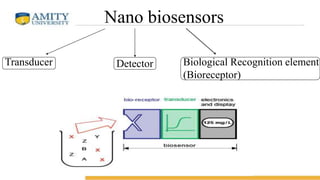
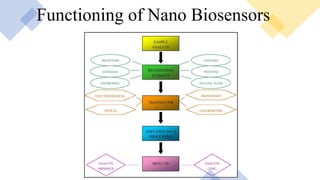
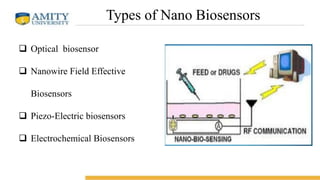
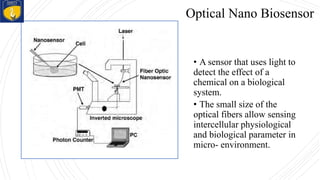
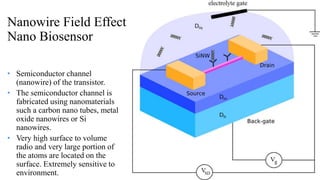
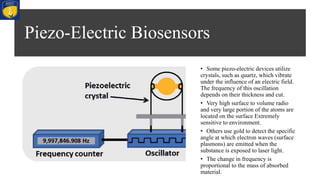
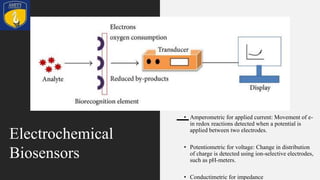
Nano-biosensors are biosensors that operate on the nanoscale. They combine a biological component with a physicochemical detector. There are several types of nano-biosensors including optical biosensors, which use light to detect chemical effects on biological systems; nanowire field effect biosensors, which use semiconductor nanowires as the transistor channel; and piezoelectric biosensors, which use crystals like quartz that vibrate under electric fields. Nano-biosensors have applications in detecting DNA, cells, bacteria, enzymes and more. They can be used for medical testing, environmental monitoring, and cancer detection by coating sensors with cancer-specific biomarkers.