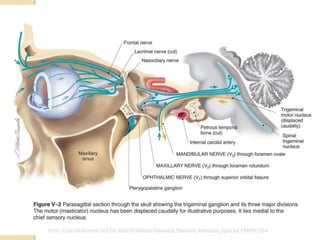
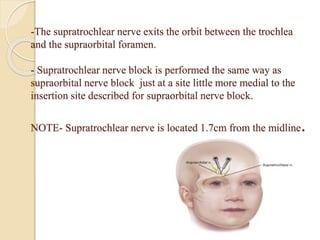
The document provides information about the trigeminal nerve and its ophthalmic division. It discusses the embryology, nuclei, functional components, and branches of the trigeminal nerve. It then focuses on the ophthalmic division, describing its introduction, branches including the lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary nerves. It also discusses the ciliary ganglion and some clinical aspects like corneal reflex and herpes zoster ophthalmicus.