Embed presentation
Downloaded 324 times




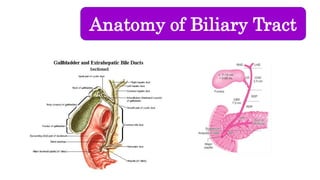
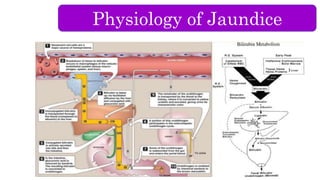
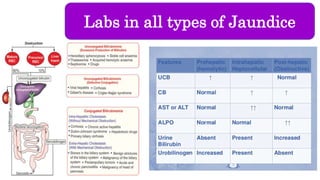

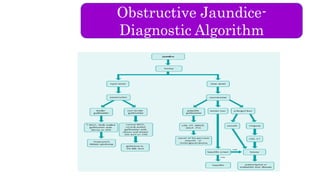


The document provides an overview of obstructive jaundice including its causes, anatomy and physiology of the biliary tract, and laboratory findings associated with it. It outlines intraluminal, mural, and extrinsic causes of jaundice and highlights key diagnostic lab results such as increased bilirubin levels and enzymes. An algorithm for diagnosing obstructive jaundice is also included, along with related clinical problems that healthcare professionals should be aware of.









