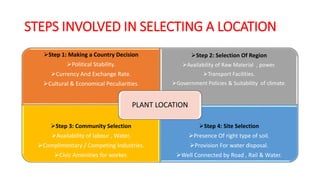
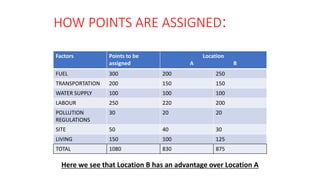
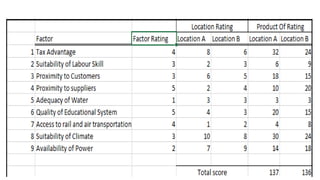
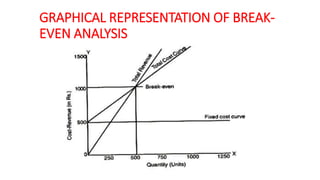
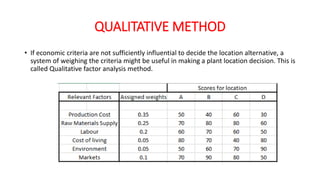
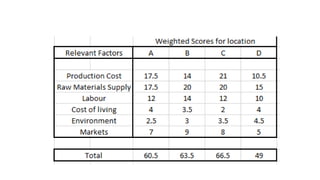
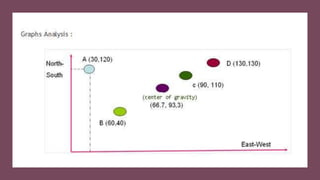
This document discusses various methods for selecting an optimal location for a new plant. It describes point rating, factor rating, break-even analysis, qualitative, and center of gravity methods. The point rating method assigns points to different location factors like fuel, transportation, water, labor, etc and chooses the location with the highest total points. The factor rating method rates each location based on factors weighted by importance. The break-even analysis examines costs and revenues at different output levels. The qualitative method weighs economic and non-economic criteria. The center of gravity method places existing locations on a grid and calculates the centroid location based on distances and shipment volumes.