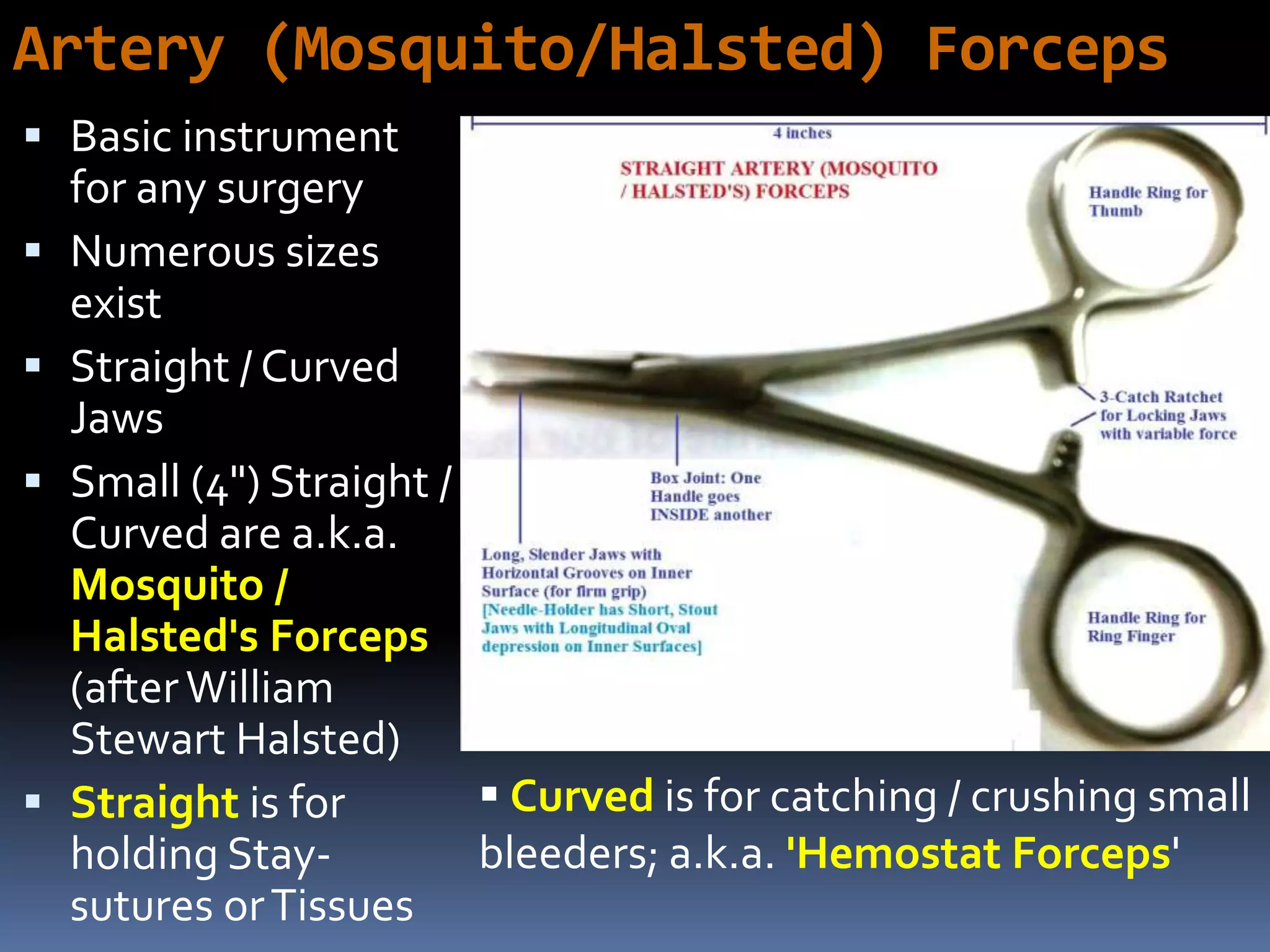
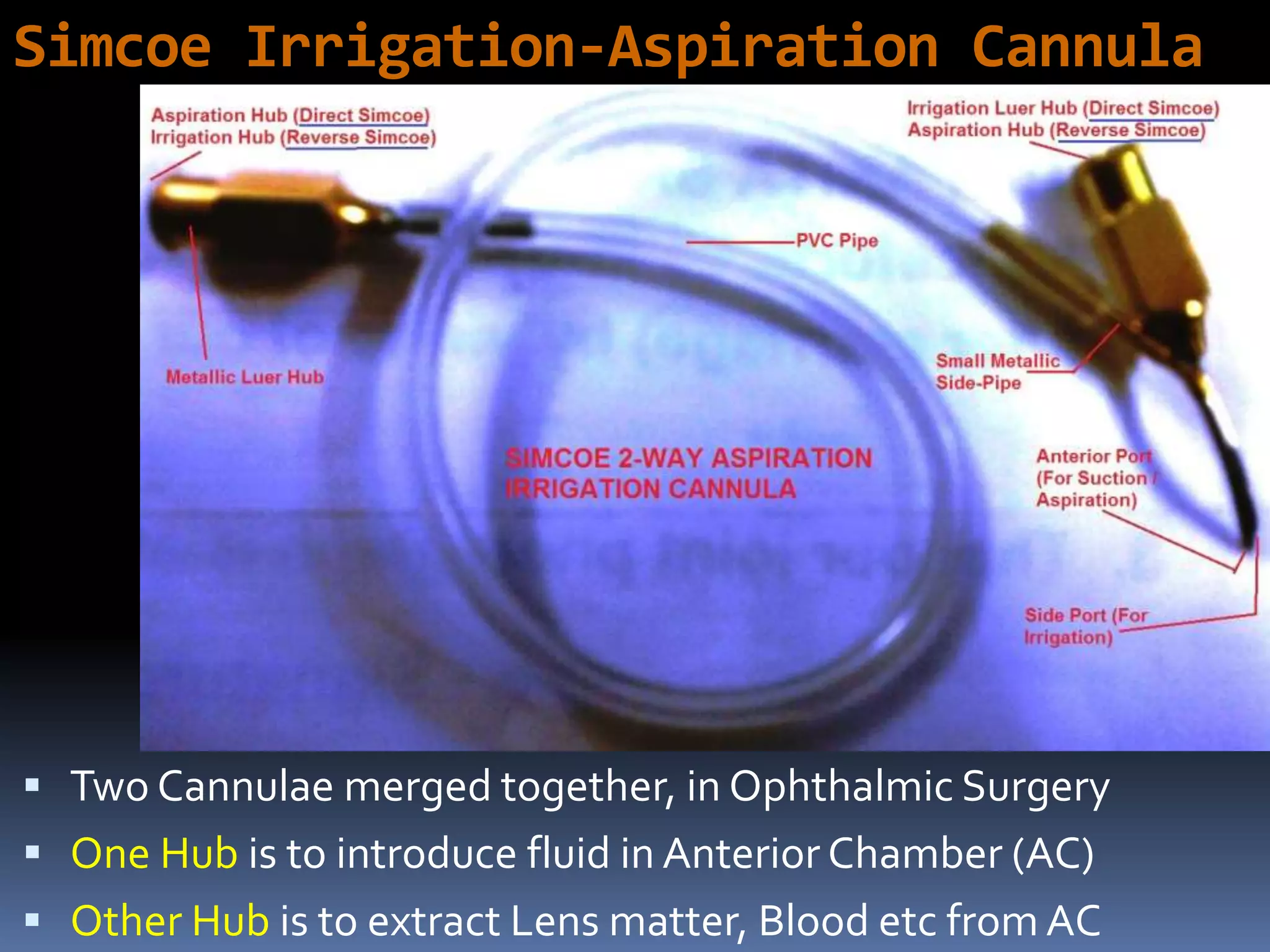
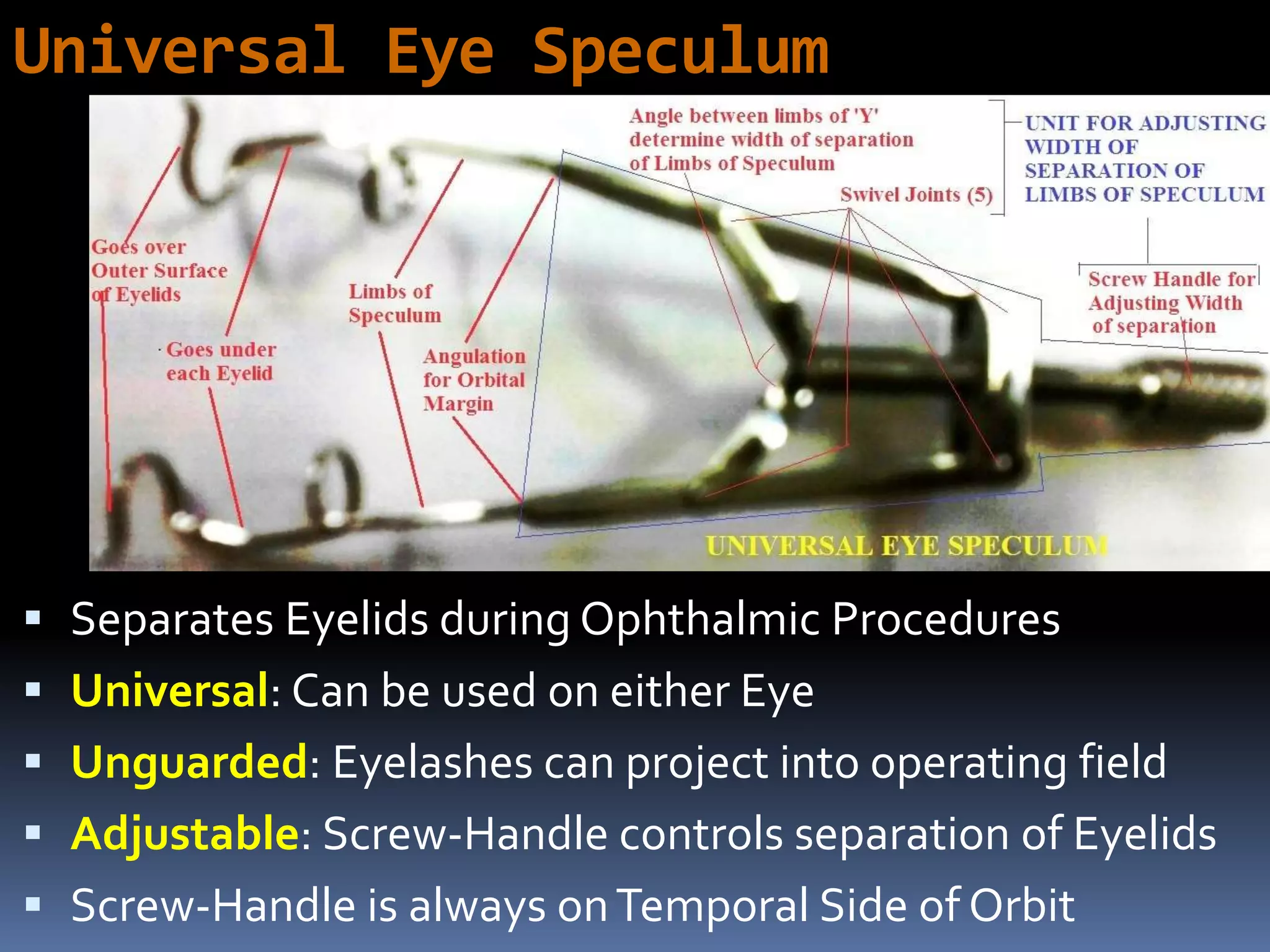
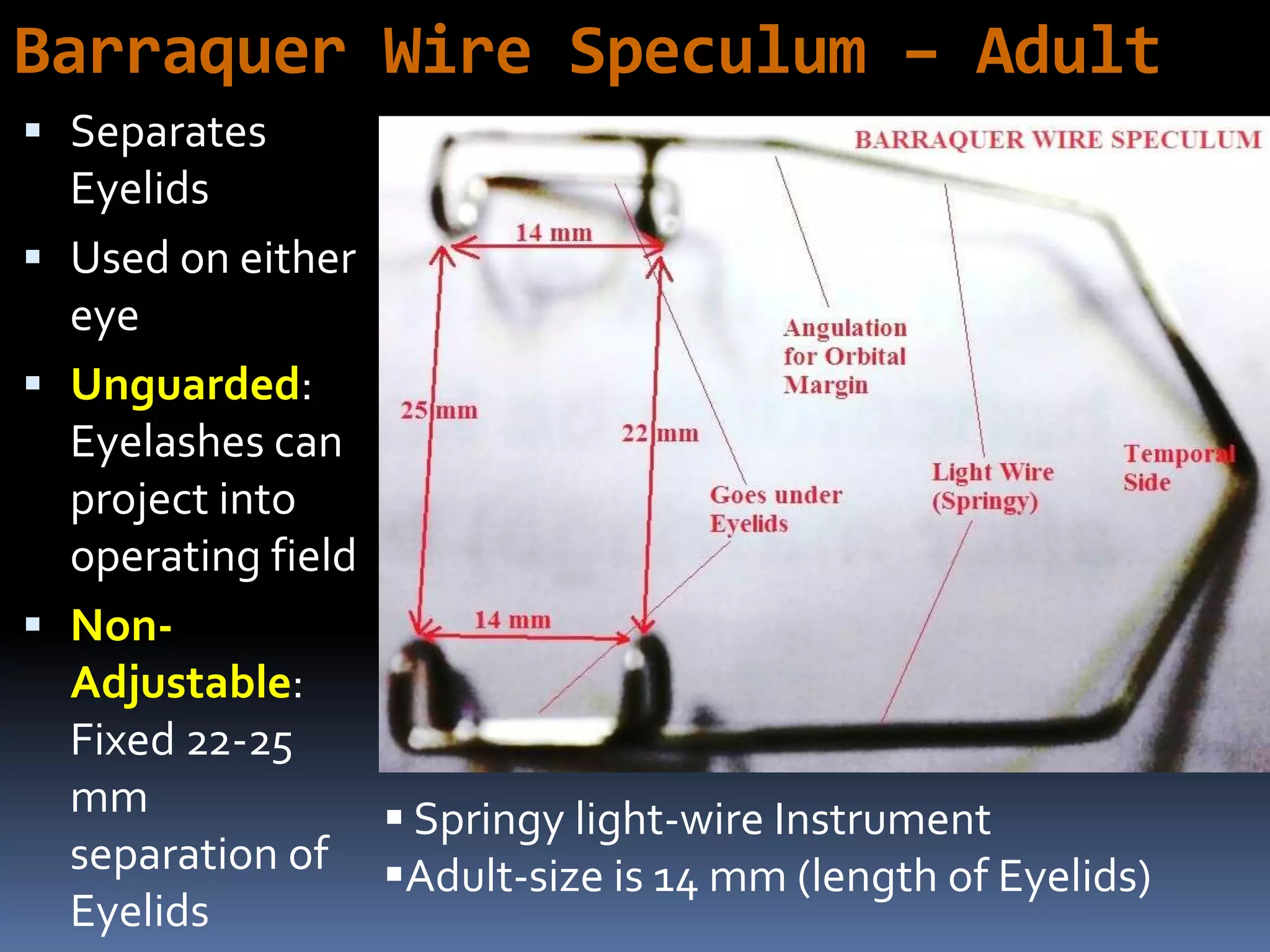
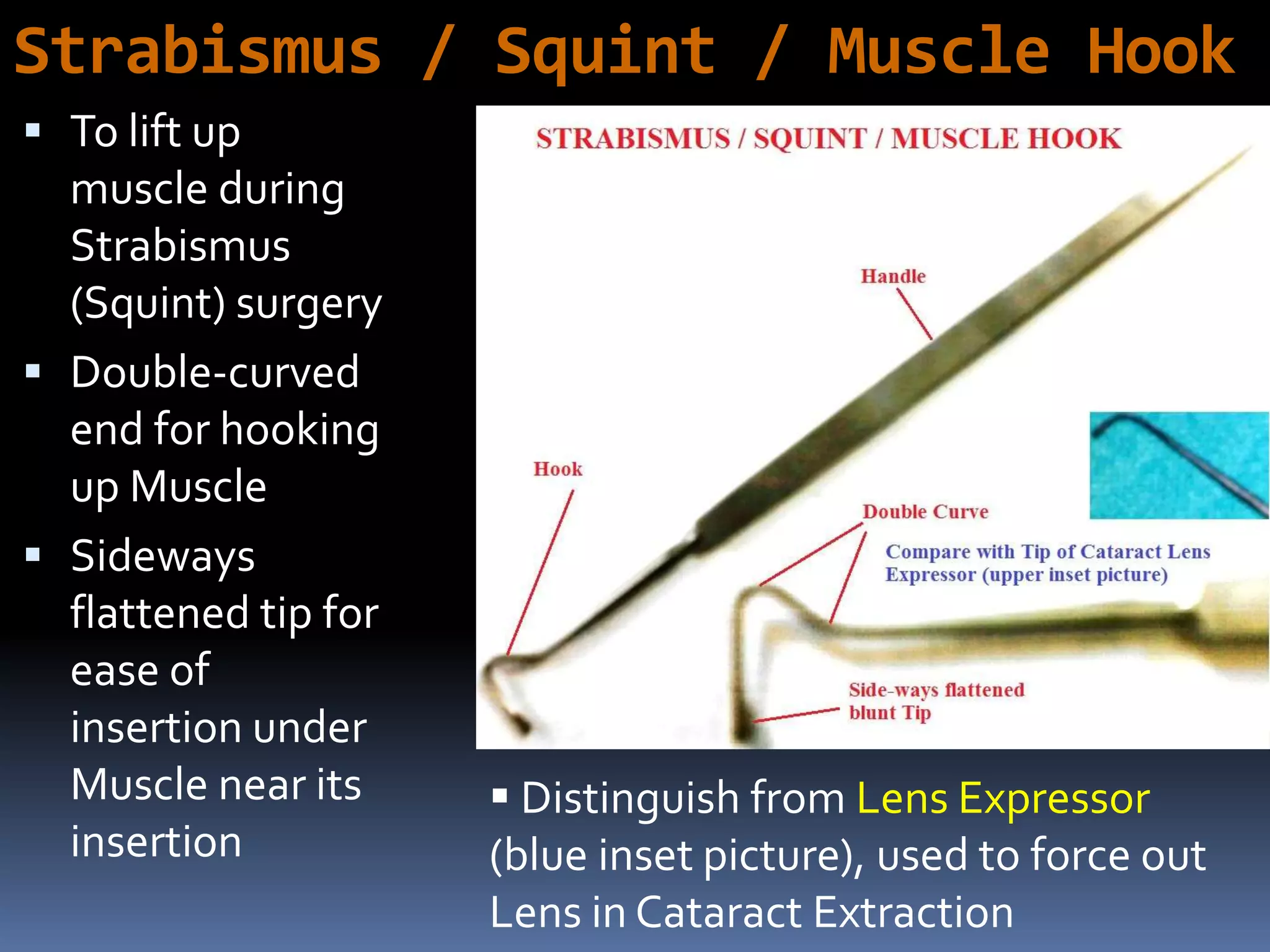
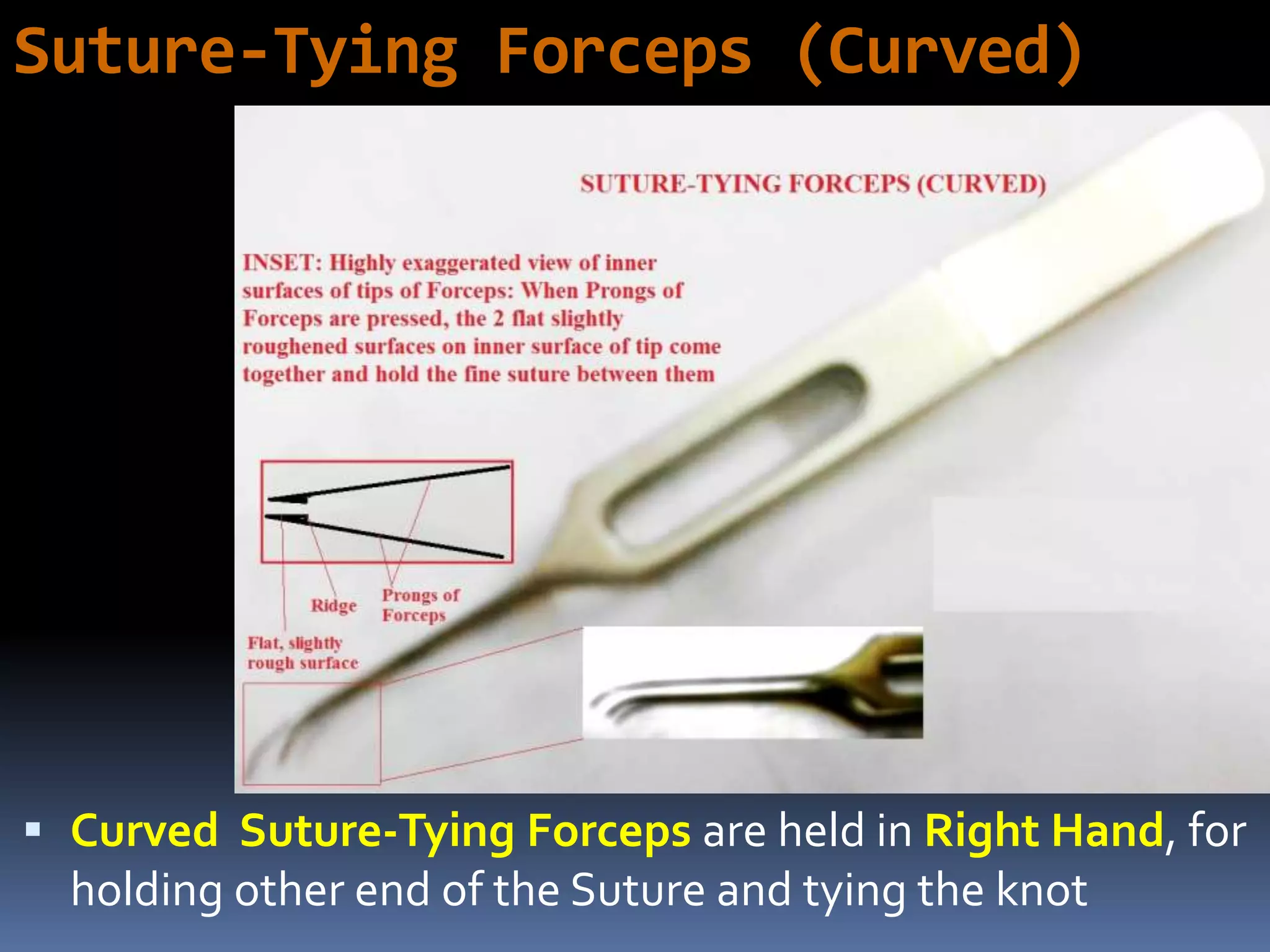
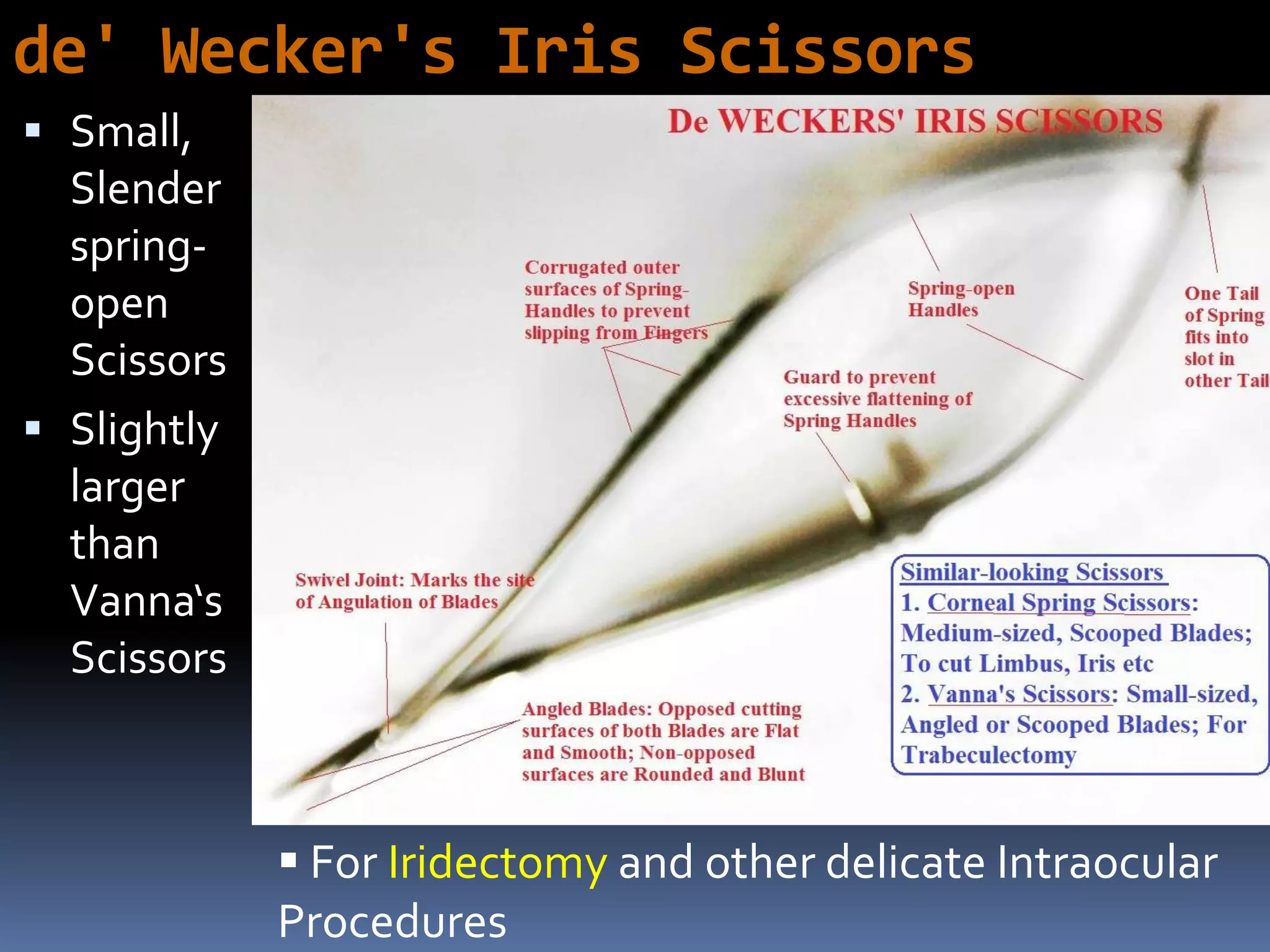
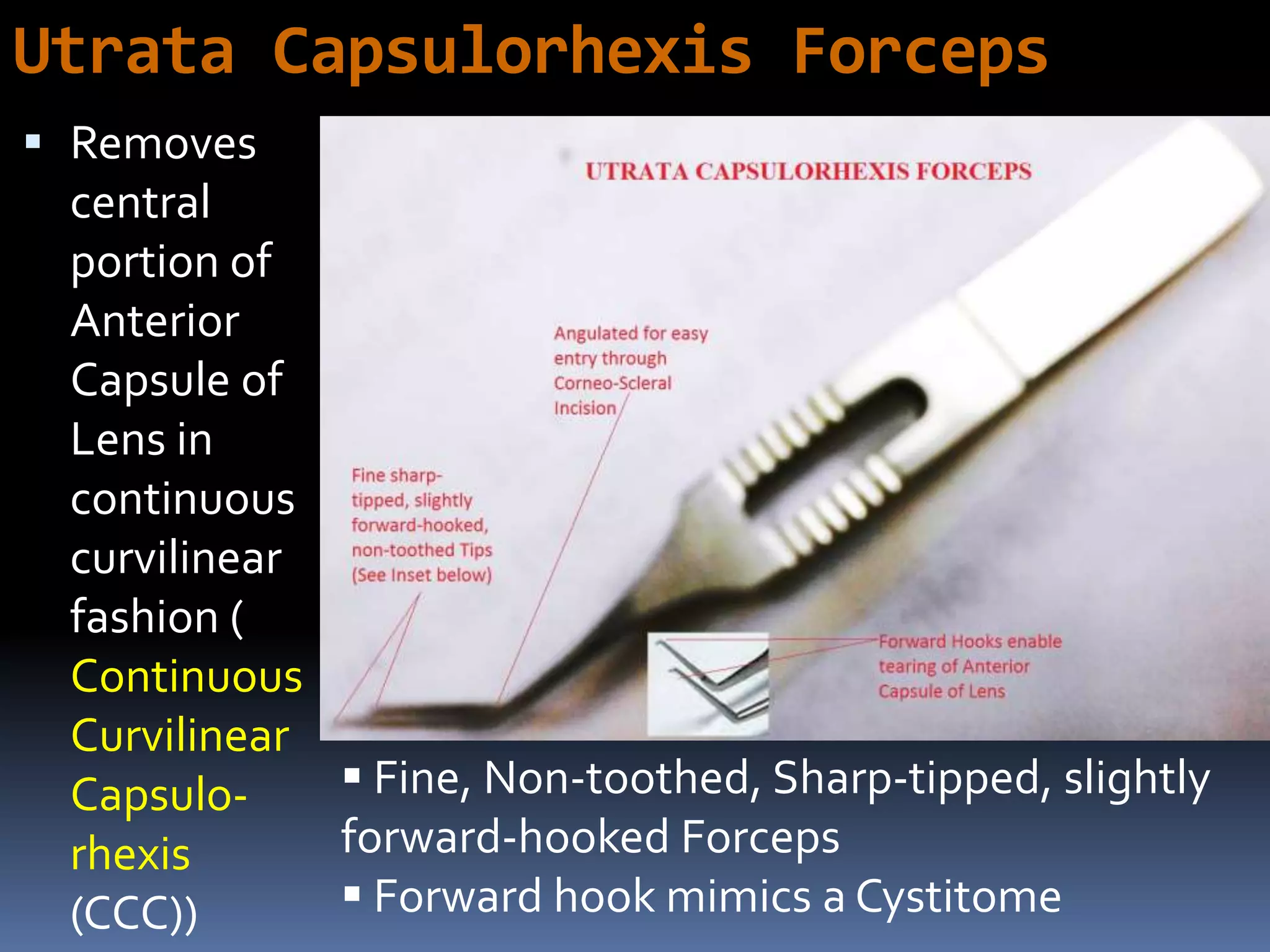
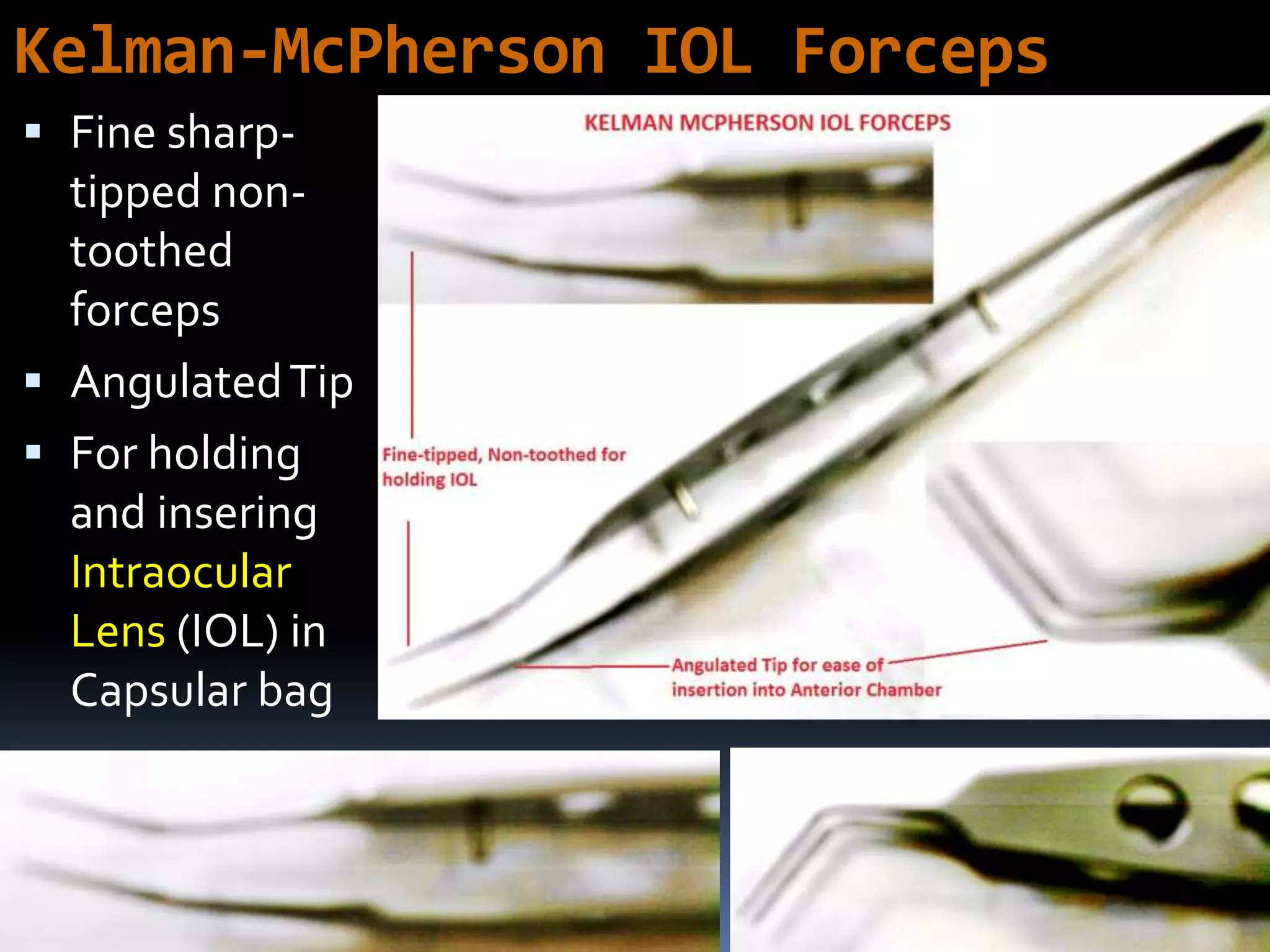
The document outlines various ophthalmic surgery instruments, their applications, and mechanical functions. It is primarily aimed at individuals involved in ophthalmic surgery, such as residents, technicians, and nurses, detailing instruments commonly used in cataract surgery. The presentation includes descriptions and images of tools like forceps, cannulae, and specula without following a specific order.