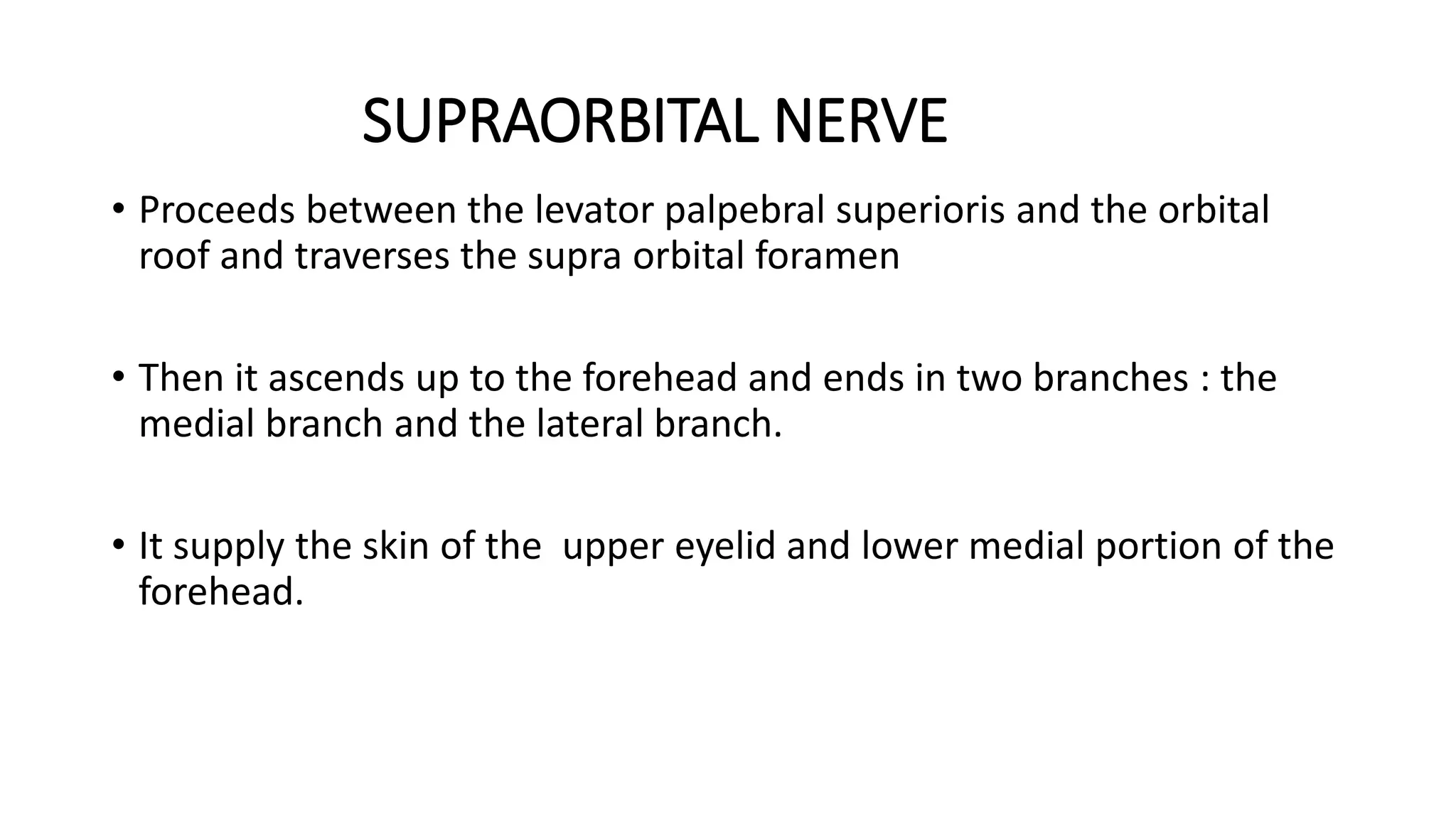
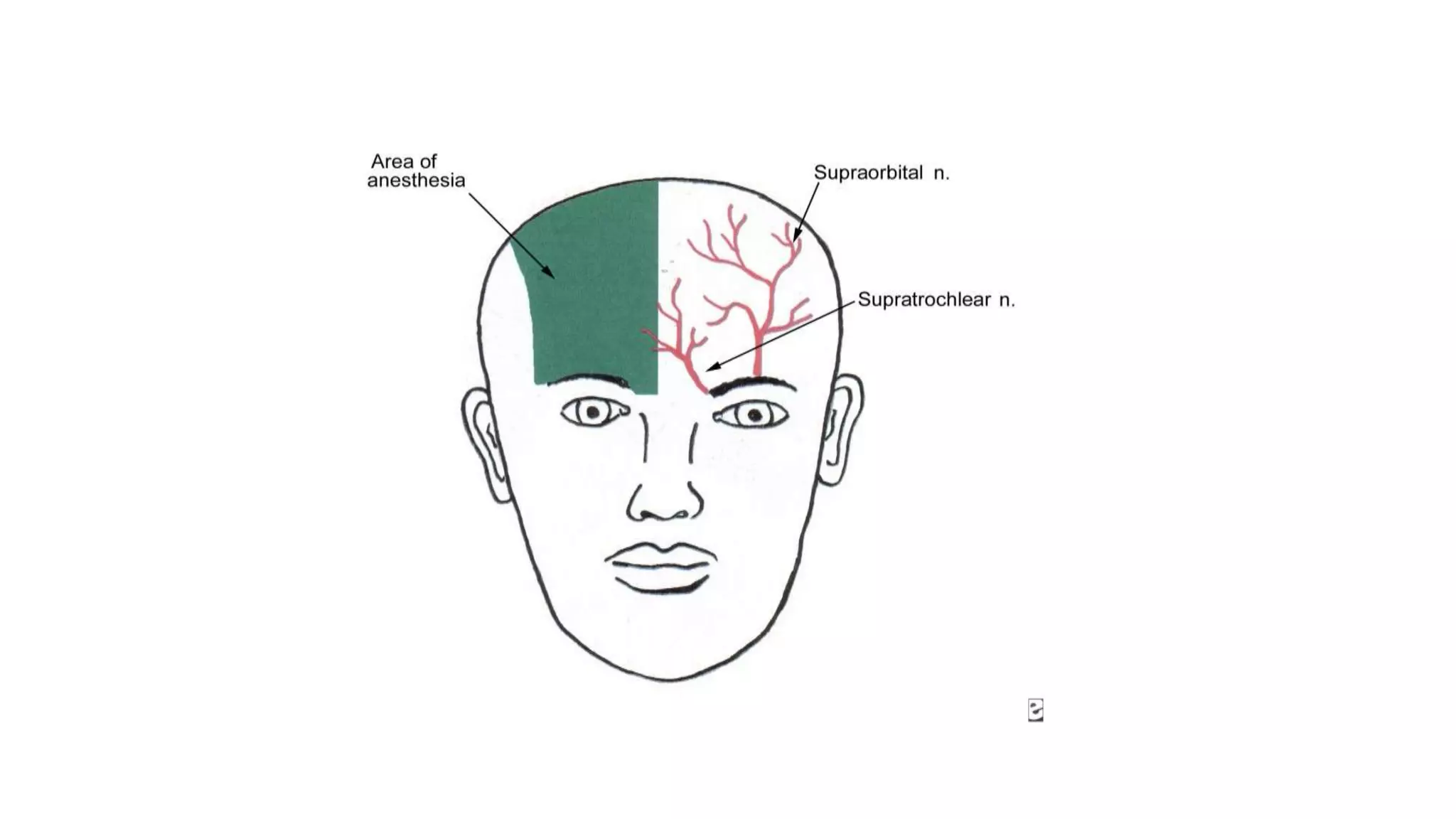
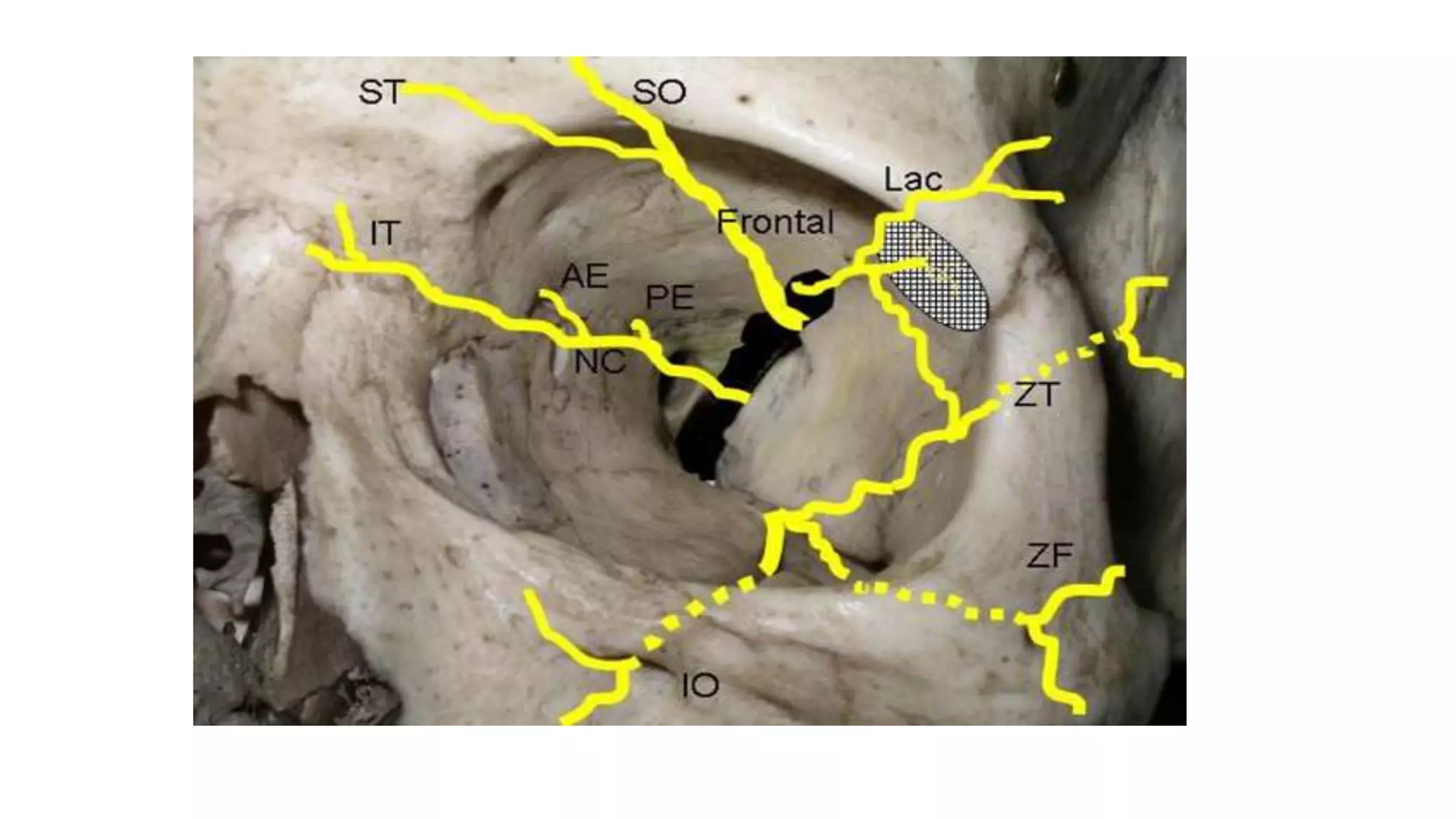
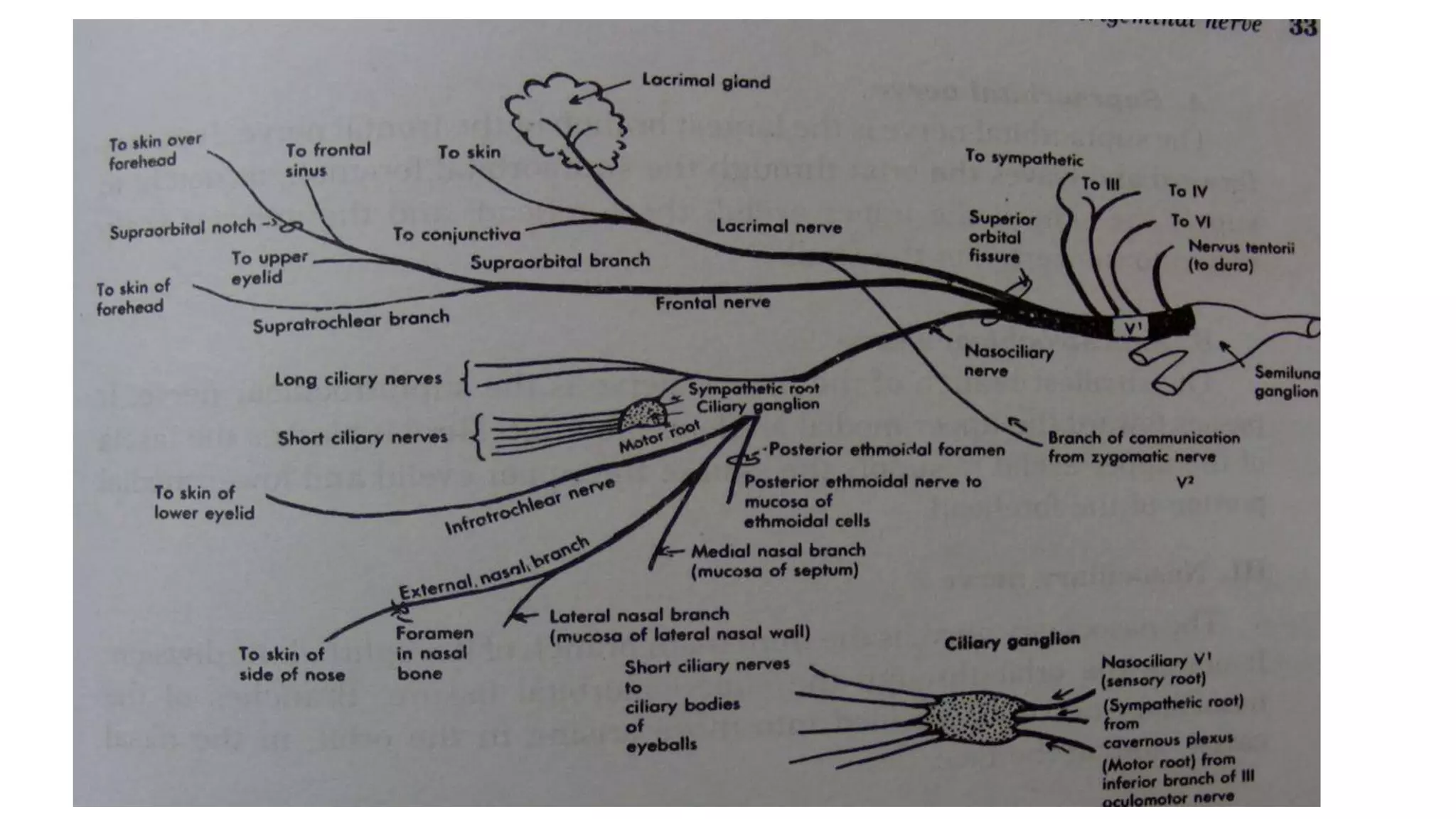
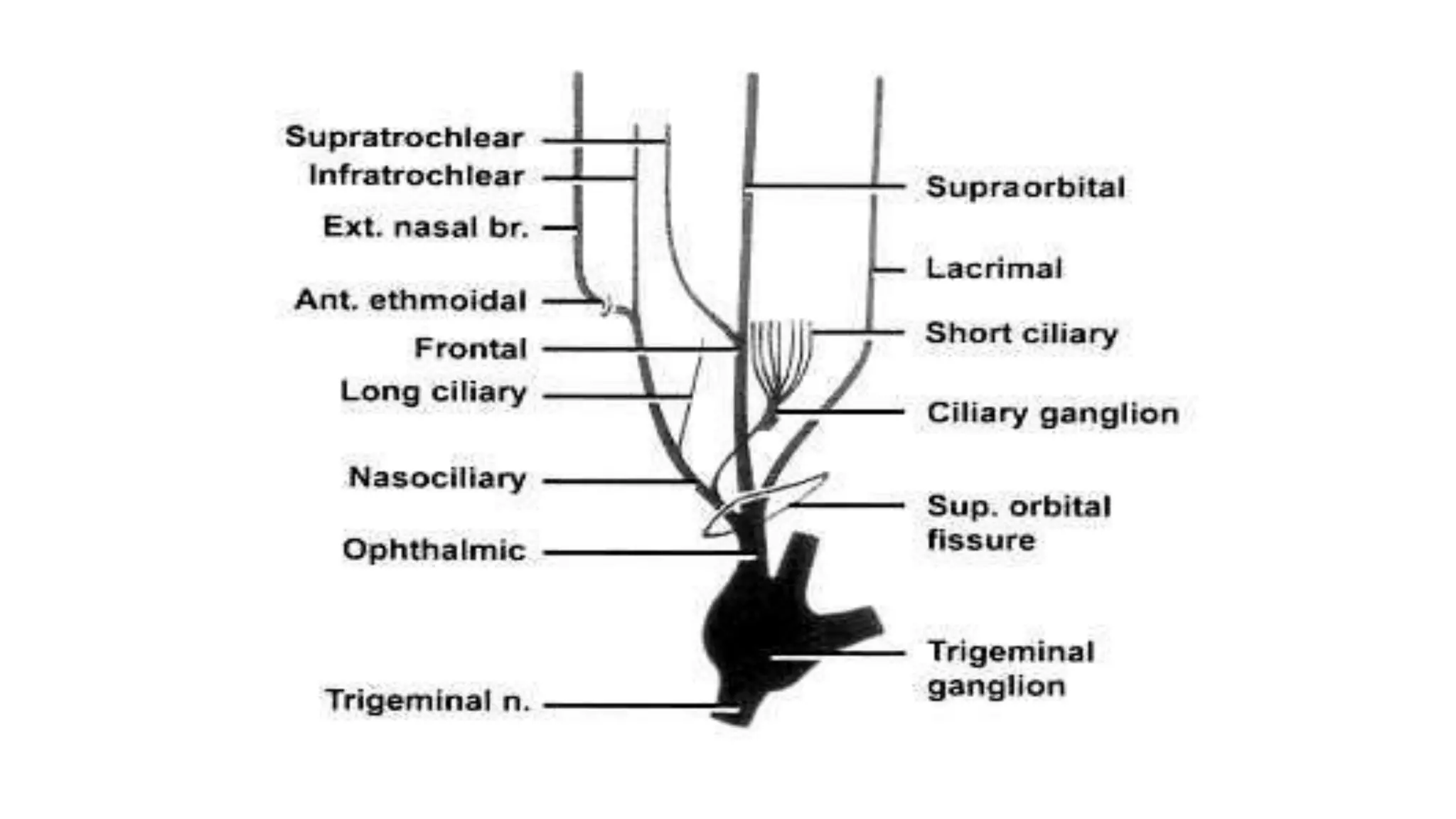
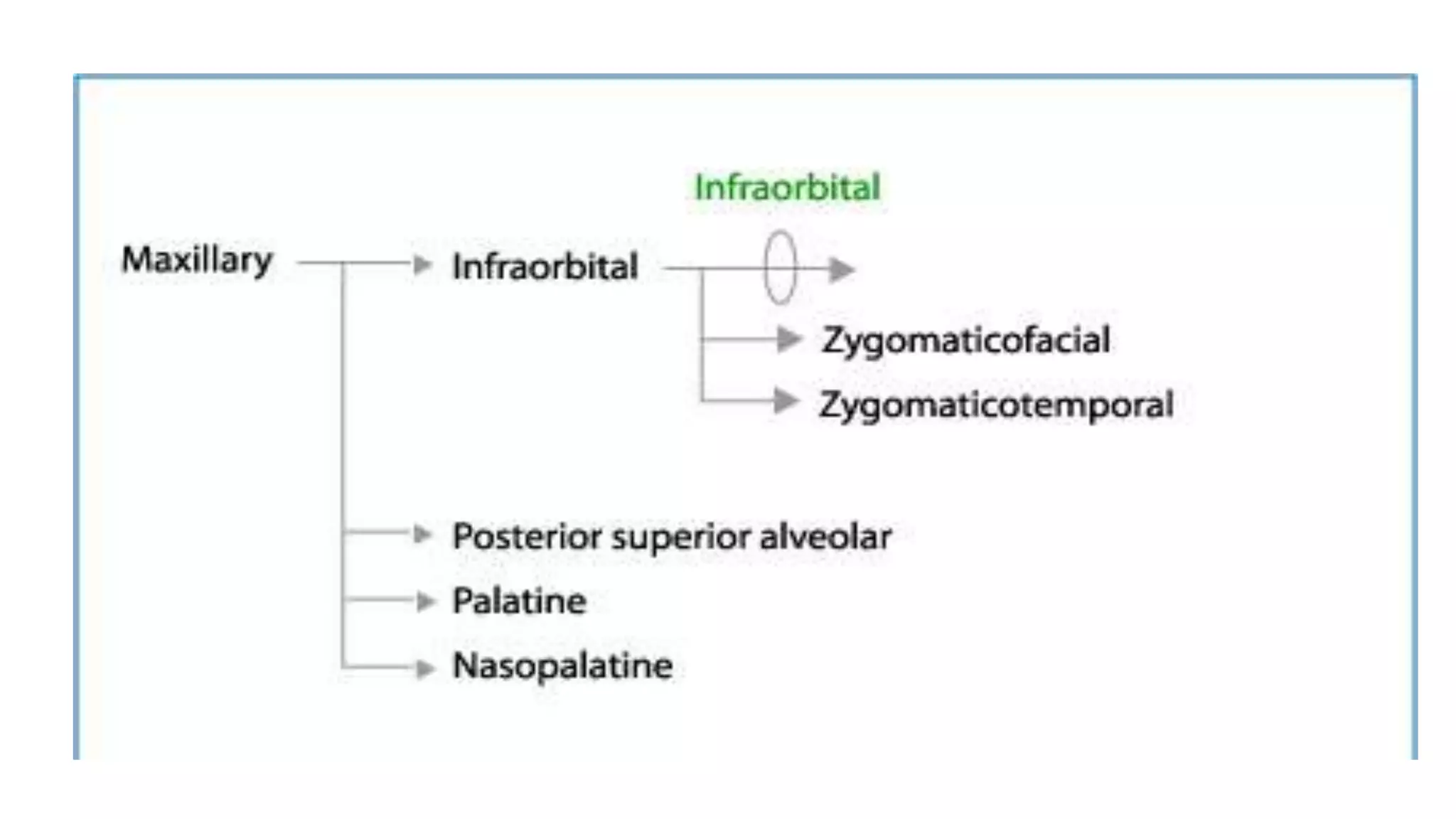
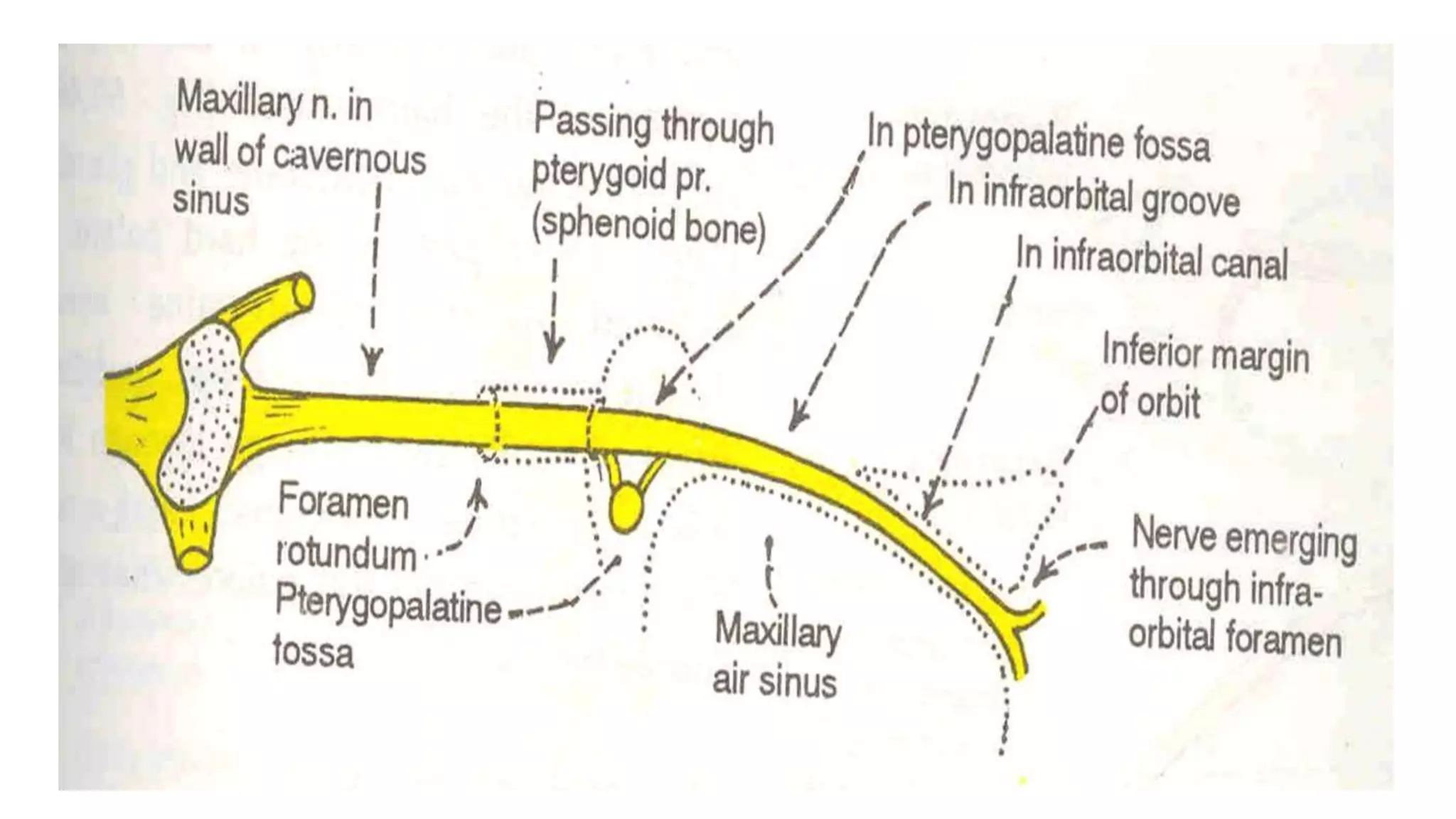
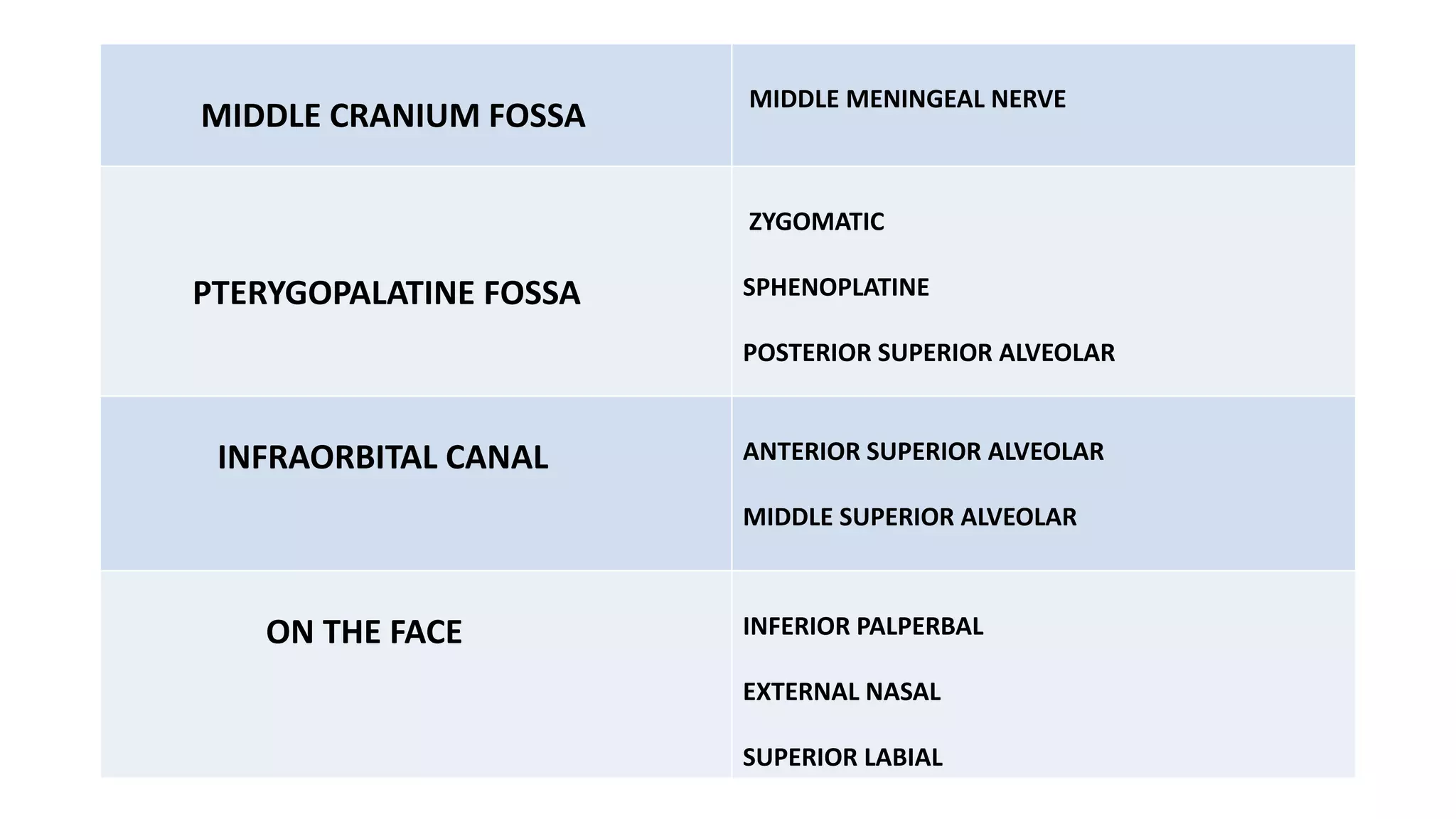
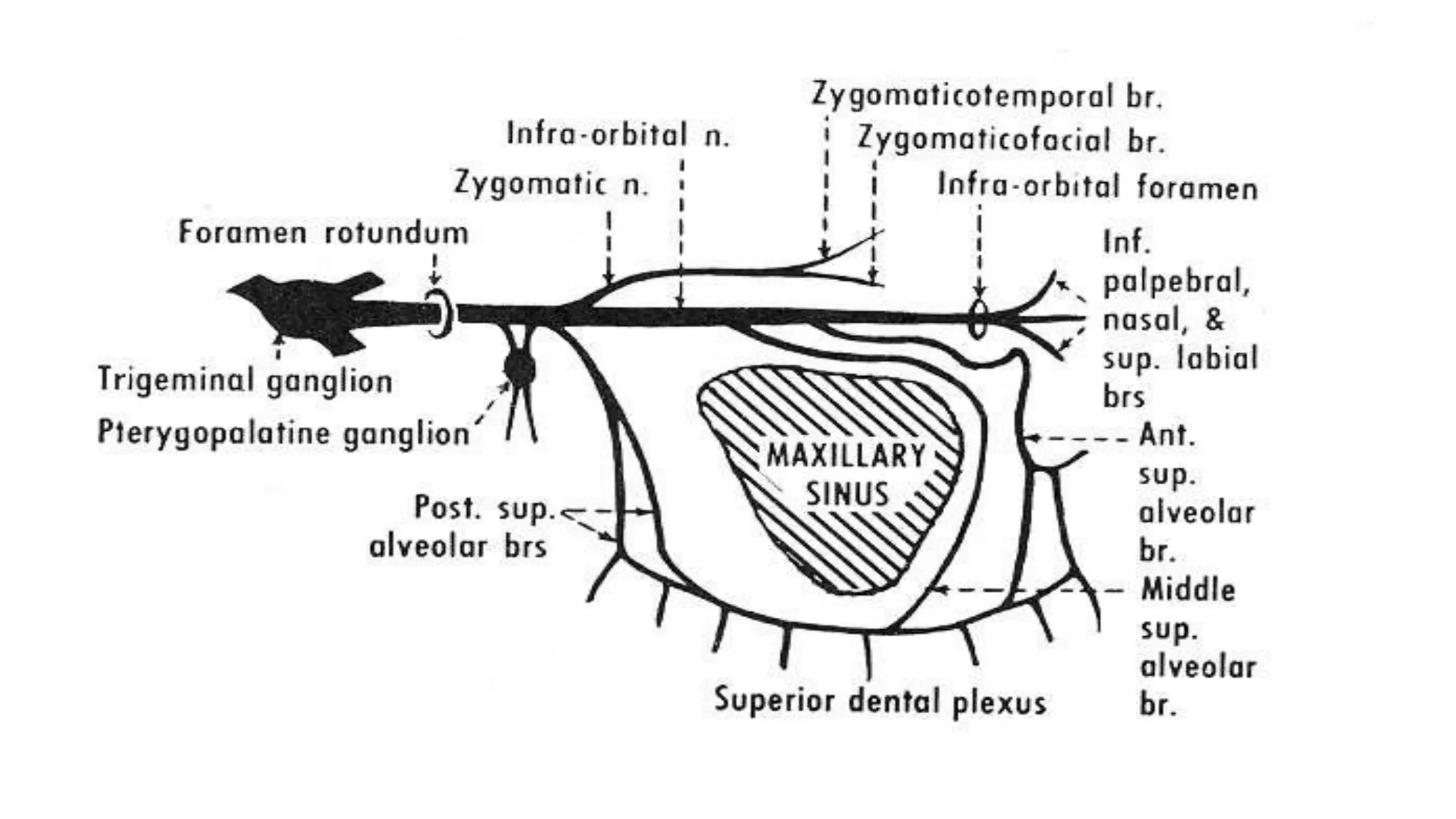
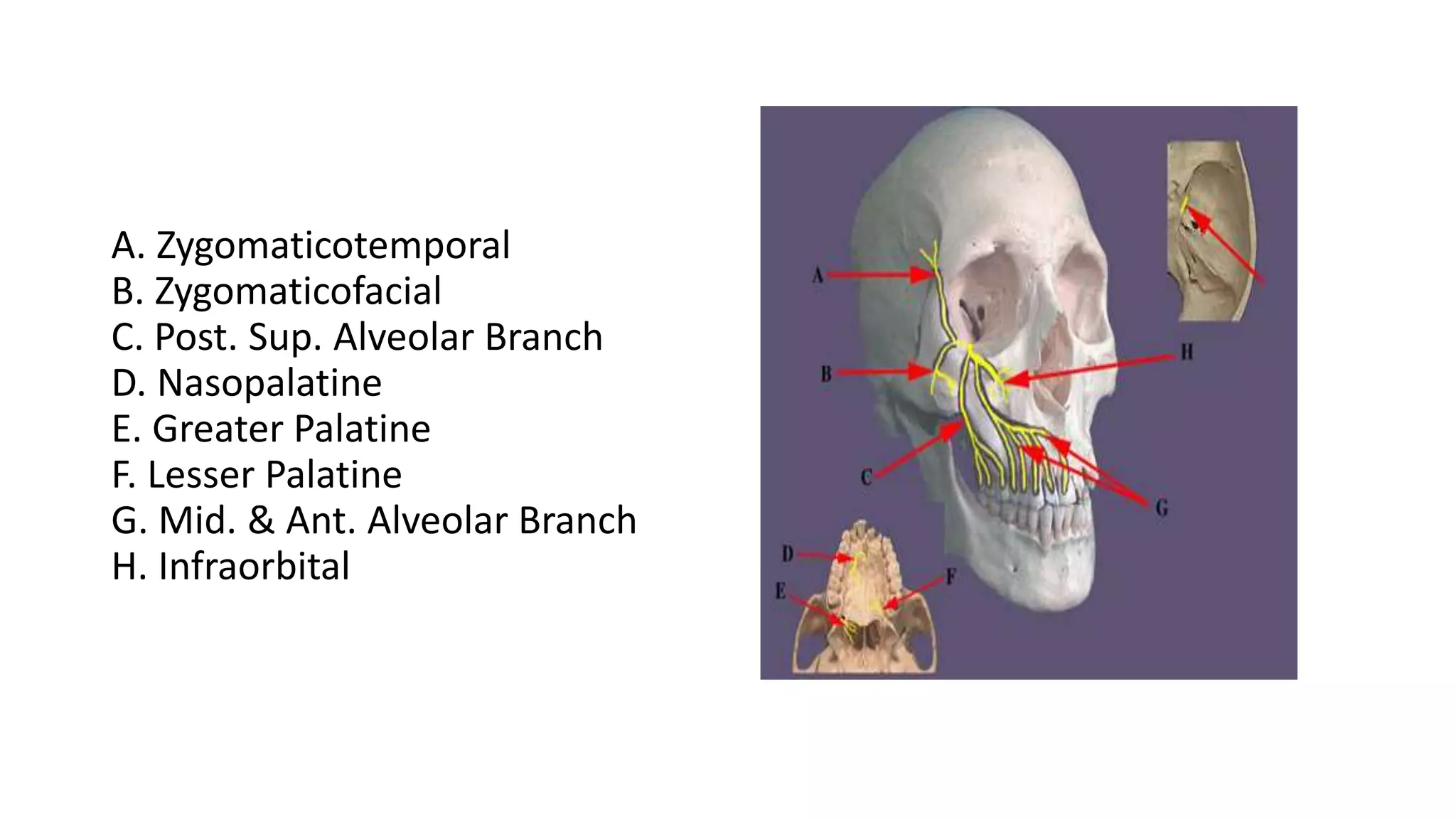
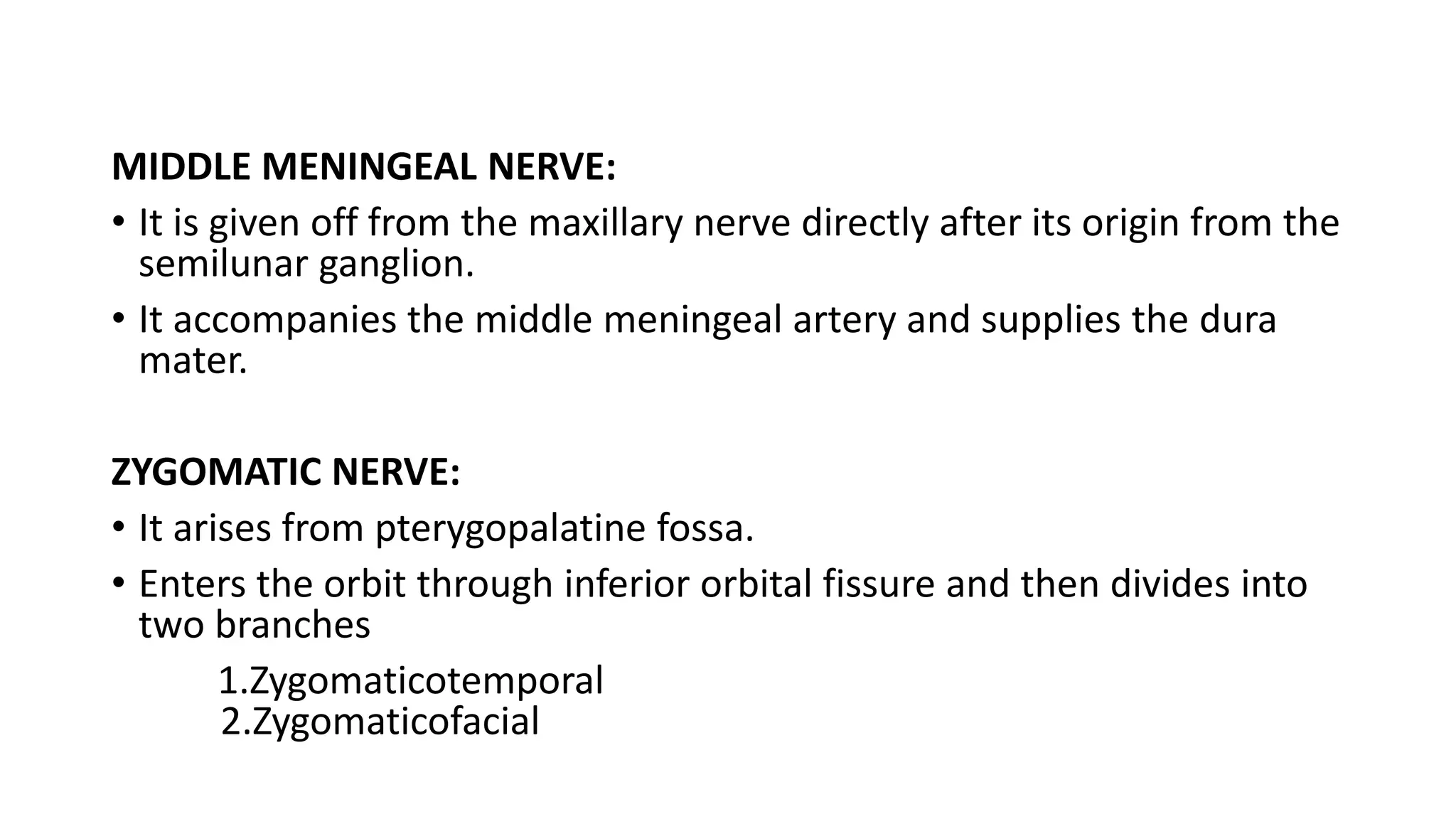
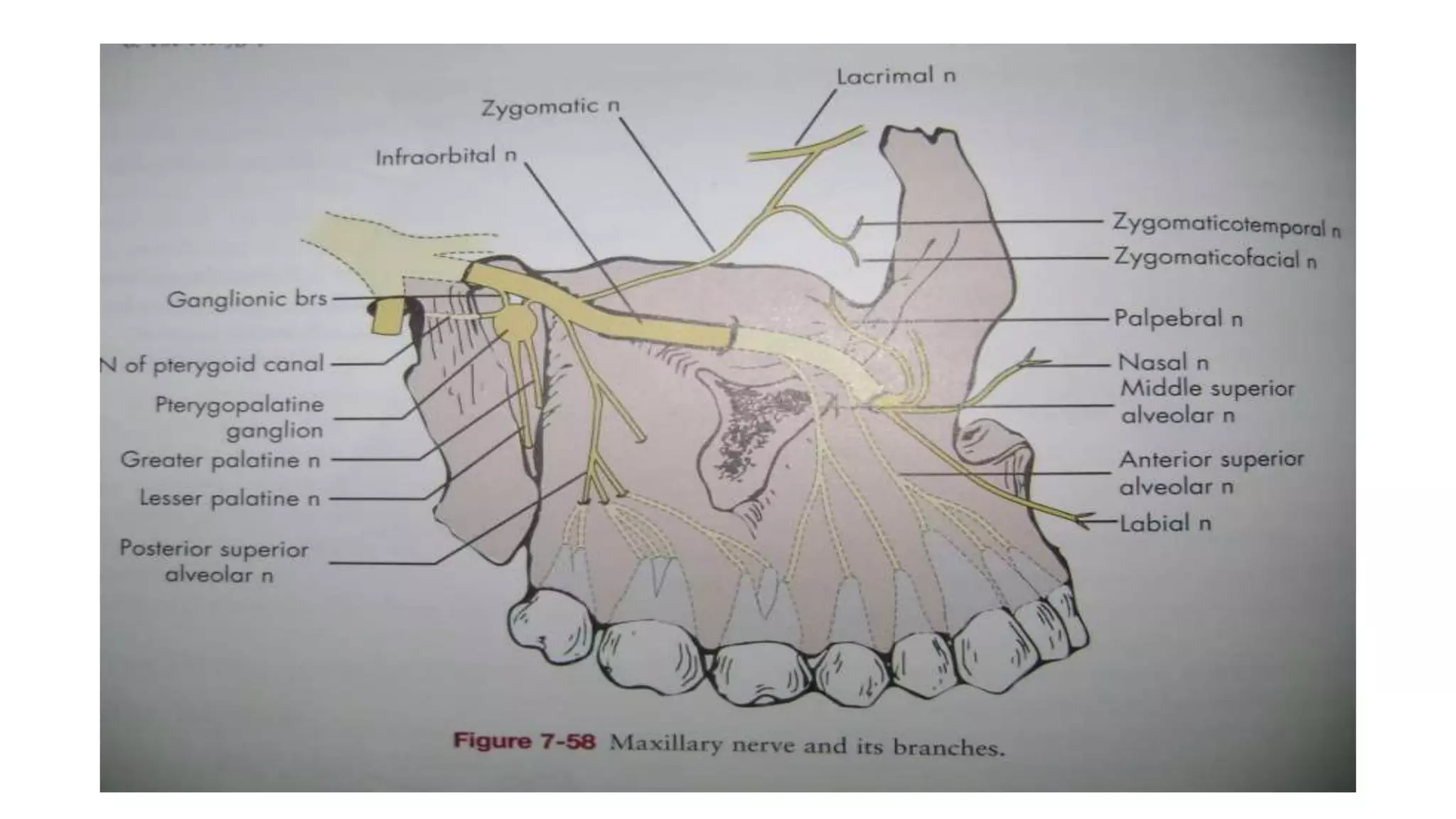
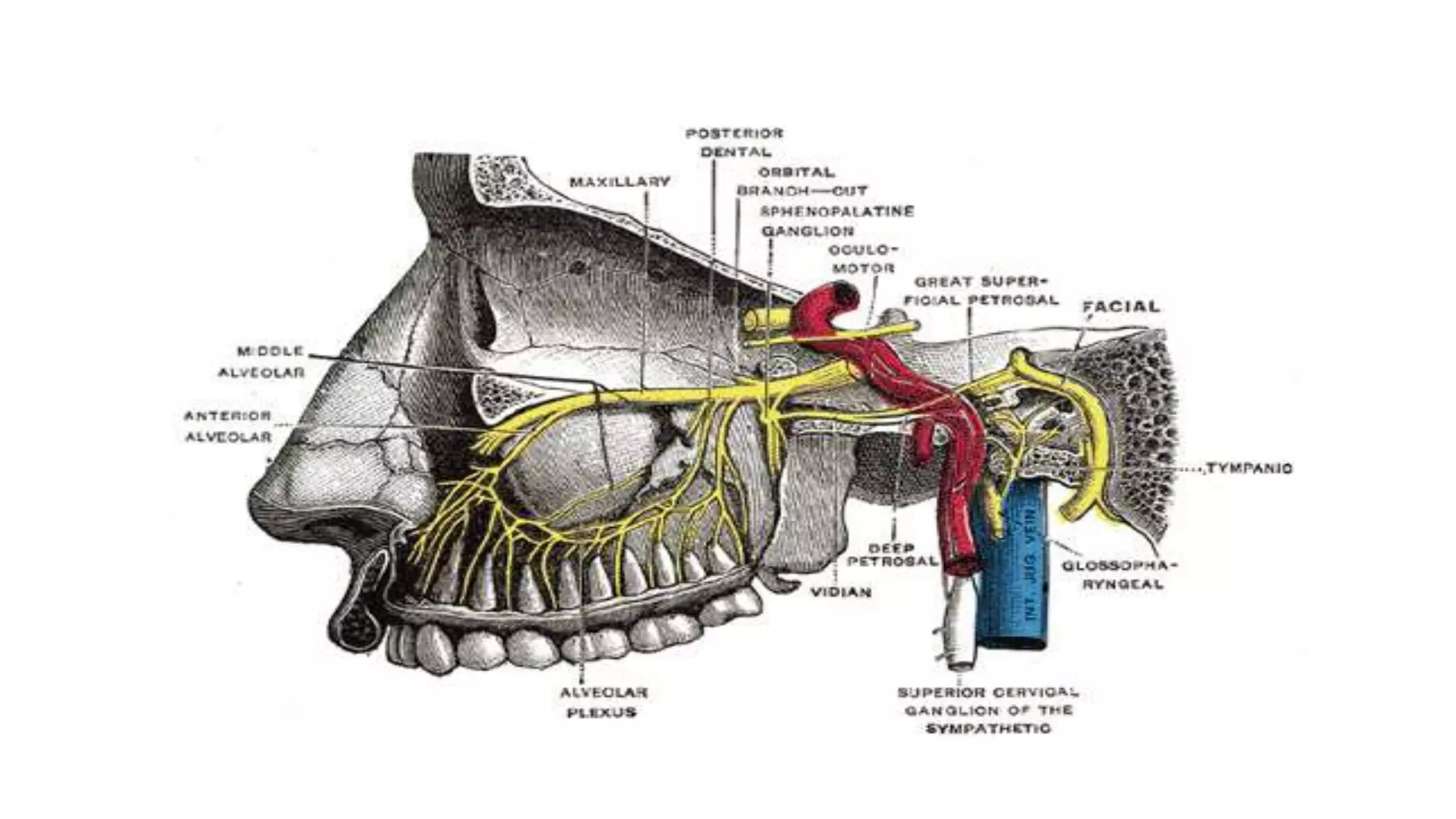
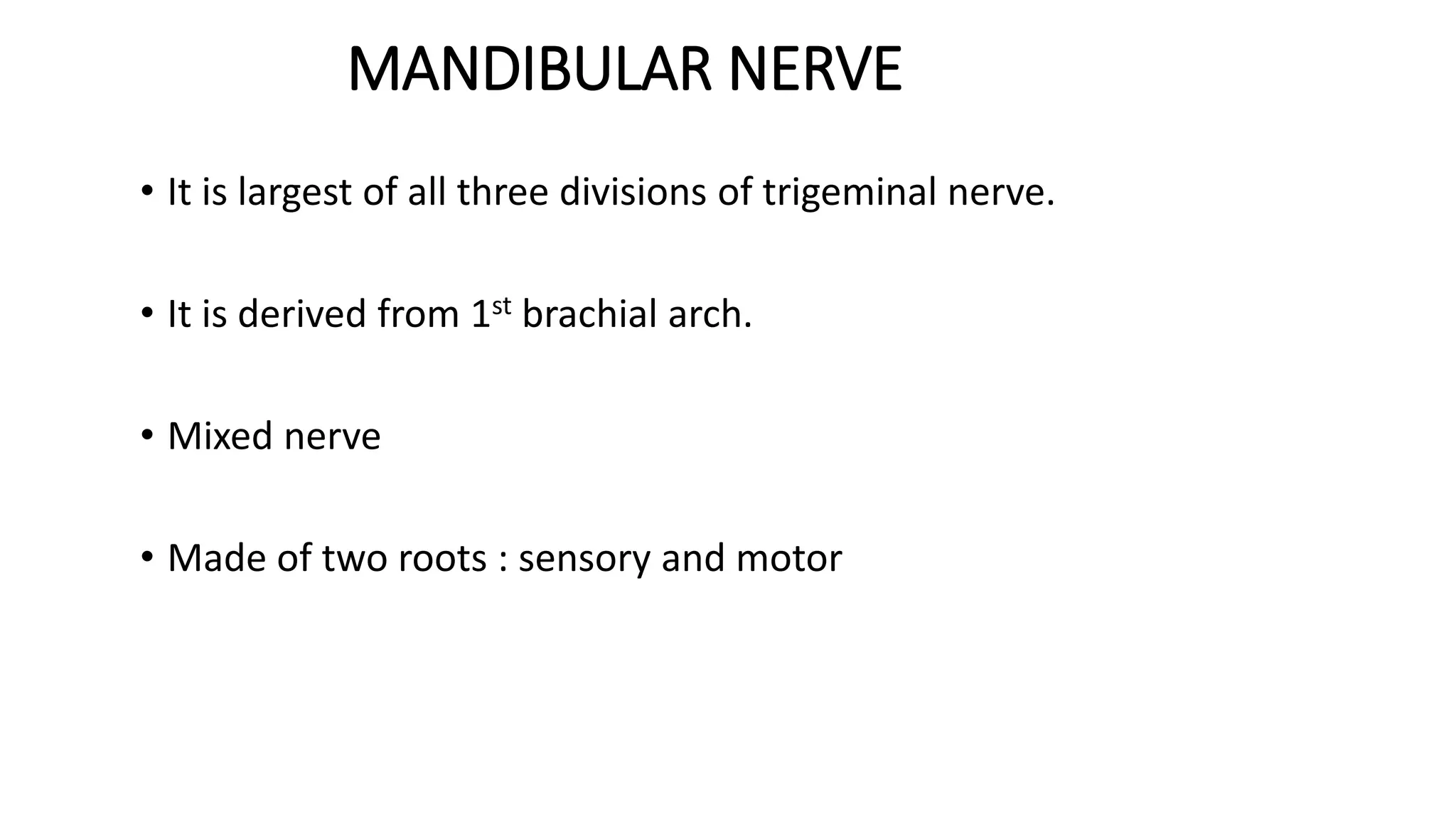
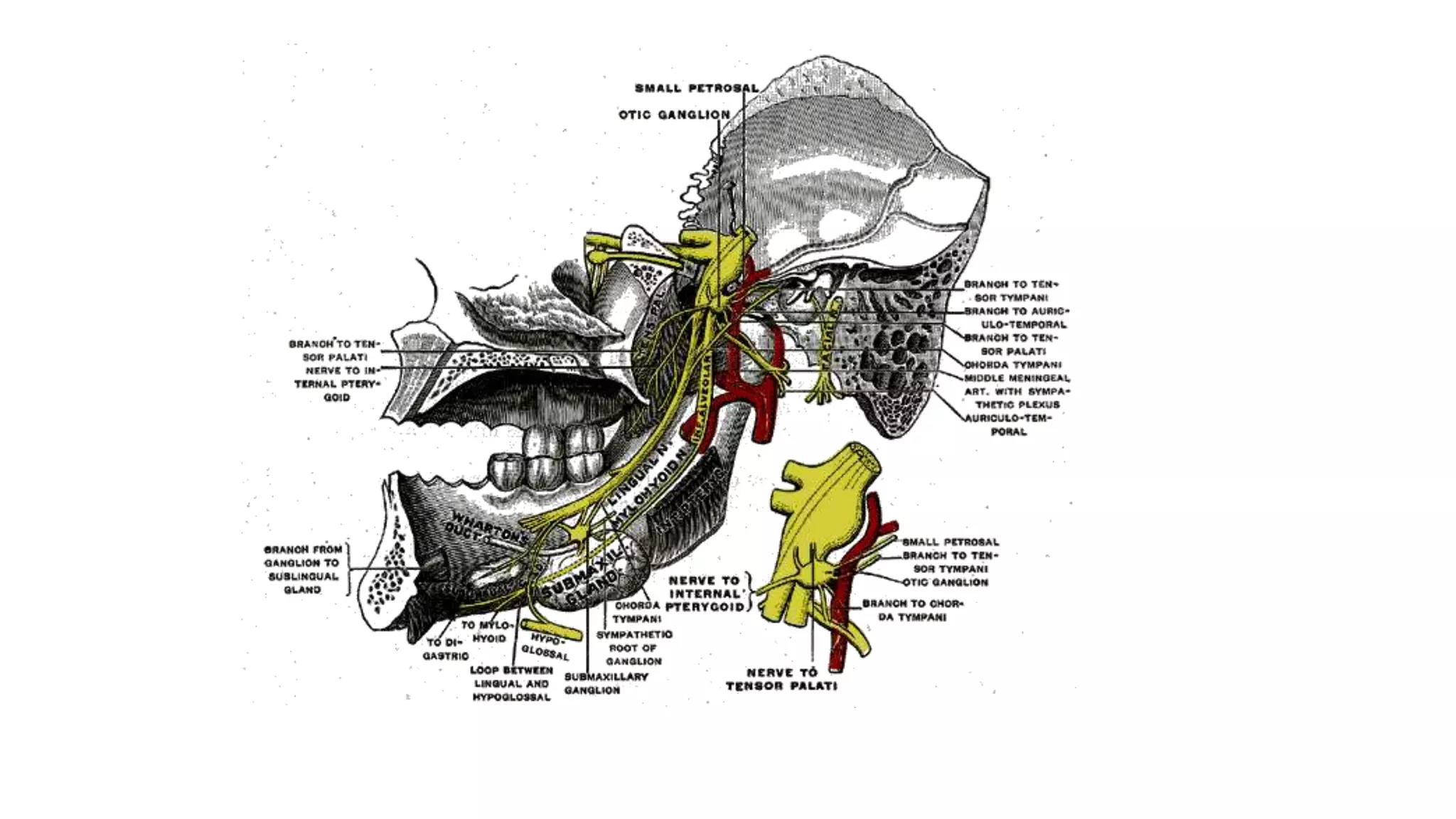
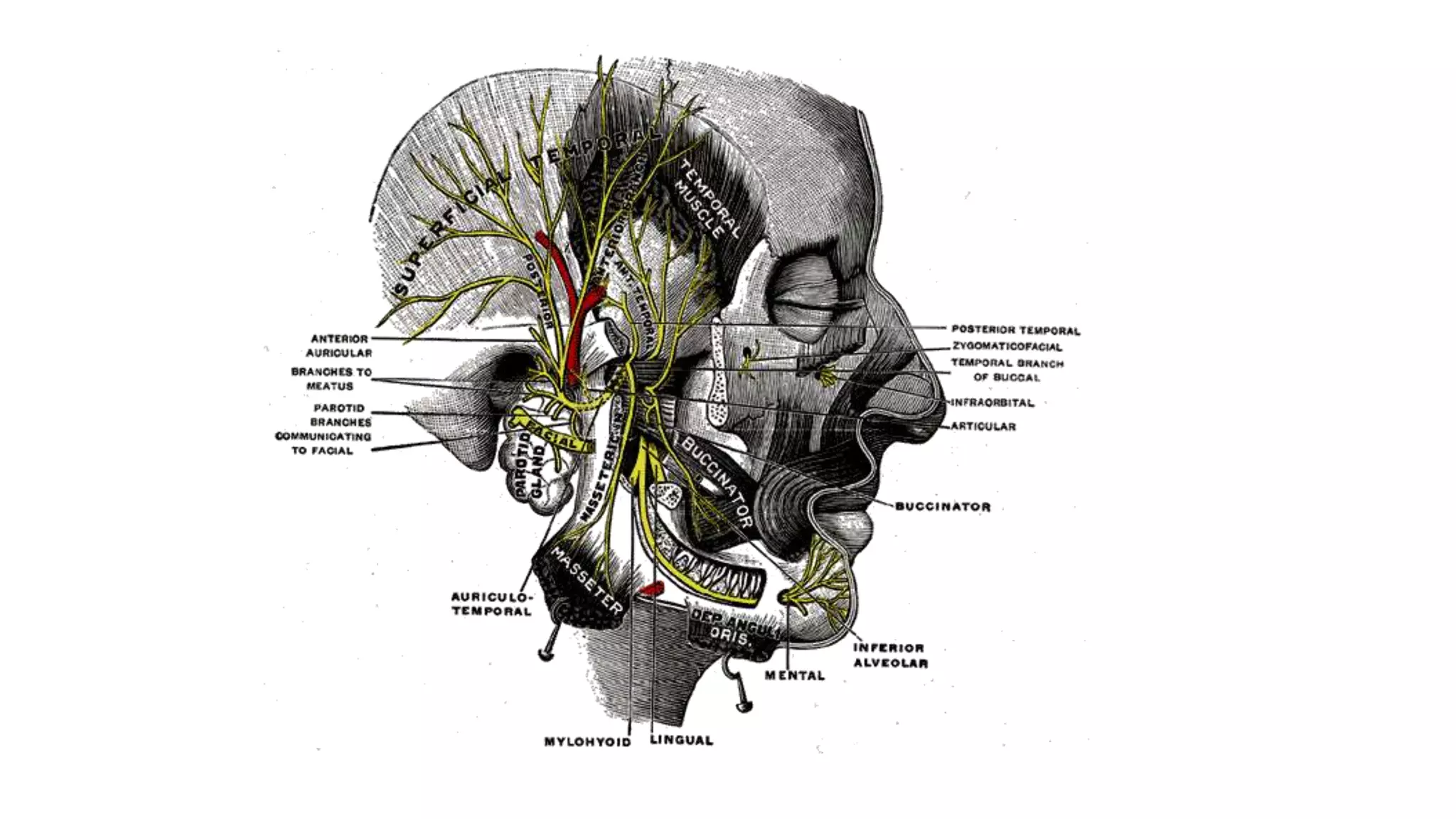
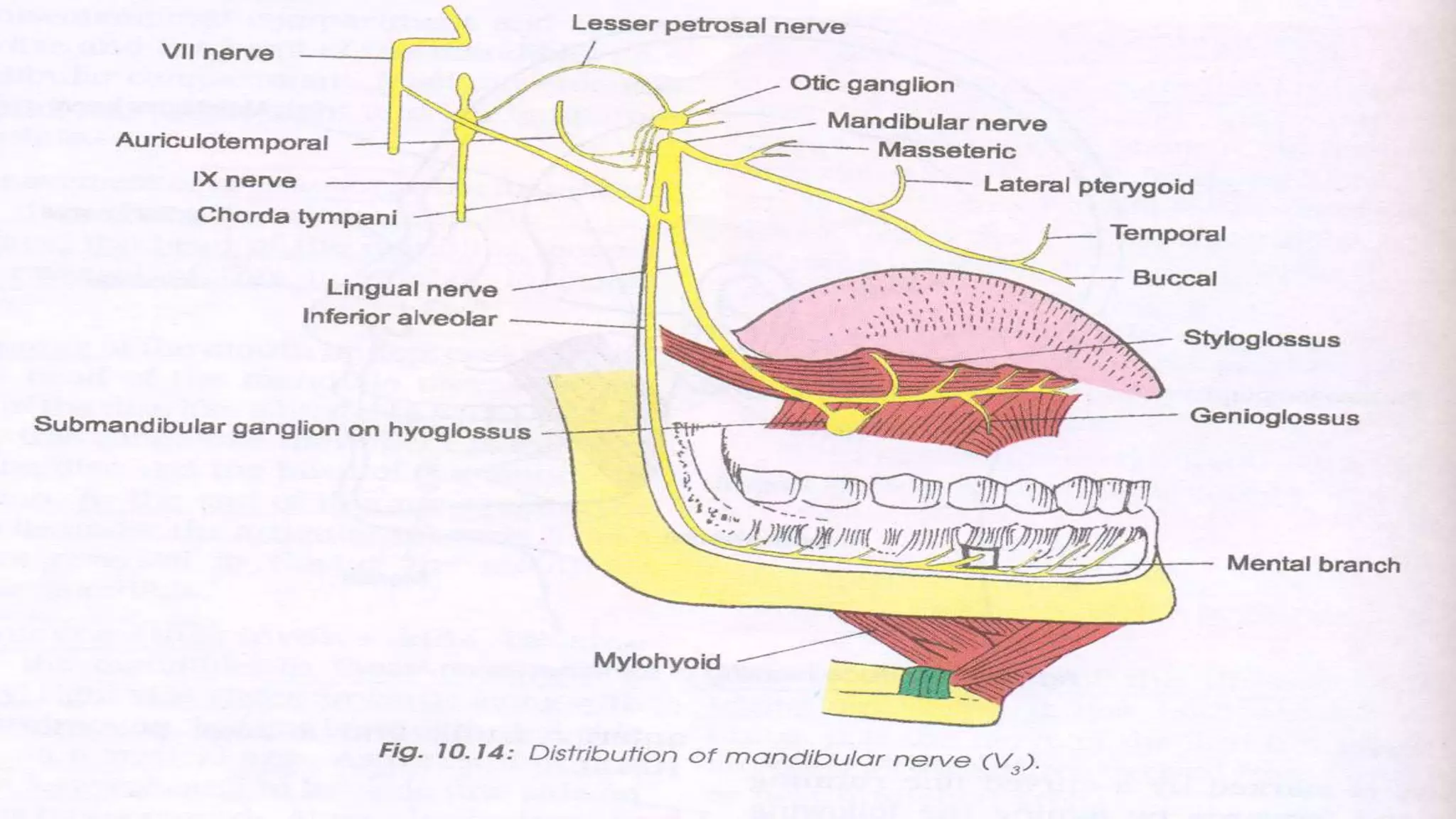
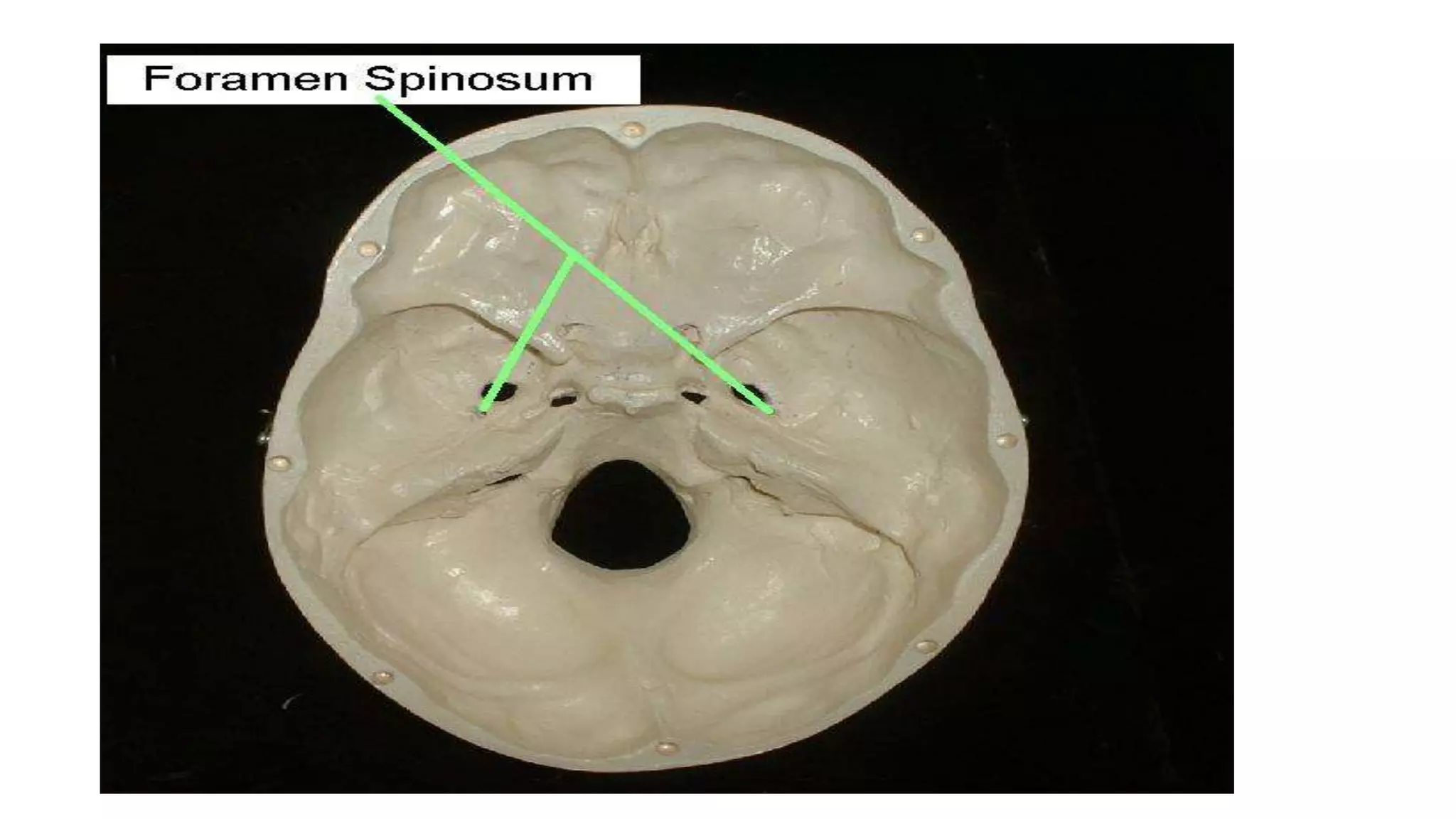
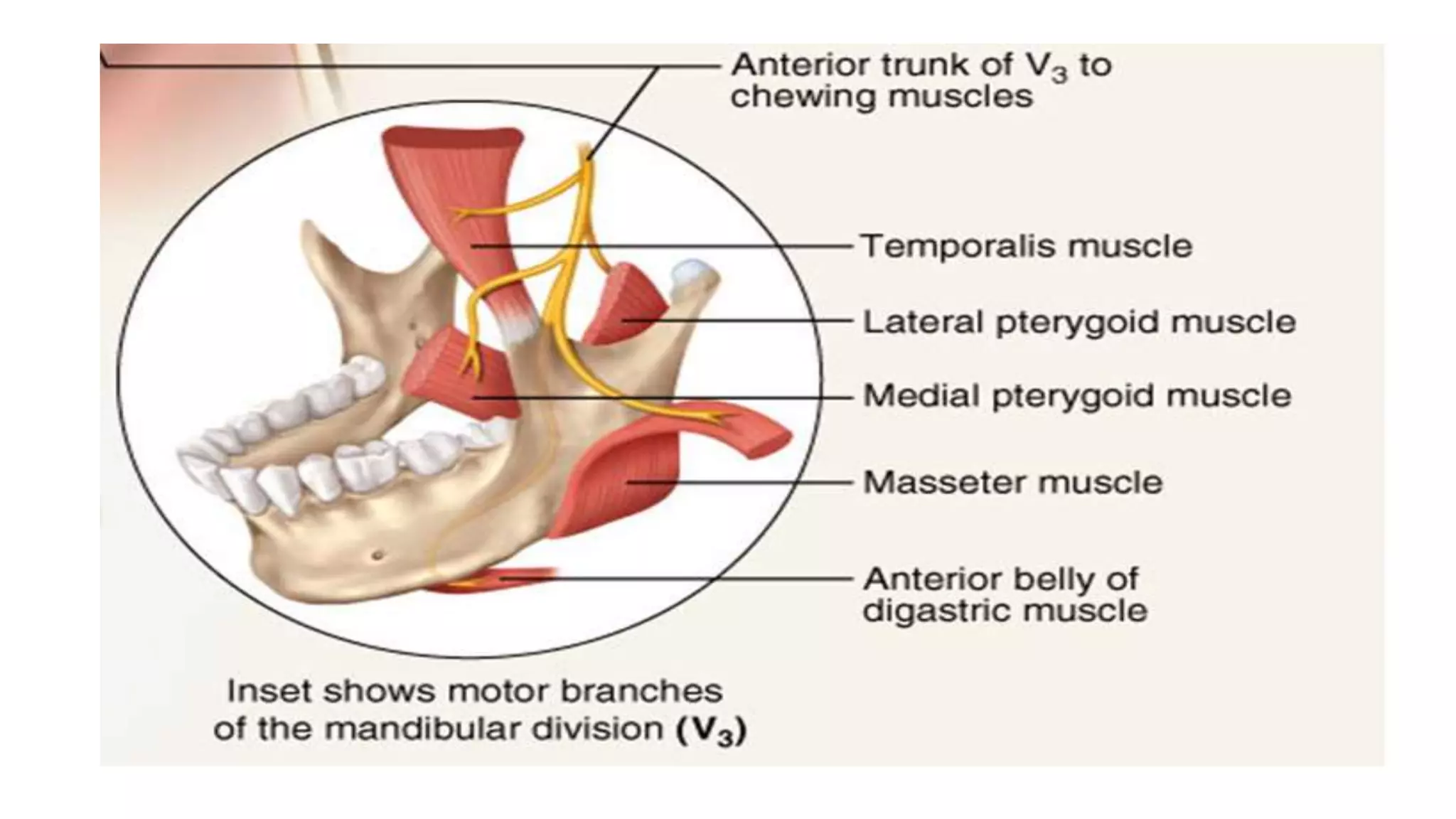
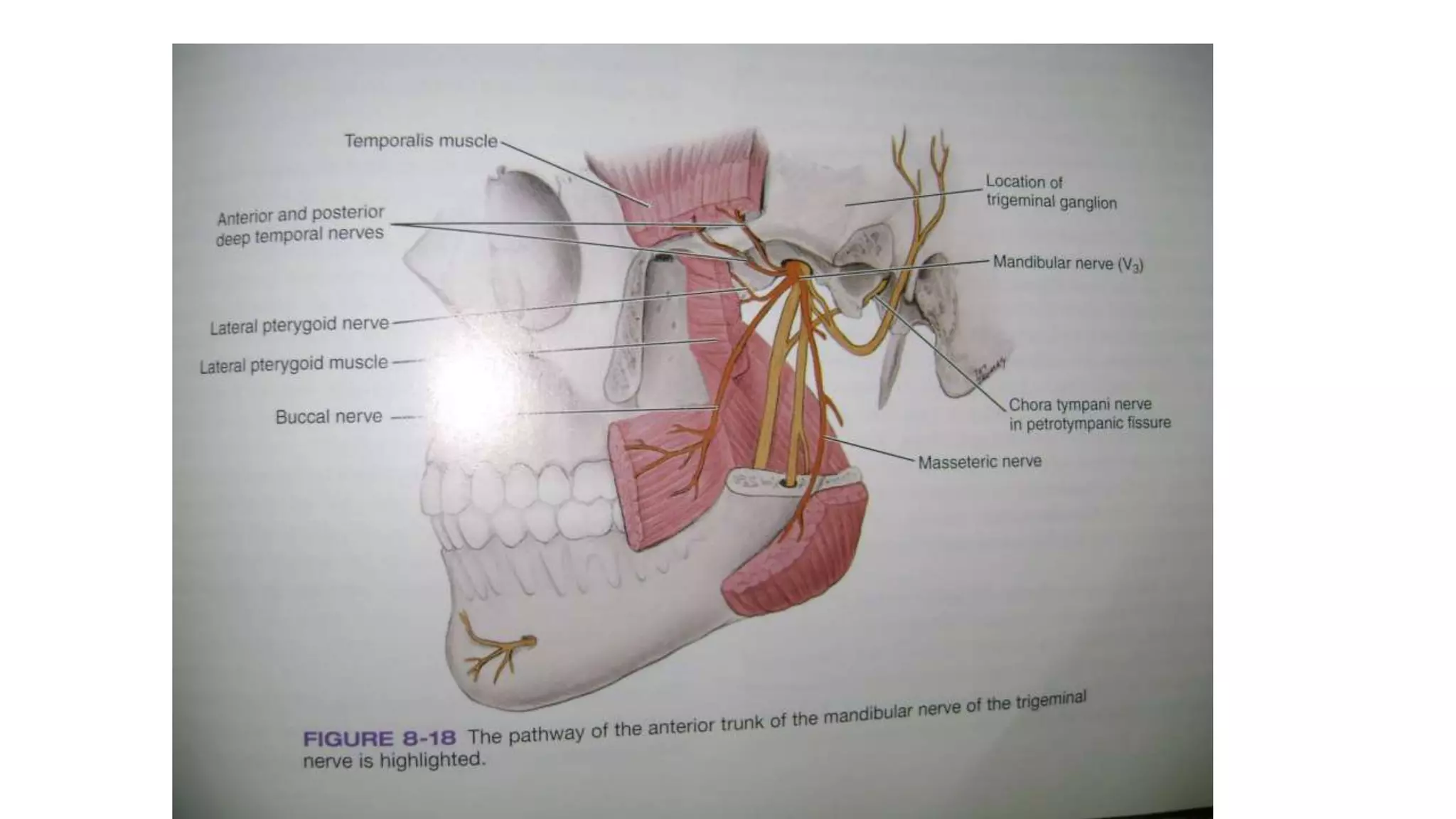
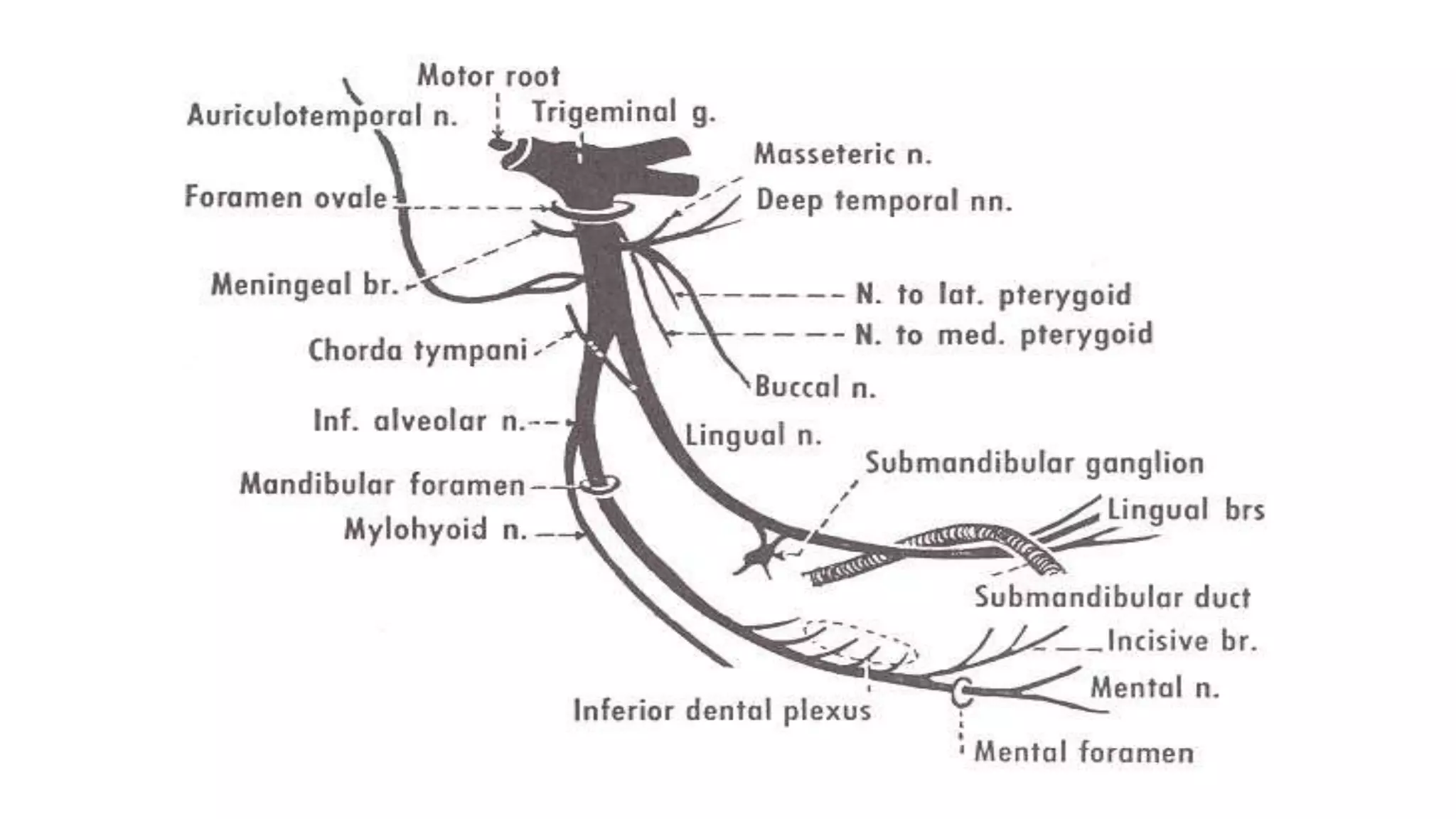
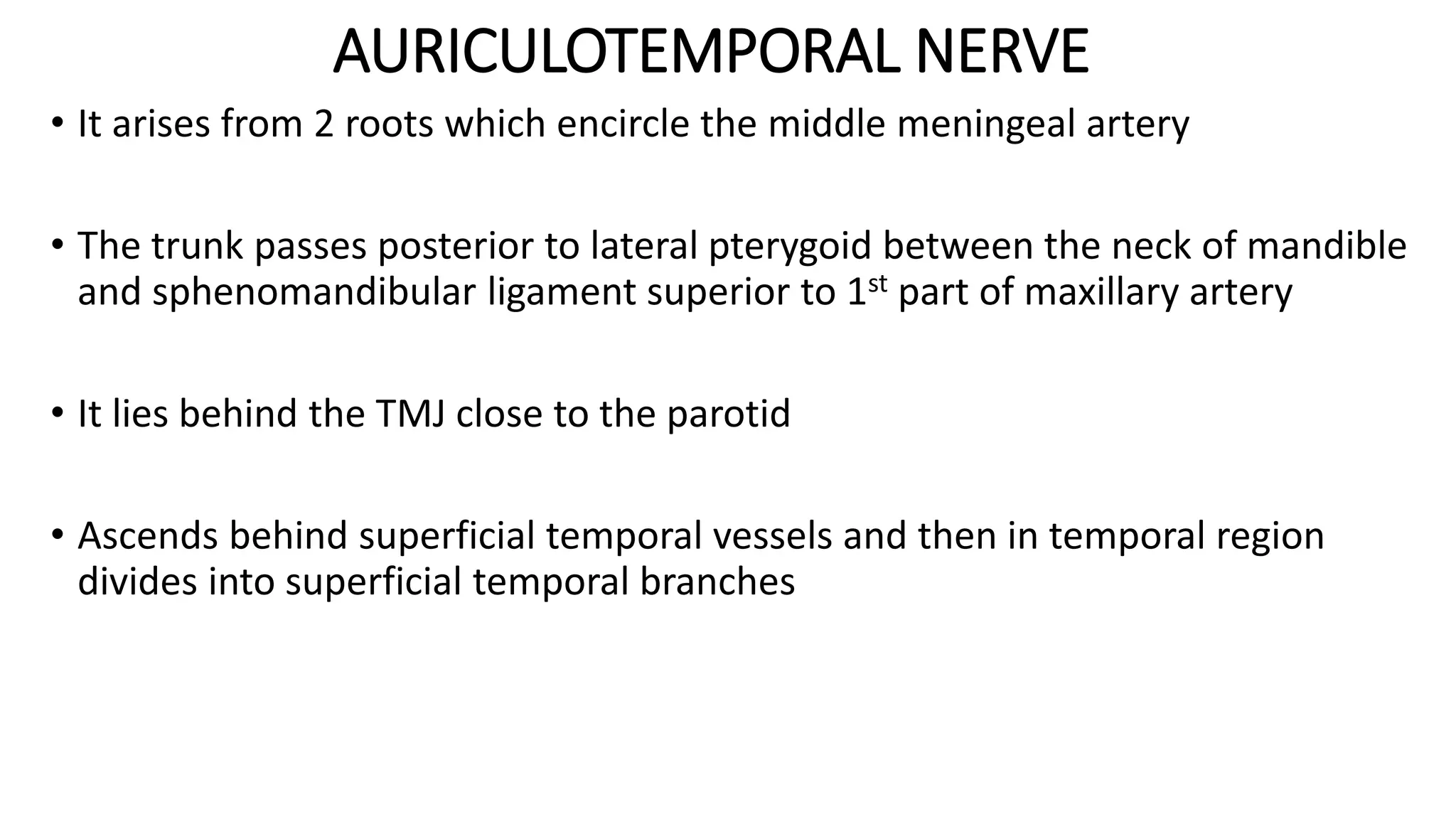
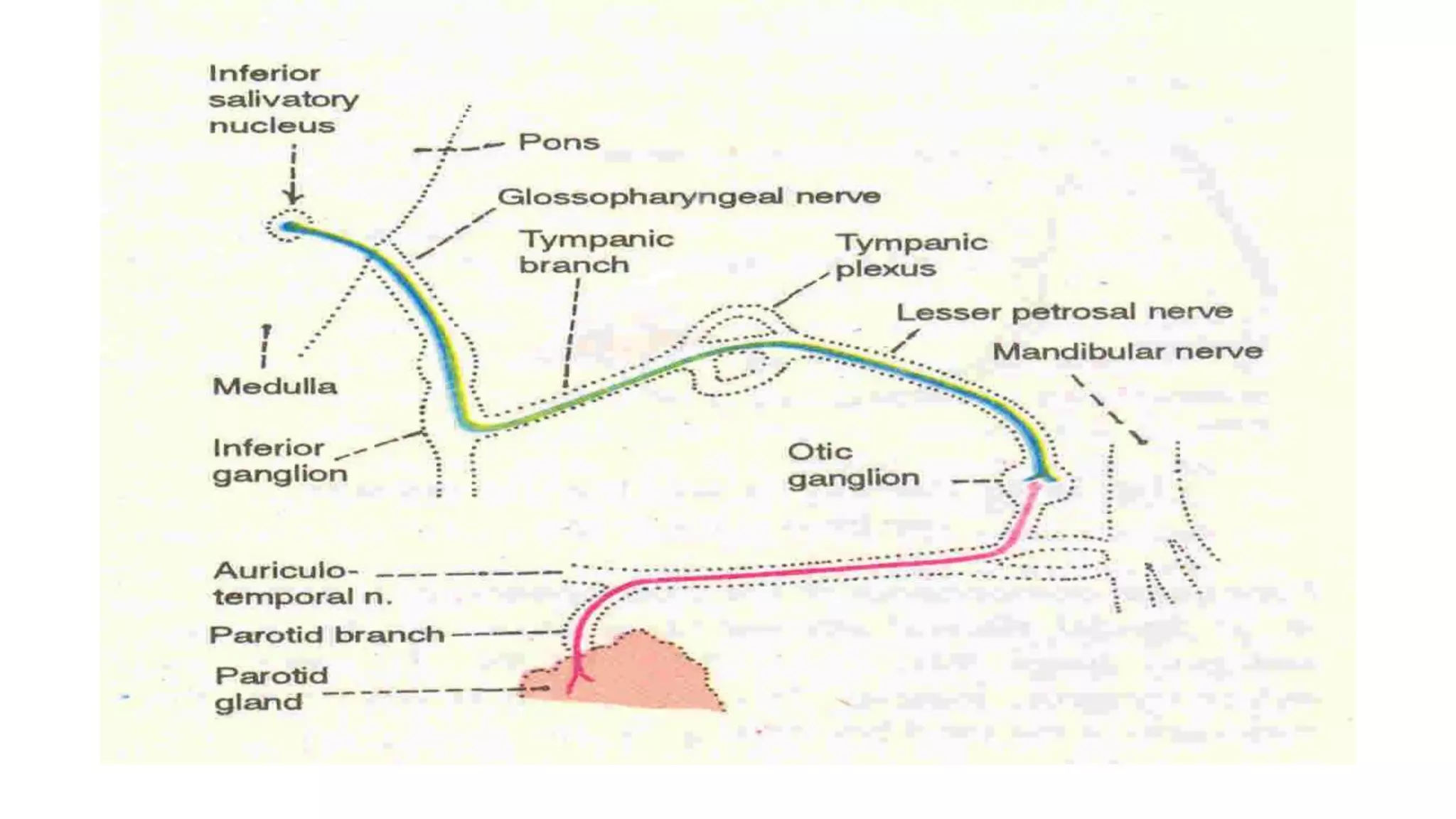
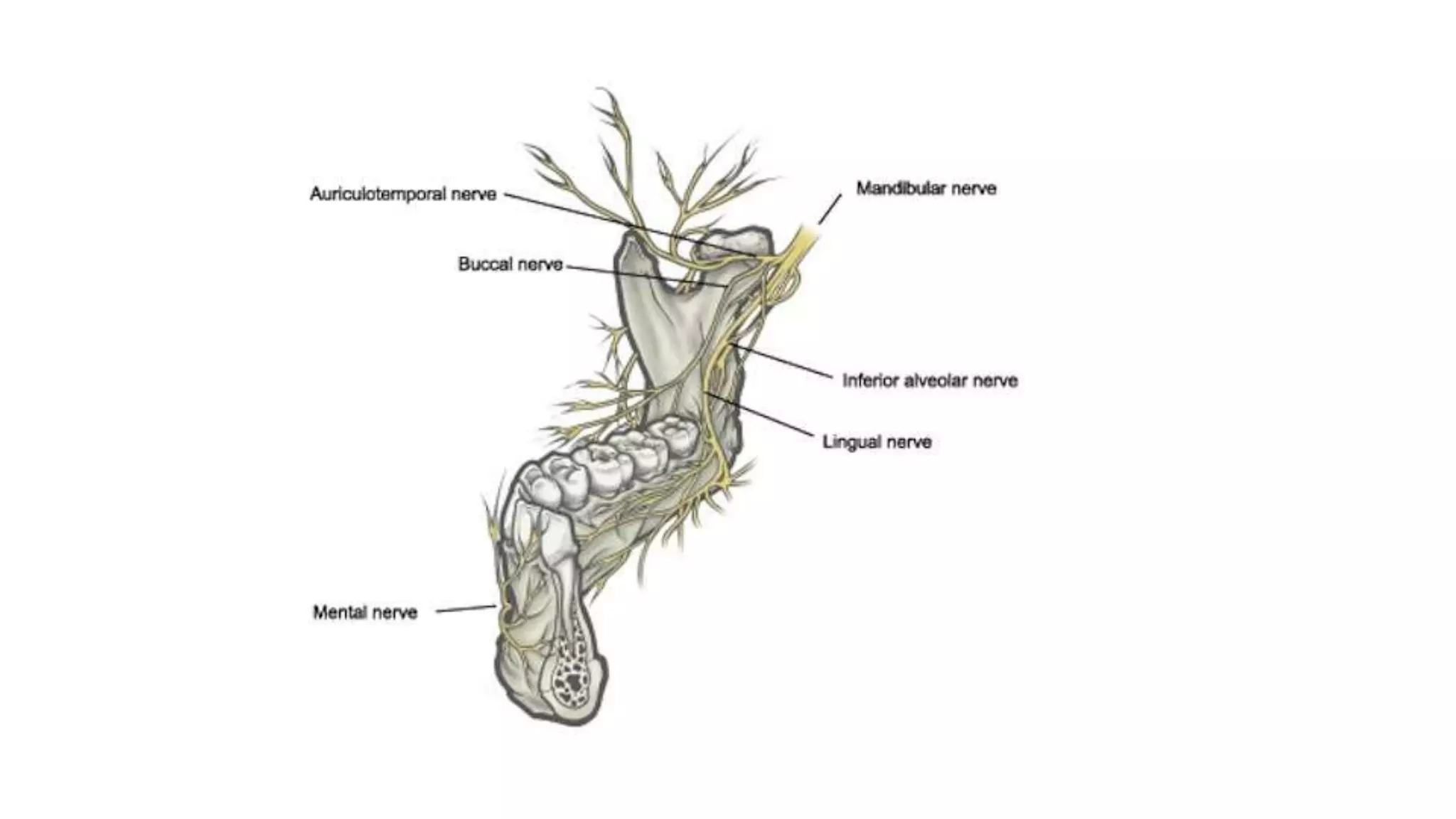
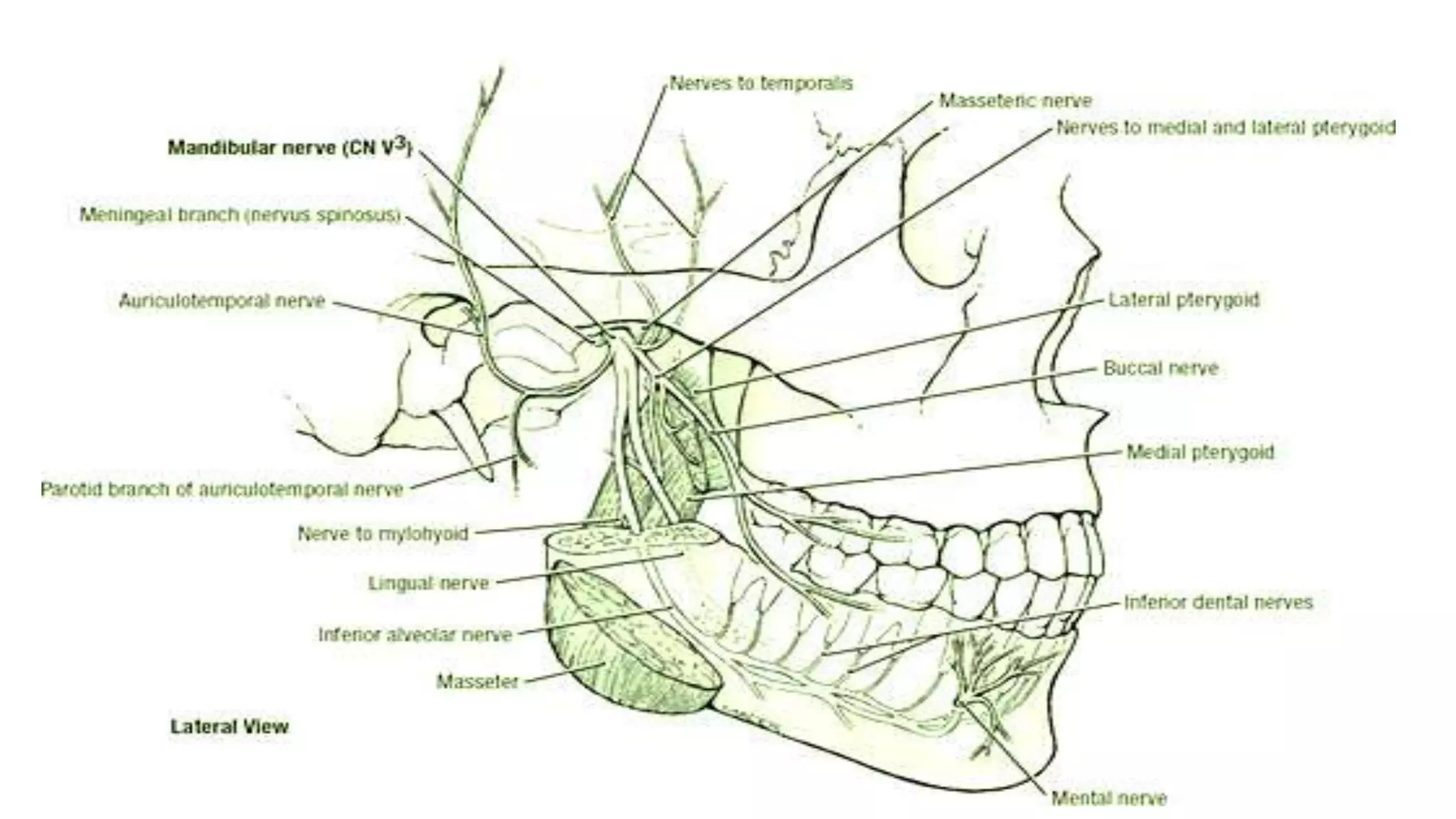
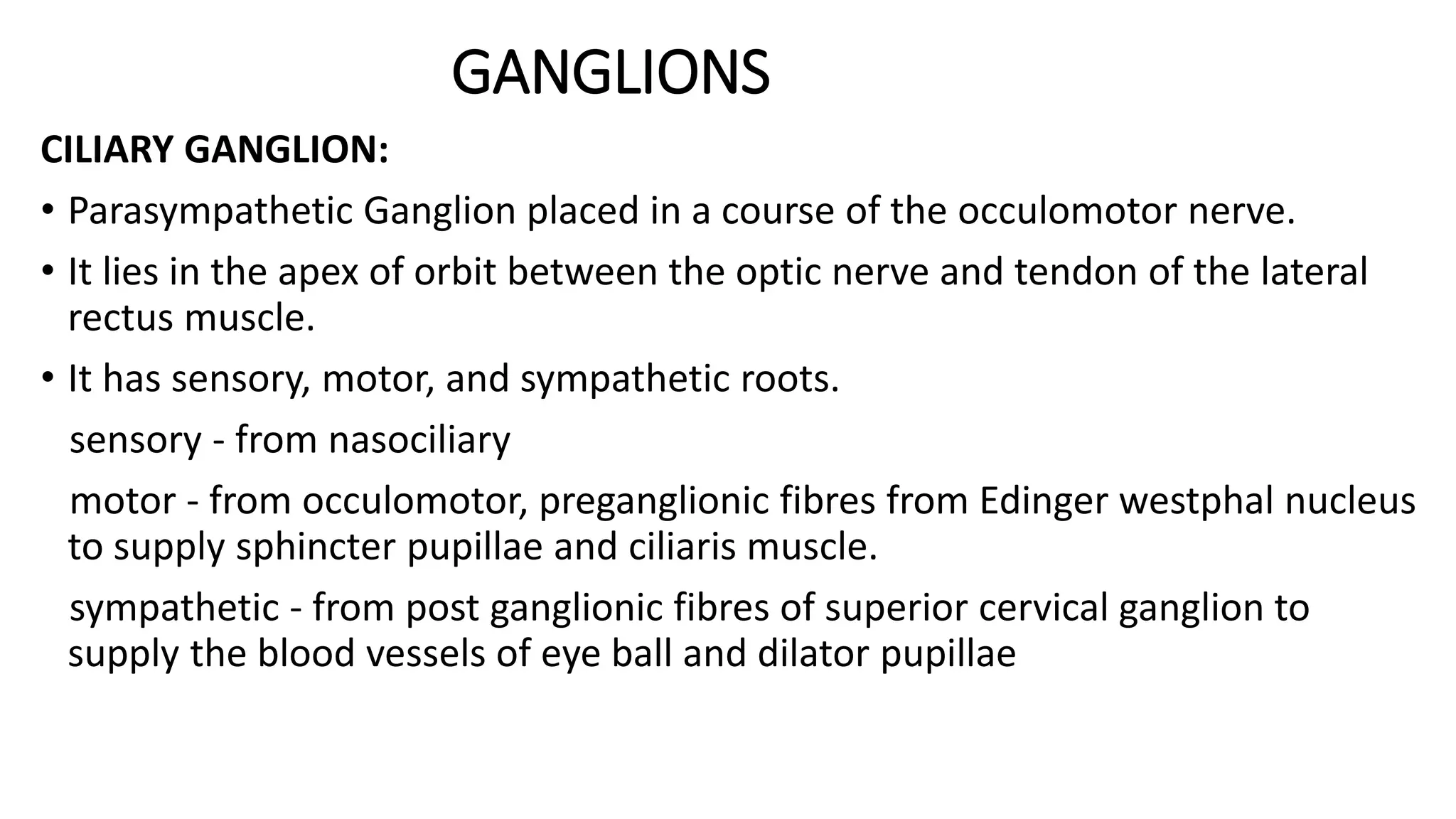
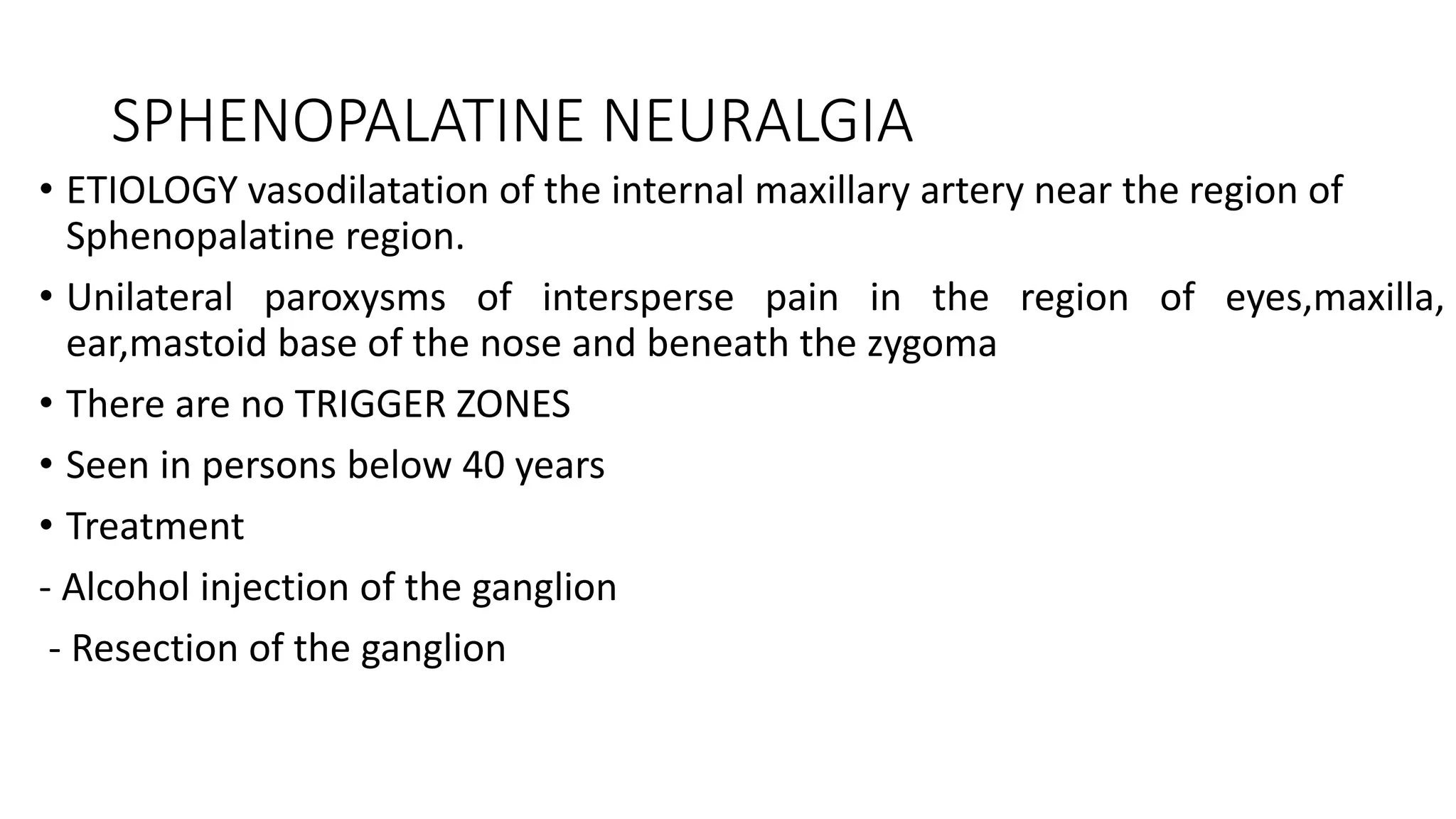
The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves. It has both sensory and motor components. The sensory component supplies sensation to the face while the motor component innervates the muscles of mastication. It exists the skull through three divisions - ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. Each division further branches to supply specific regions of the face. The trigeminal ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory fibers and is located in the posterior cranial fossa.