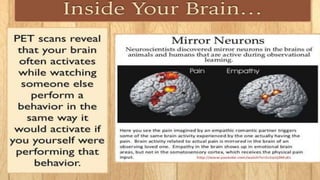
The document discusses observational learning, defined as acquiring knowledge and skills through observing and imitating others, with key contributions from psychologist Albert Bandura, who introduced social learning theory and the concept of self-efficacy. It outlines the stages of observational learning, including attention, retention, motor reproduction, motivation, and reinforcement, emphasizing the impact of role models, especially during childhood. The conclusion highlights the potential of digital technology to transform learning paradigms, advocating for greater interaction and engagement in learning environments.