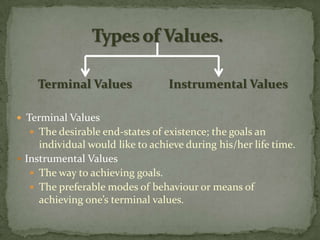
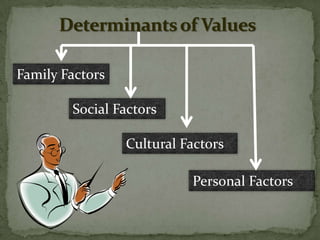
This document discusses values and ethics in organizational behavior. It defines values as basic convictions that determine what is right and wrong. Values form the basis for ethical behavior and are part of a value system. Values influence judgements and attitudes. Ethics is about acting in accordance with one's values and societal norms. Values are learned from culture, religion, family and experiences. They influence behavior and are difficult to change. Values determine attitudes and play an important role in organizational culture.