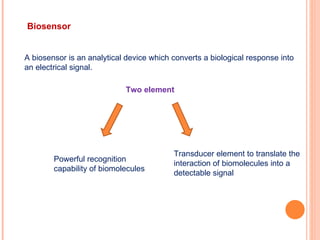
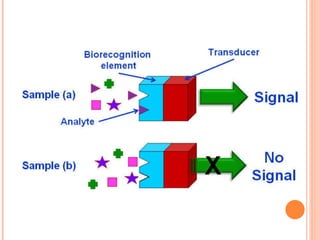
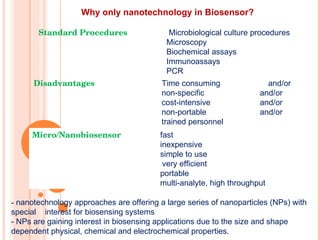
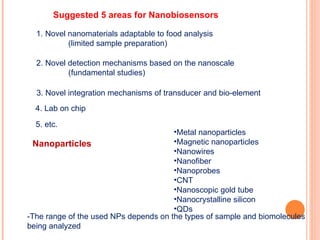
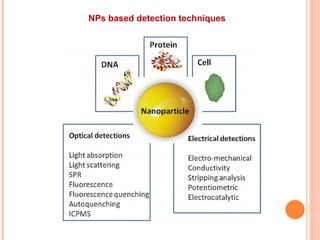
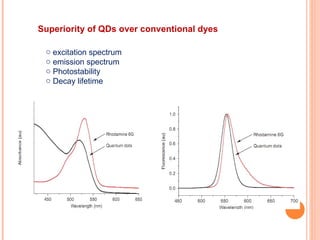
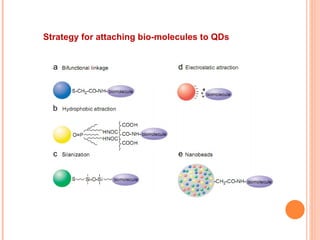
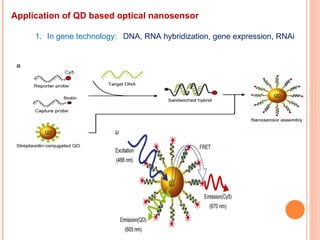
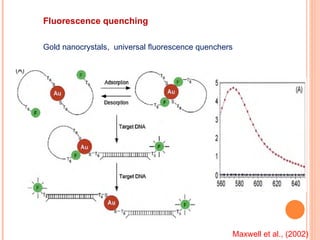
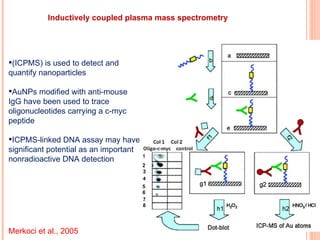
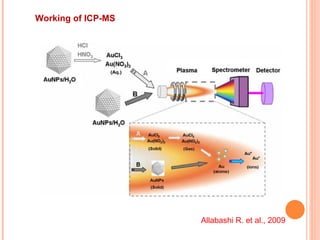
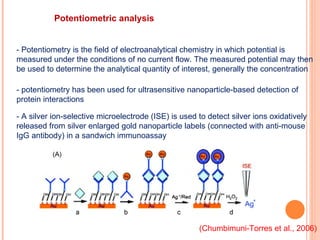
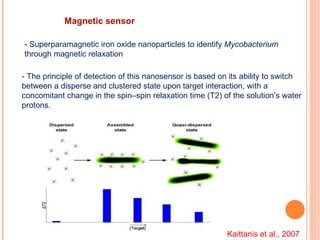
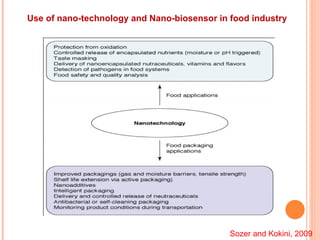
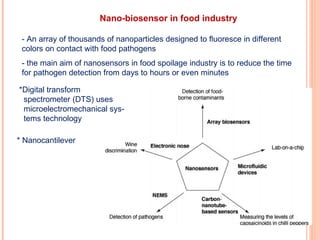
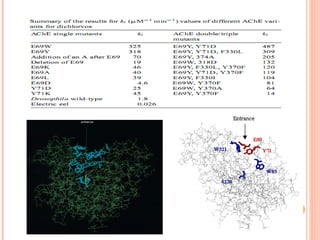
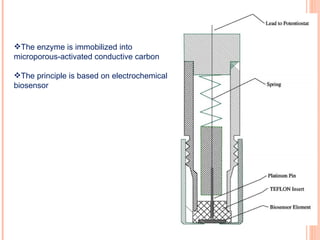
The document discusses the application of nanotechnology in biosensors. It begins by defining nanotechnology and biosensors. Nanoparticles are gaining interest in biosensing applications due to their size-dependent properties. Standard procedures for detection are time-consuming, non-specific, costly, and require trained personnel. Nanoparticles can be used to develop micro/nanobiosensors that are fast, inexpensive, simple to use, efficient, and portable. Various types of nanoparticles and detection techniques using nanoparticles like fluorescence, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, and potentiometric analysis are then described.