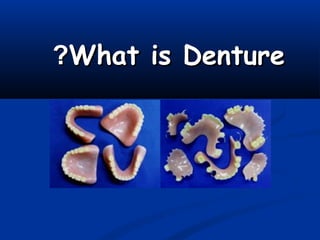
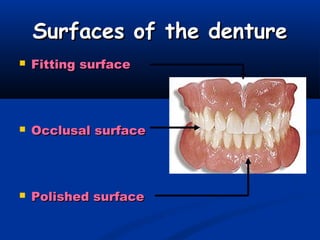
This document defines dentures and their components. It discusses the different types of dentures - total versus partial. The main parts of a denture are the denture base and artificial teeth. Heat-cured polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is described as the most common denture base material. The setting process and requirements of denture base materials are outlined. Compression molding and injection molding techniques for constructing denture bases are also summarized.