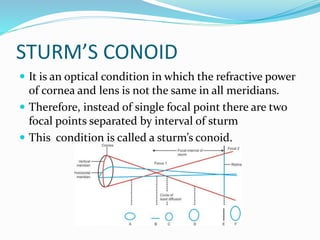
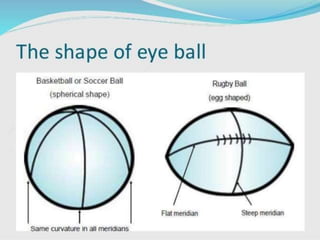
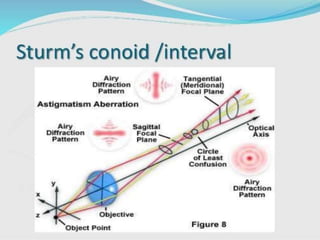
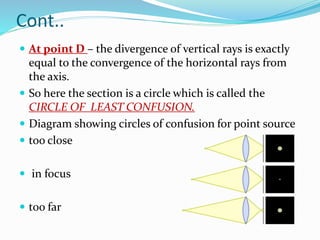
Sturm's conoid is an optical condition where the refractive power of the cornea and lens are not equal in all meridians, resulting in two focal points separated by an interval. This causes the image formed to change shape from oval to line to oval as the object moves from one focal point to the other, passing through a minimum circle of confusion in between where blur is lowest. The diagram shows how the image shape changes at different points along this path.