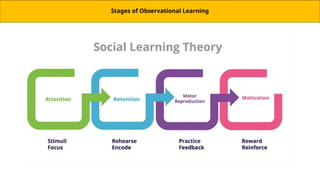
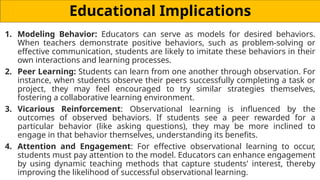
Observational learning, developed by Albert Bandura, is a theory explaining how people learn behaviors by observing others and has applications in education, therapy, and social behavior. The process involves four key stages: attention, retention, motor reproduction, and motivation, each crucial for successful learning. Bandura's Bobo doll experiment highlighted the impact of reinforcement on behavior imitation, showing that children are more likely to replicate behaviors seen in models receiving rewards or experiencing no consequences.