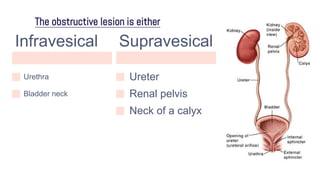
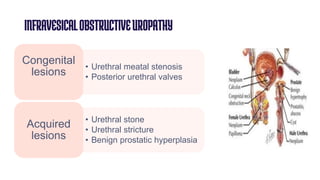
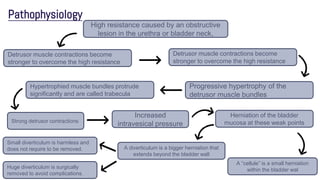
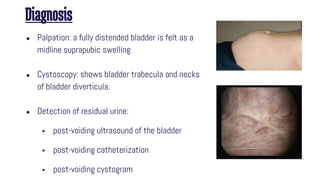
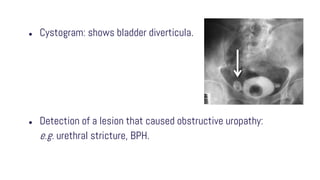
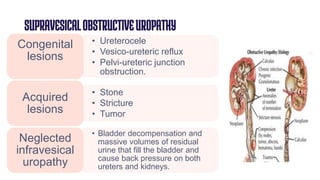
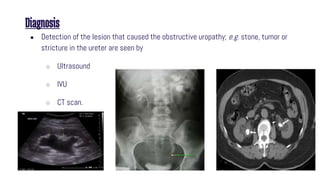
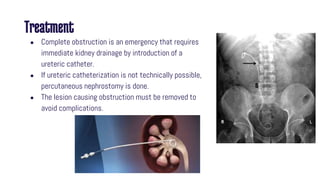
Obstructive uropathy occurs when there is a partial or complete blockage in the urinary tract that obstructs the normal flow of urine. This can be caused by infravesical obstructions like urethral strictures or prostatic hyperplasia, or supravesical obstructions like ureteral stones or tumors. Over time, the blockage can lead to complications like hydronephrosis, hydroureters, and eventual kidney damage or failure if left untreated. Treatment involves relieving the obstruction through procedures like catheterization, lithotripsy, or surgery to remove the underlying cause.