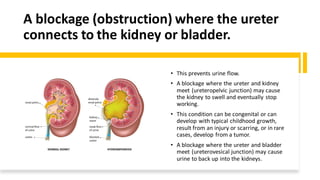
This document discusses ureteral obstruction, which is a blockage in the ureters that connect the kidneys to the bladder. It can be caused by various congenital issues, injuries, tumors, or other problems that prevent the normal flow of urine. Left untreated, ureteral obstruction can lead to urinary tract infections, kidney damage, and even kidney failure or sepsis. Treatment aims to remove or bypass the blockage through minimally invasive or open surgical procedures, with the goal of restoring urine flow and preventing long-term kidney damage.