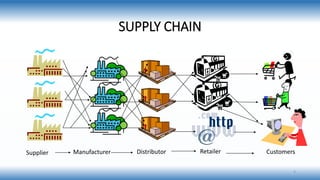
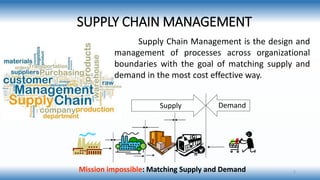
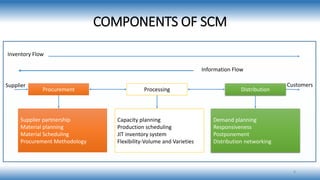
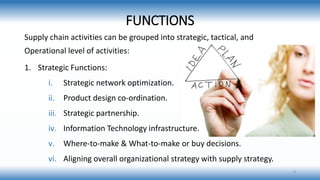
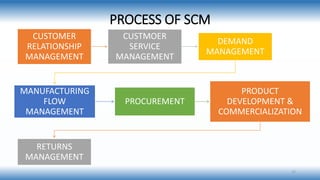
A supply chain is a network involved in the procurement, production, and distribution of goods, which supply chain management (SCM) aims to optimize for cost-effectiveness while meeting demand. Various types of supply chains exist, such as raw, ripe, and outsourced, and SCM includes strategic, tactical, and operational functions to manage these processes. Key factors influencing SCM include customer demand, globalization, and competition, while its importance lies in reducing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction and trust among partners.