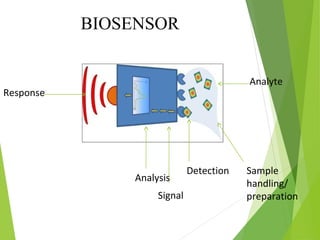
Carbon nanotubes have potential applications in biosensor development due to their electrical and physical properties. A biosensor consists of a biological recognition component and a transducer. Carbon nanotubes can act as both the immobilization platform for the biological recognition element and as an electronic mediator in the transducer. Their high conductivity and surface area make them suitable for creating bionanoelectroanalytical devices with applications in food analysis, medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring and other fields.