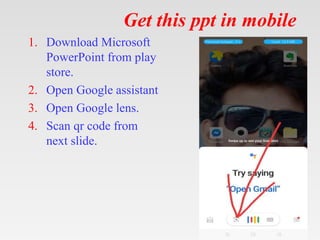
This document provides tips for using a PowerPoint presentation on hydronephrosis:
1. The slides can be freely downloaded, edited, and modified. Blank slides are included to engage students by asking what they know about each topic before showing the content slide.
2. This active learning approach involves showing the blank slides, soliciting student input, and then presenting the content slide. This cycle repeats for each topic.
3. Users can also study on their own by viewing blank slides, thinking about the topic, and then reading the content slide.
The presentation encourages an interactive approach to learning about the causes, features, diagnosis, and management of hydronephrosis. Blank slides promote student participation before