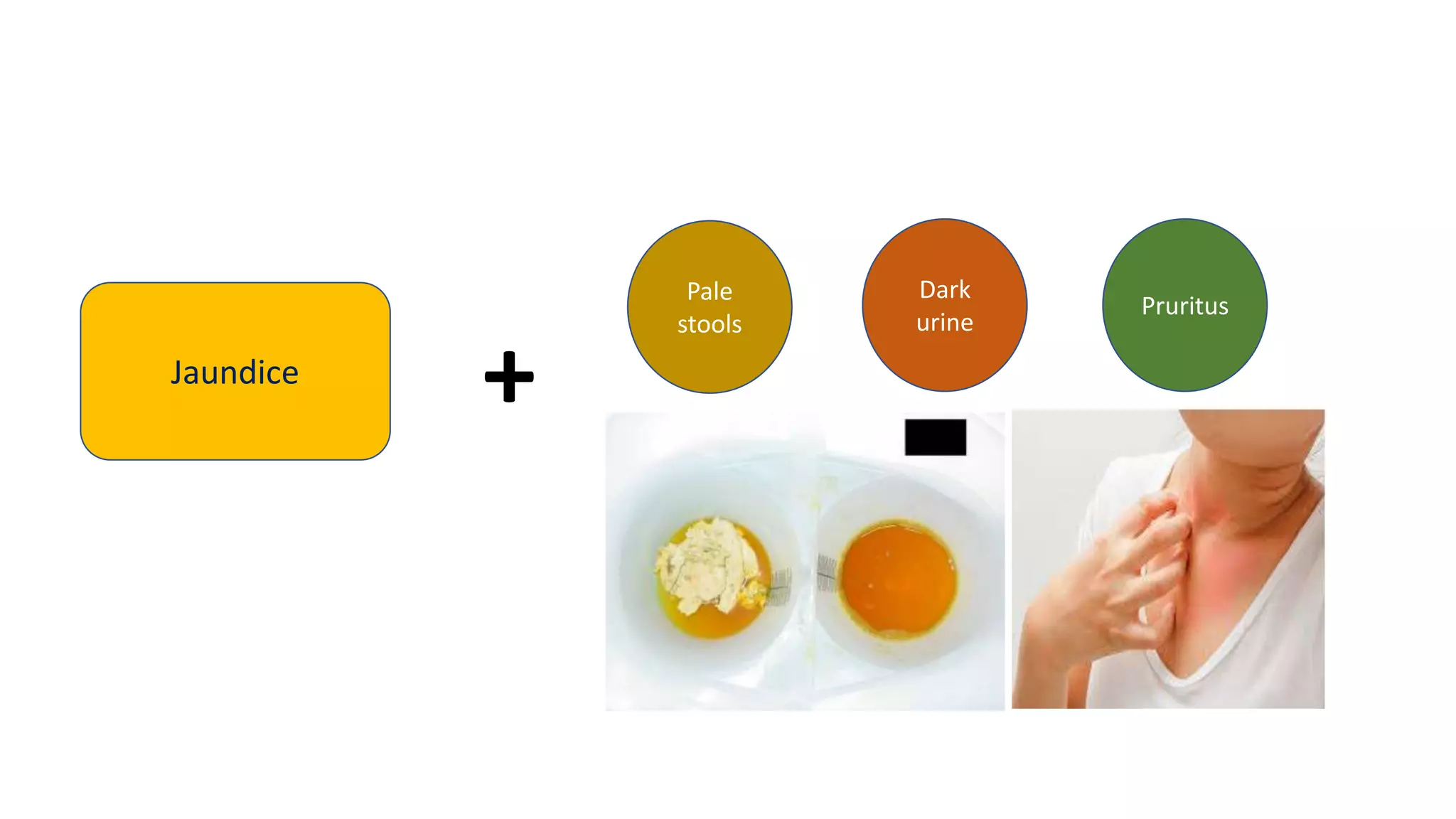
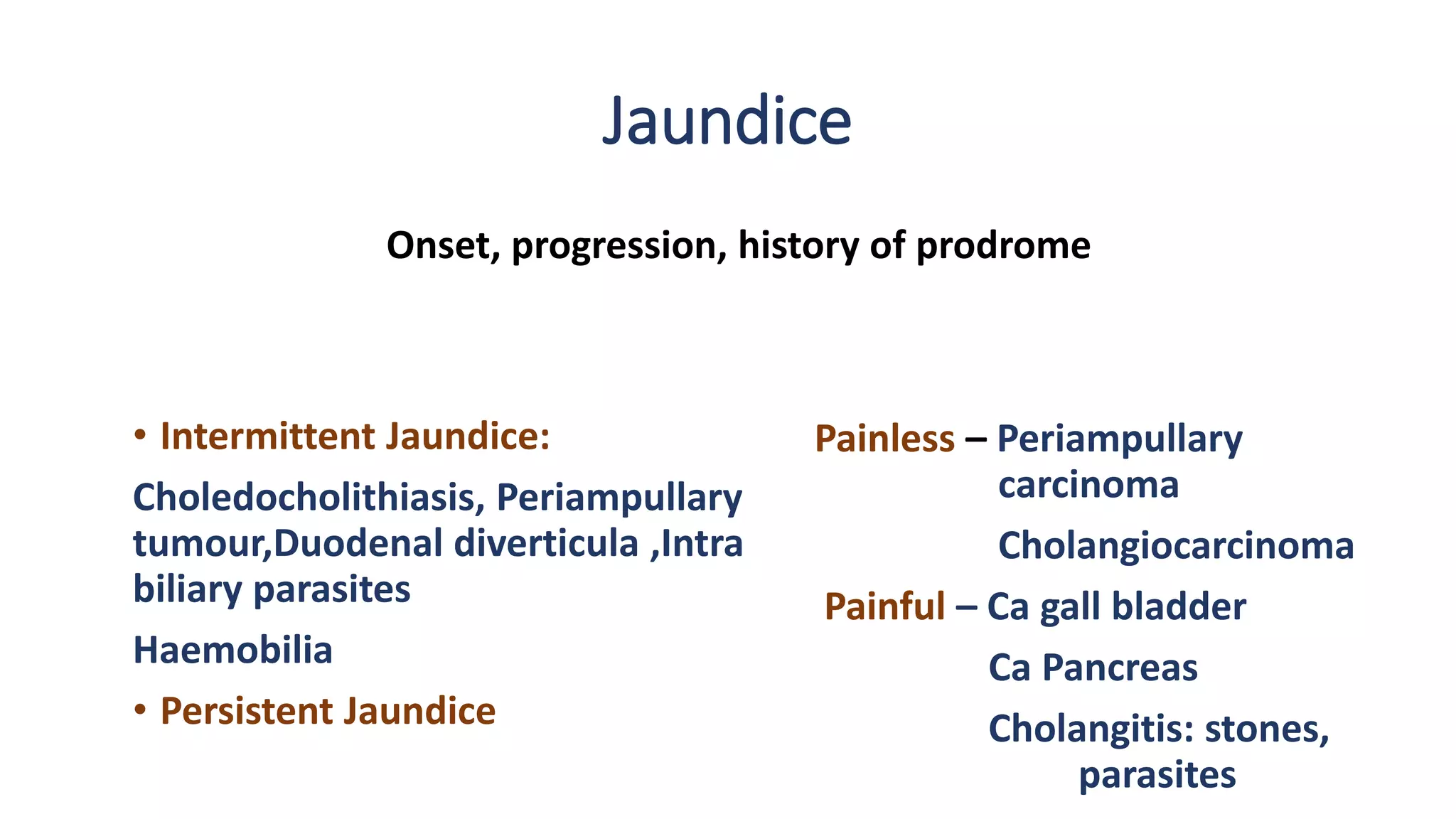
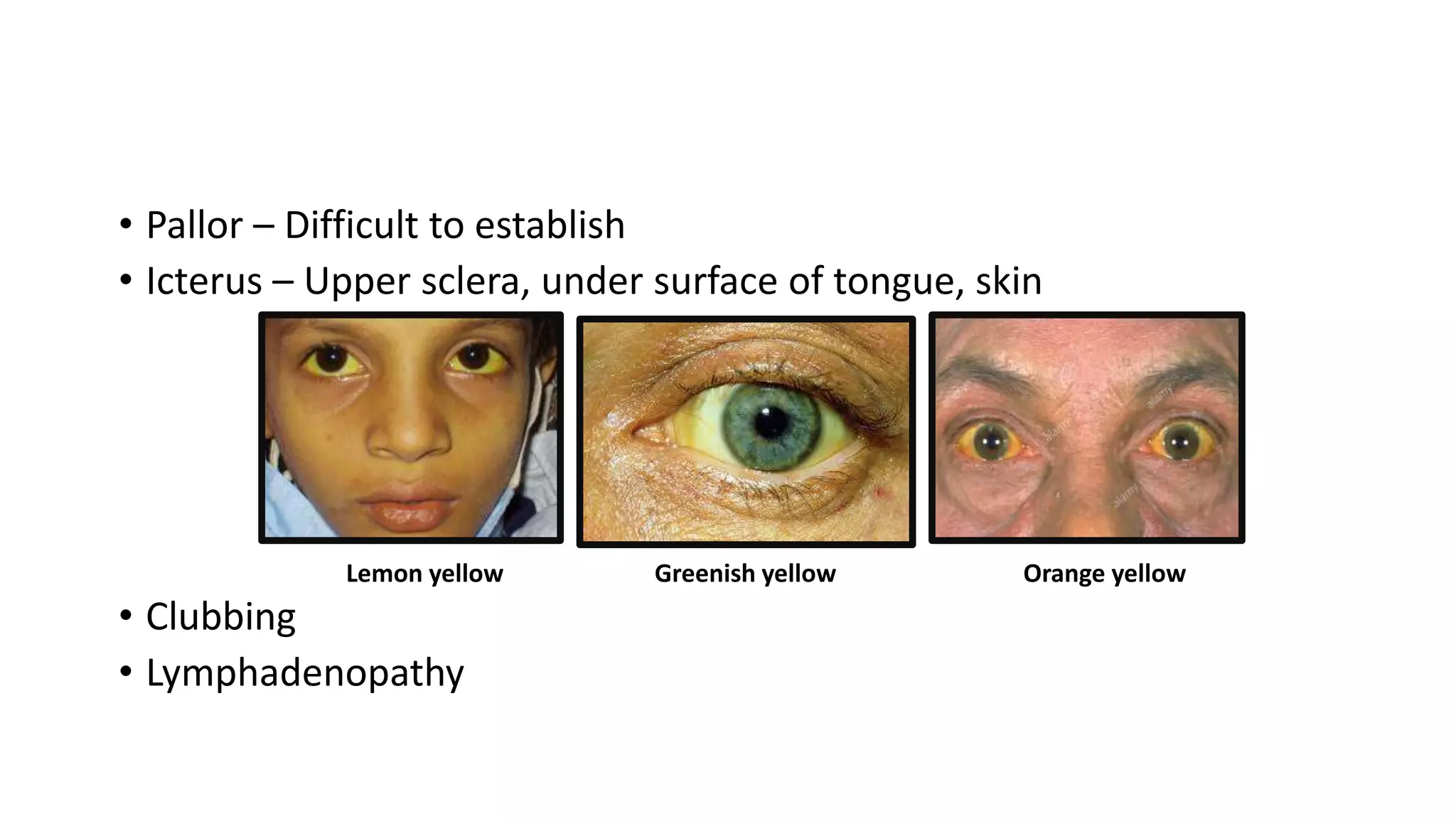
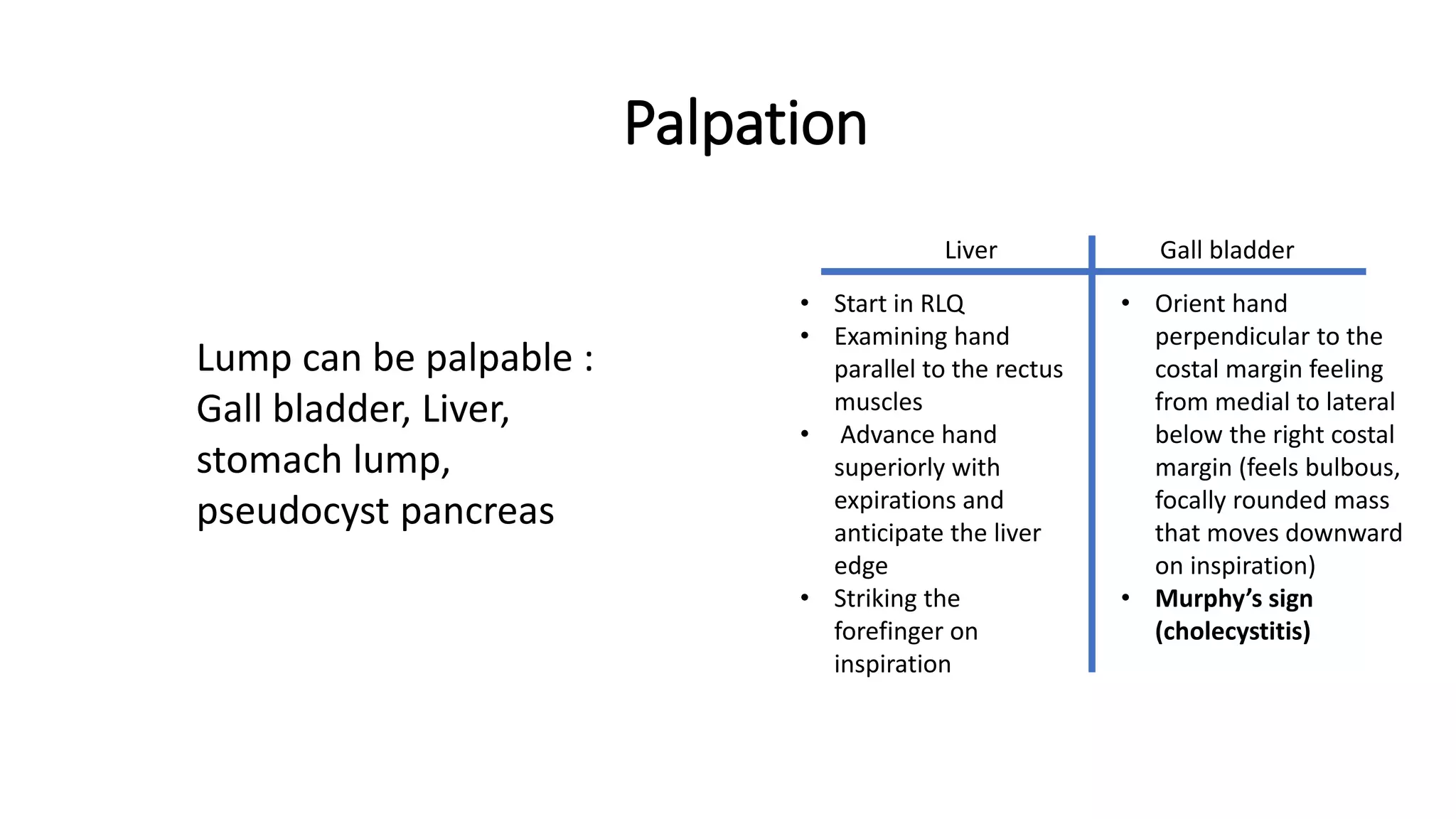
1) The document discusses obstructive jaundice, defining it as jaundice resulting from widespread tissue deposition of bilirubin due to impaired bile formation or flow.
2) A thorough history and physical exam is important to determine if the cause is intrahepatic or extrahepatic. Clues to each are provided.
3) Common extrahepatic causes include choledocholithiasis, benign strictures, primary sclerosing cholangitis, malignancies such as cholangiocarcinoma and pancreatic cancer.
Common intrahepatic causes include viral hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis.