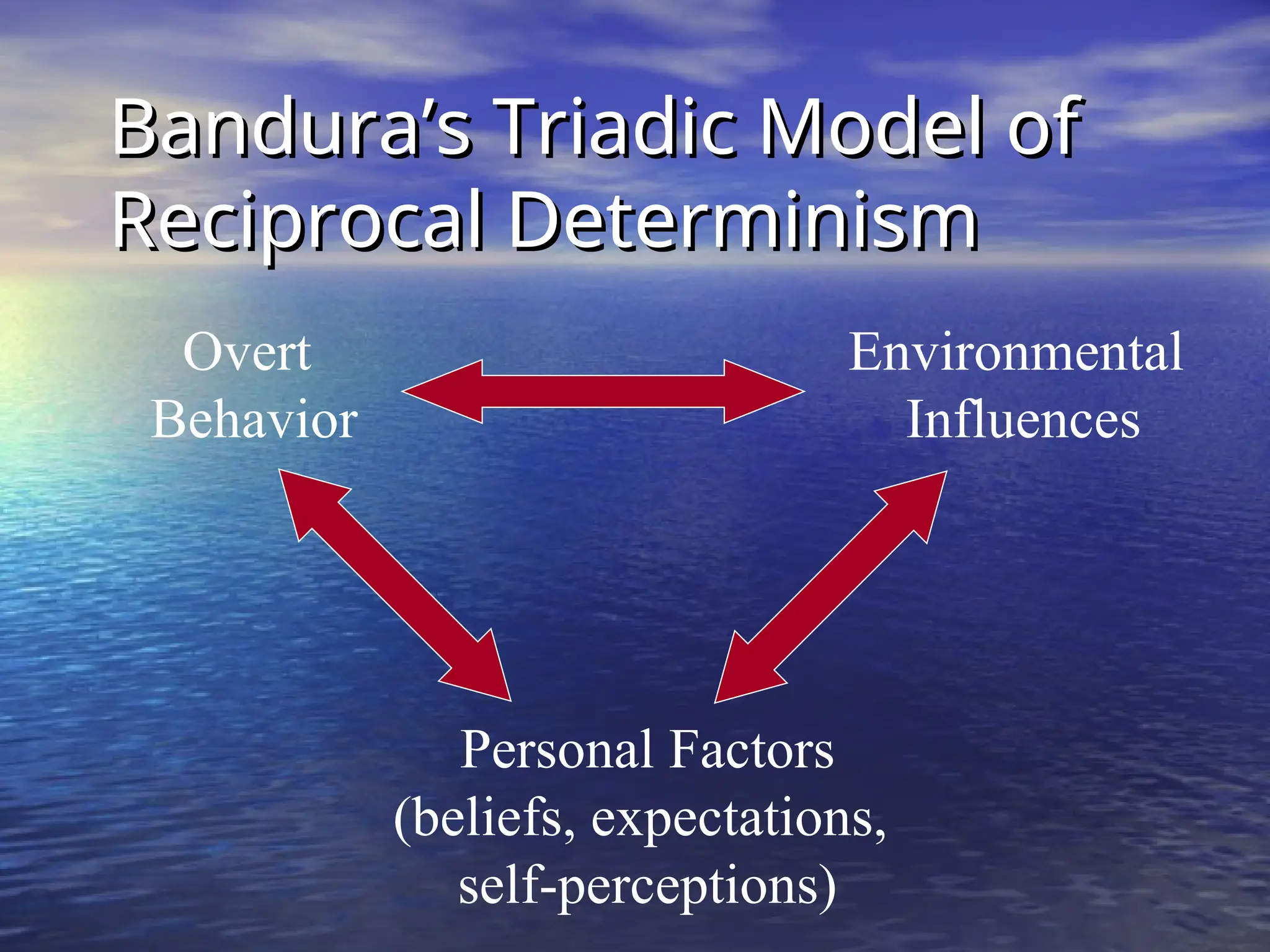
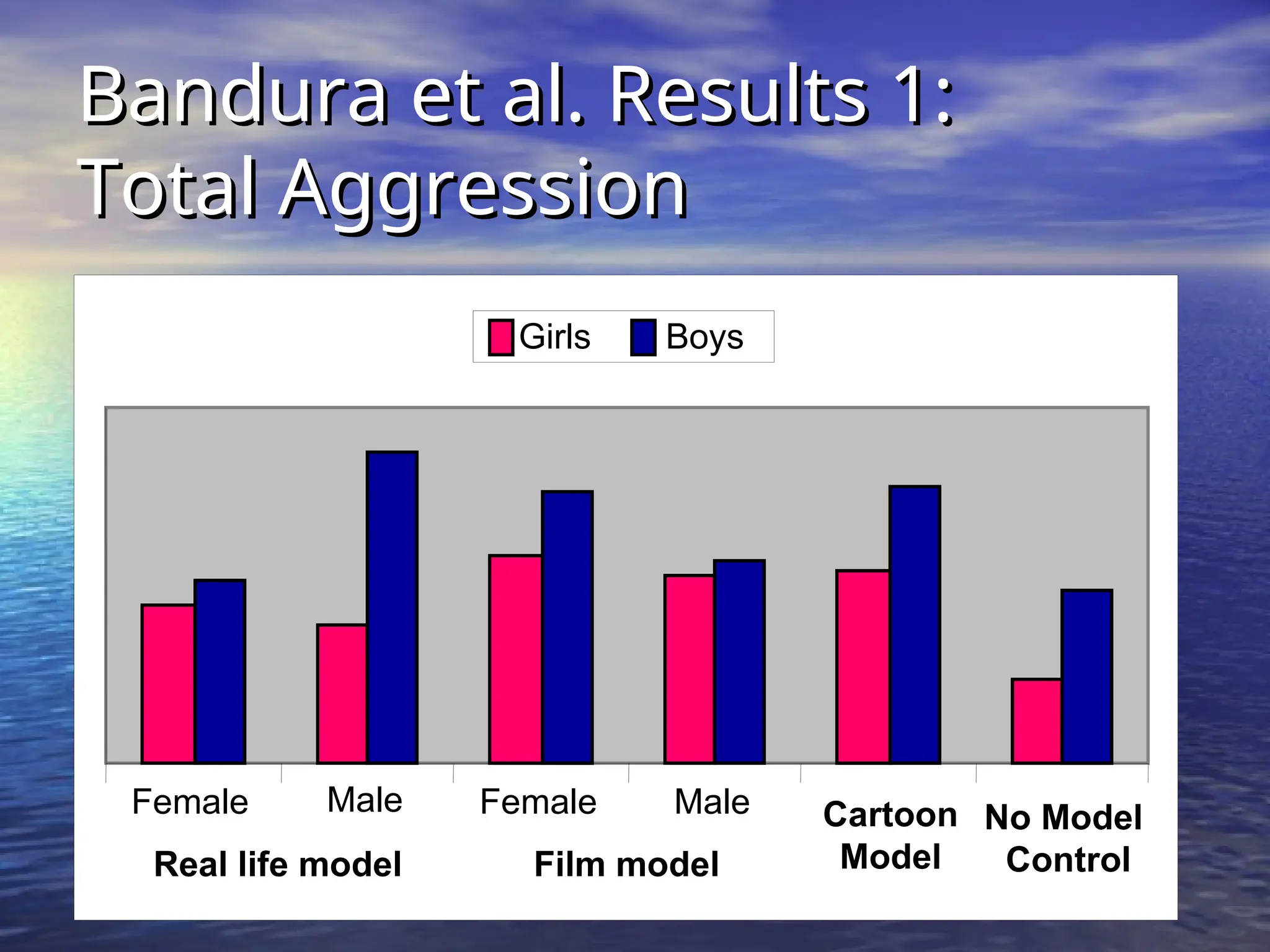
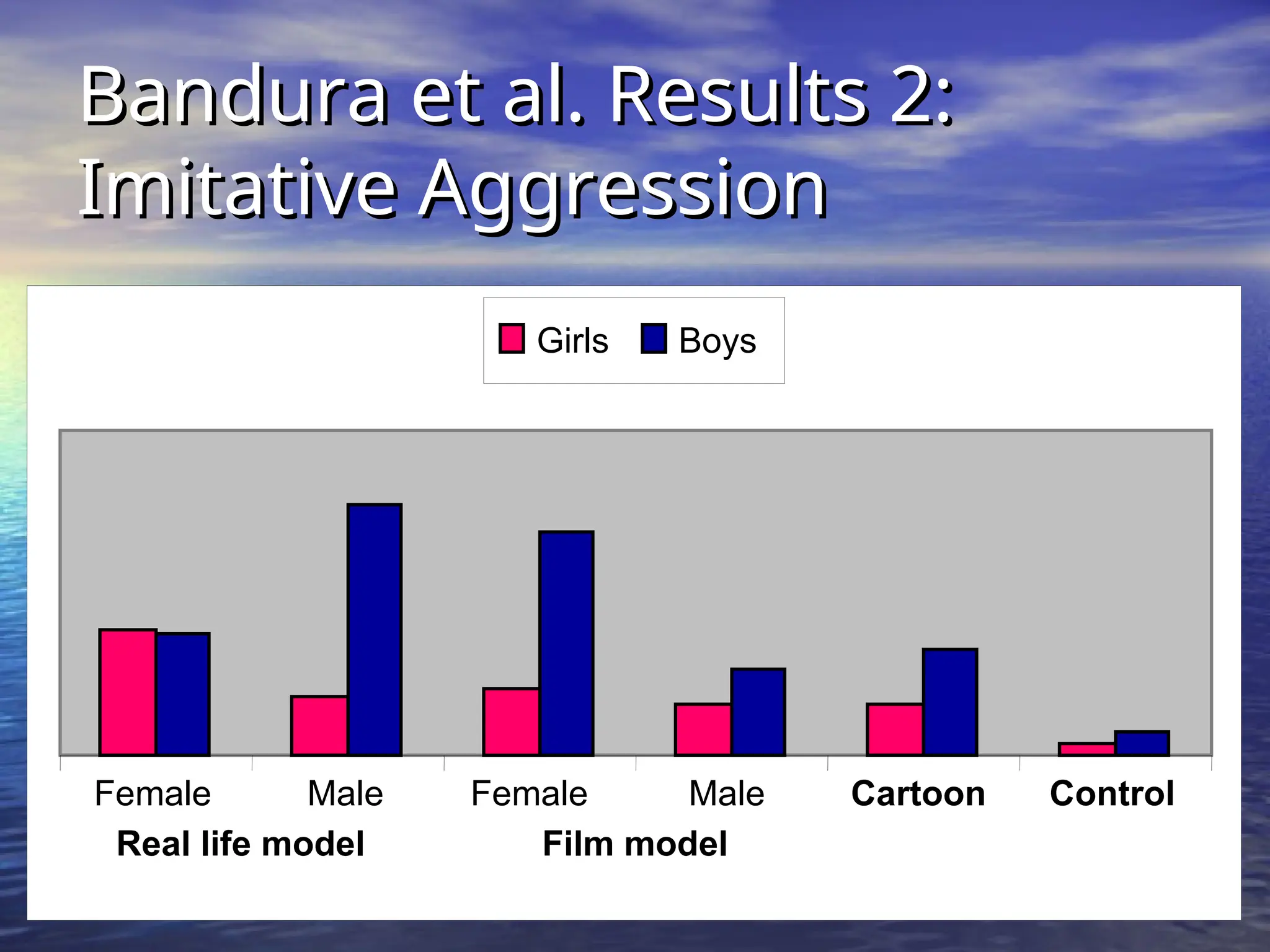
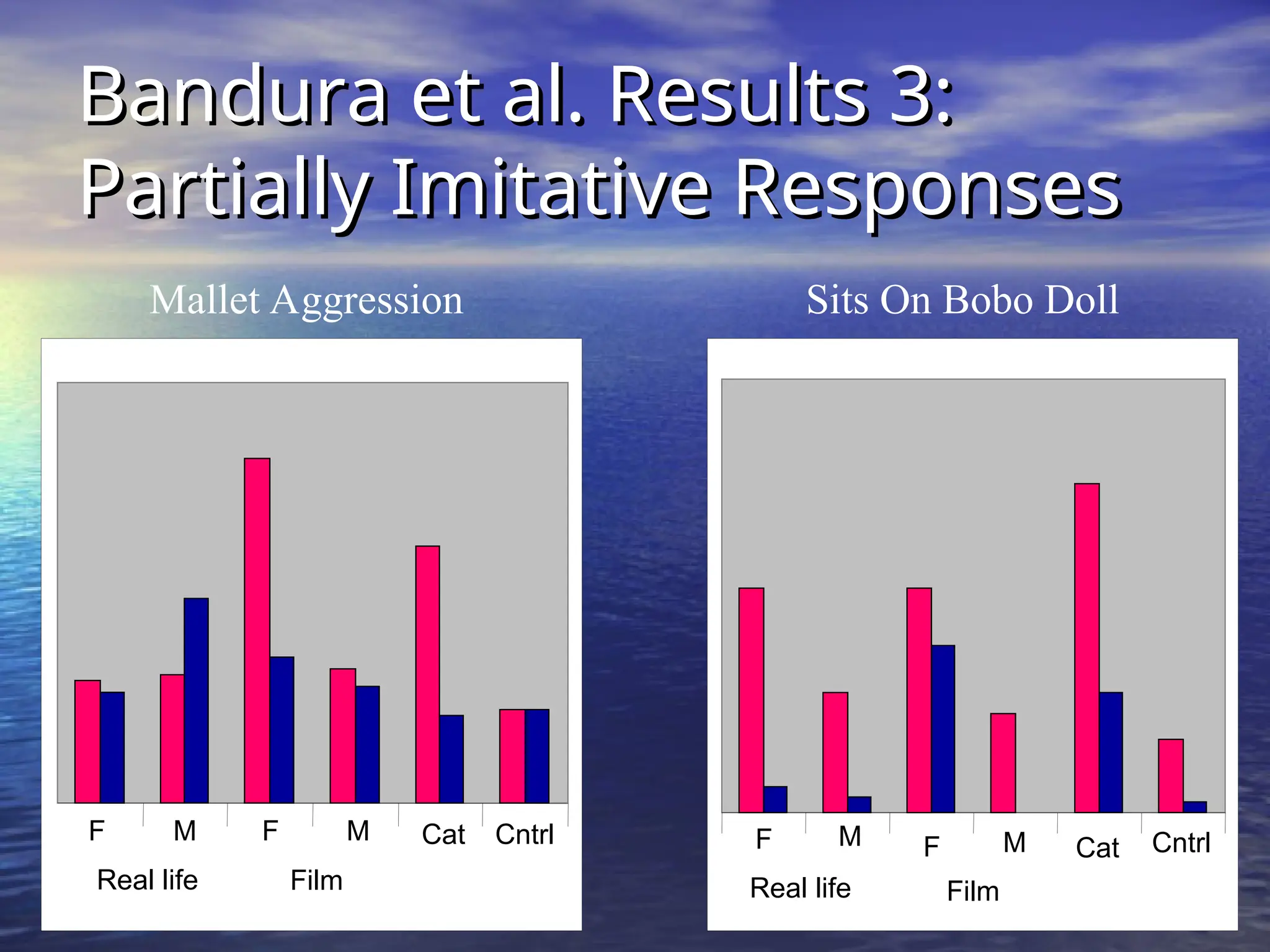
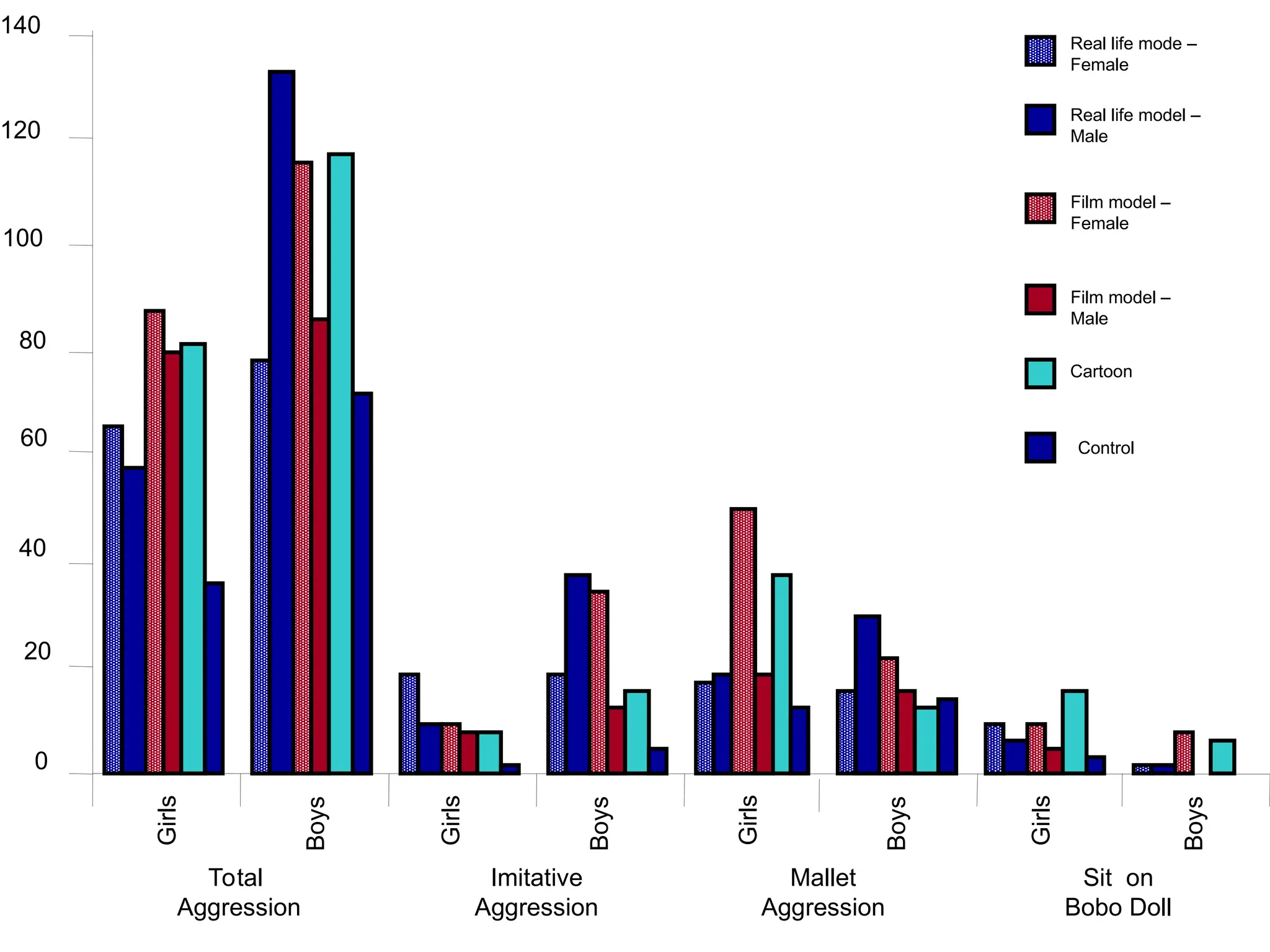
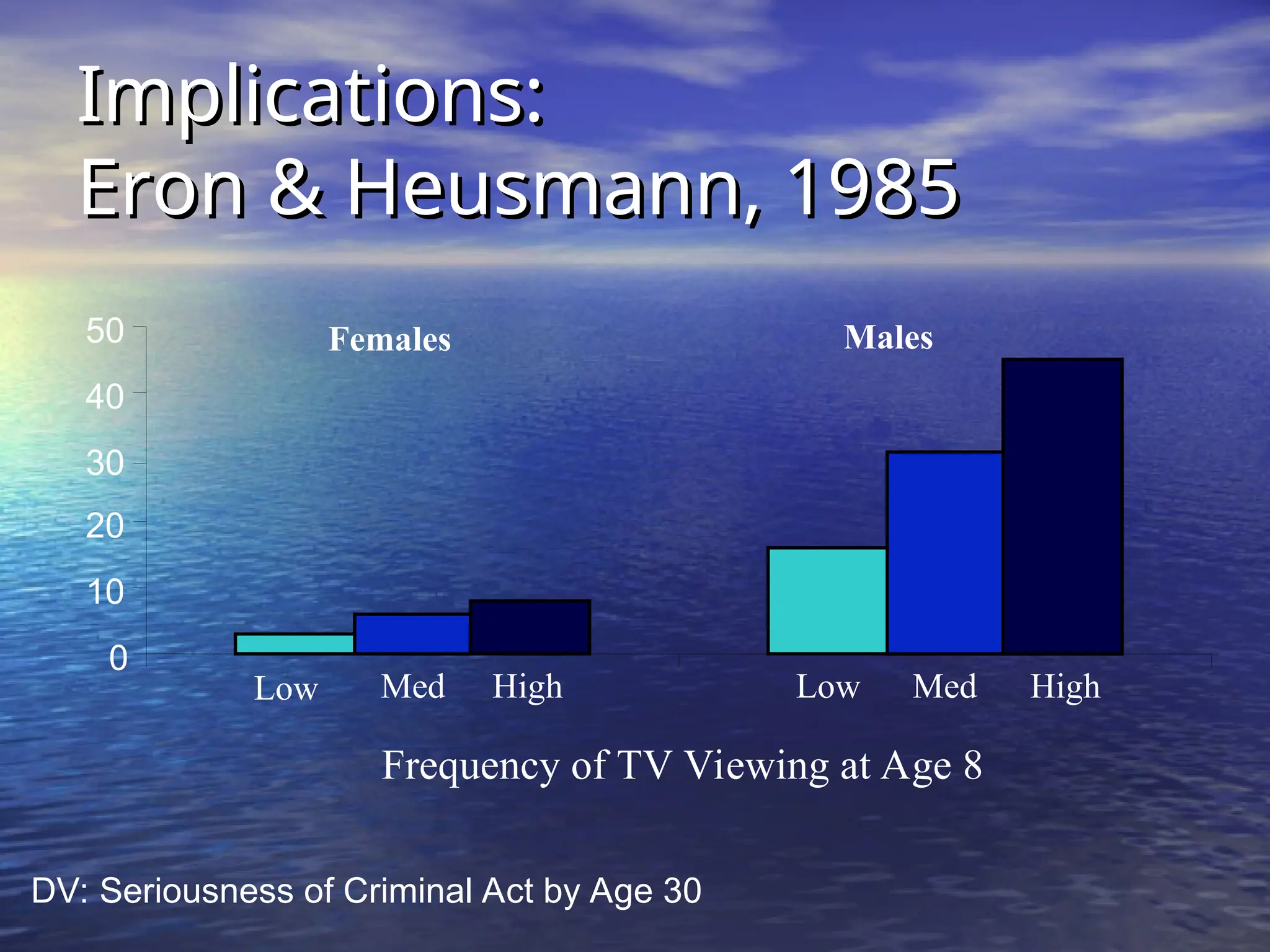
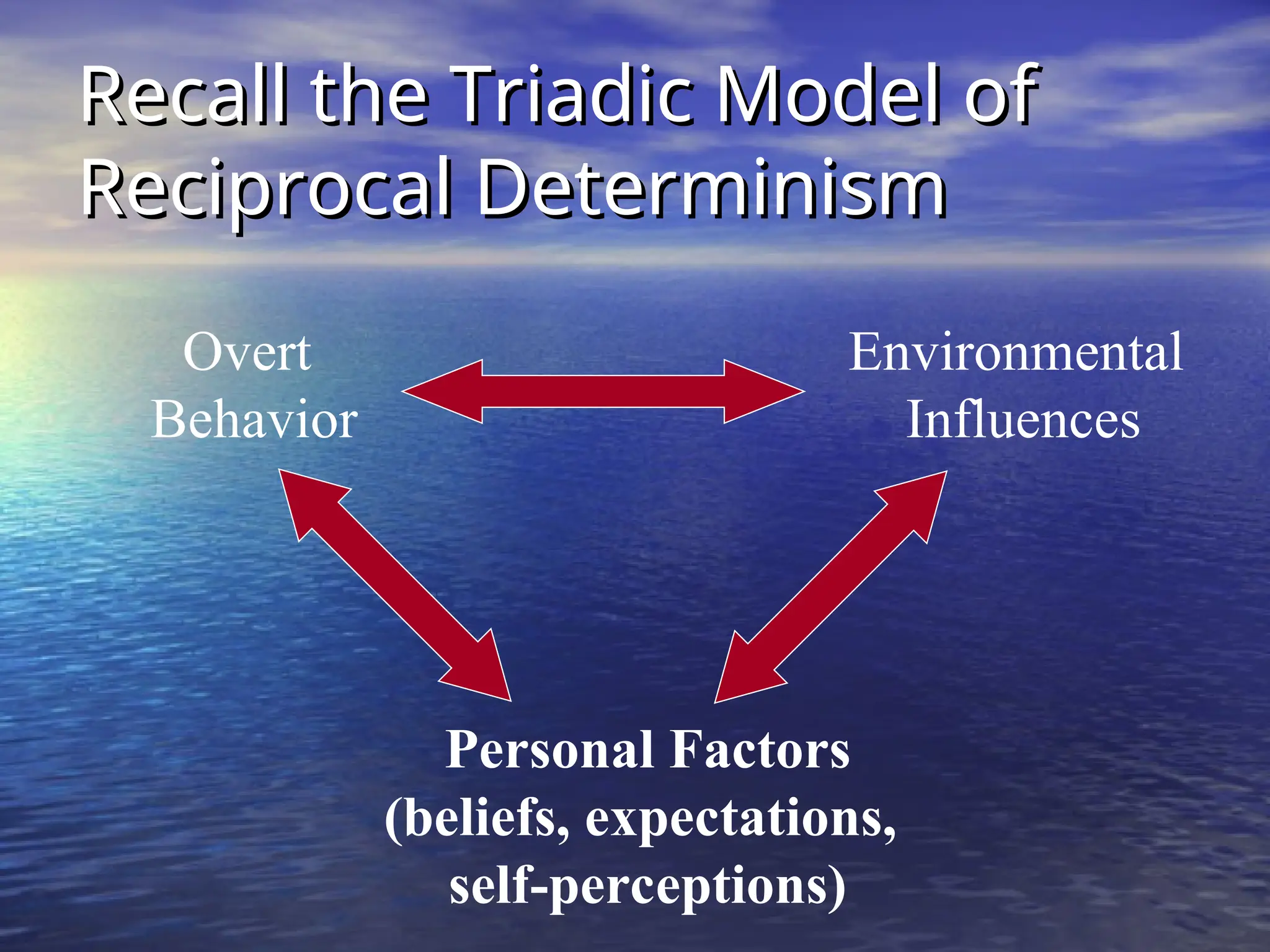
Social learning theory emphasizes the importance of cognitive processes in behavior acquisition, suggesting that individuals learn not just through direct reinforcement, but also by observing others. Albert Bandura's model highlights the interplay of environmental influences, personal factors, and behavior, permitting self-regulation and free will. Observational learning involves attention, retention, motor reproduction, and motivation, influencing how behaviors are adopted based on observed consequences.