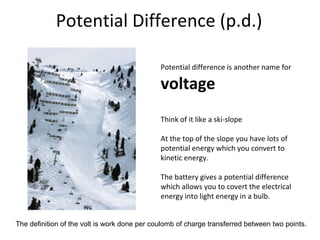
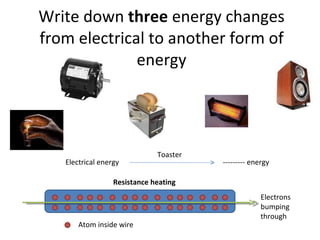
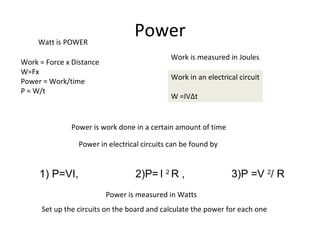
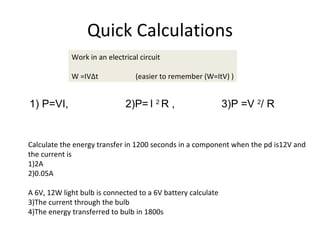
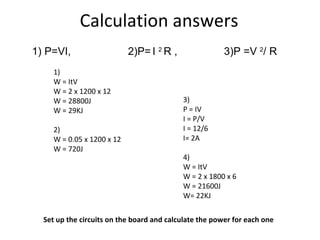
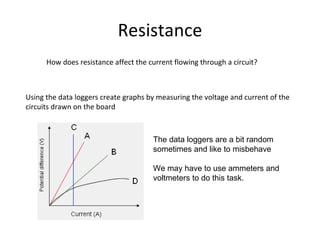
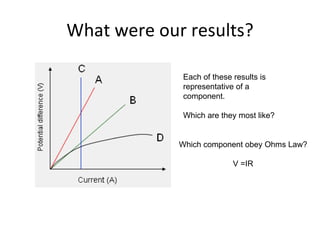
This document covers potential difference, power, and resistance in electrical circuits. It defines potential difference as another term for voltage and describes how batteries provide potential difference to allow the conversion of electrical energy into other forms like light. It gives examples of electrical energy being converted to energy in a toaster or heat in a wire. It defines power as the rate of doing work, measured in watts, and provides the formulas to calculate power as P=VI, P=I^2R, and P=V^2/R. It describes using data loggers and circuits to measure voltage, current, and calculate power, and how resistance affects current in a circuit. Components that obey Ohm's law are identified.