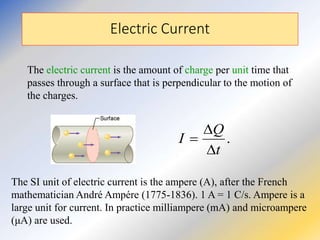
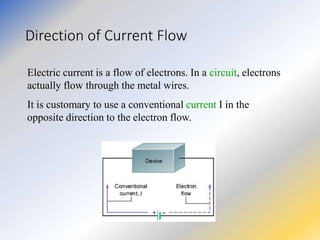
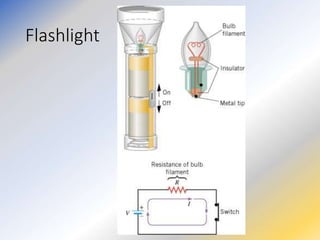
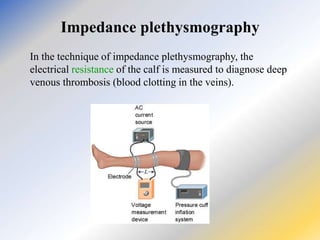
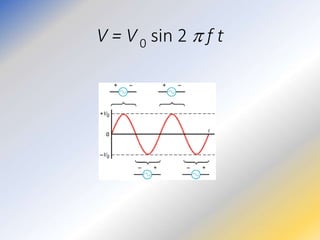
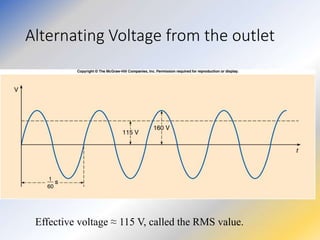
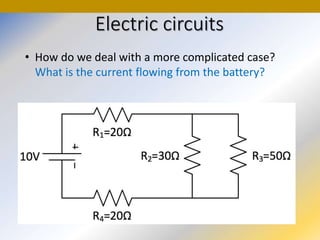
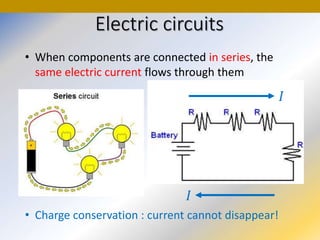
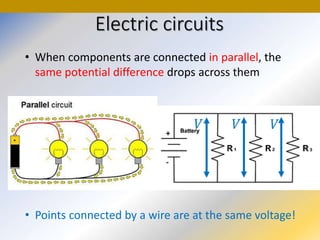
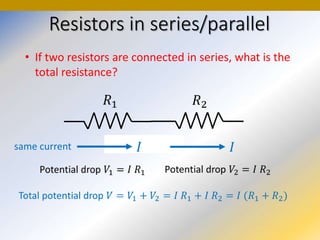
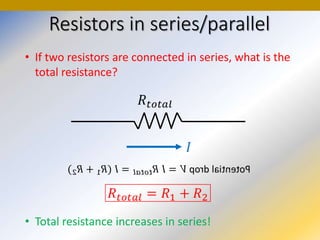
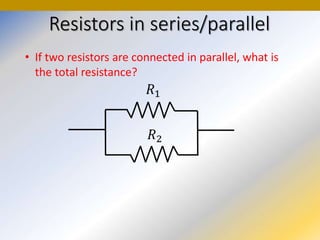
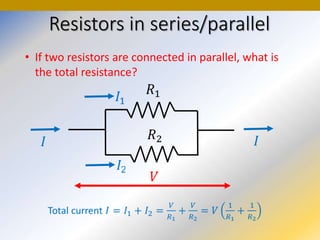
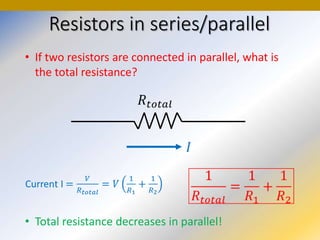
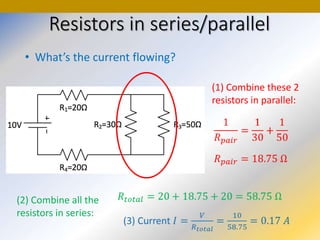
This document discusses key concepts in medical physics related to electric current and circuits. It begins by defining electric current as the flow of charge and discusses its units. It then explains how potential difference and a conduction pathway are needed to produce current. Electromotive force is introduced as the maximum potential difference provided by a battery due to chemical reactions. Ohm's law relates current, voltage, and resistance. Resistors in series and parallel are examined. Alternating current is also covered.