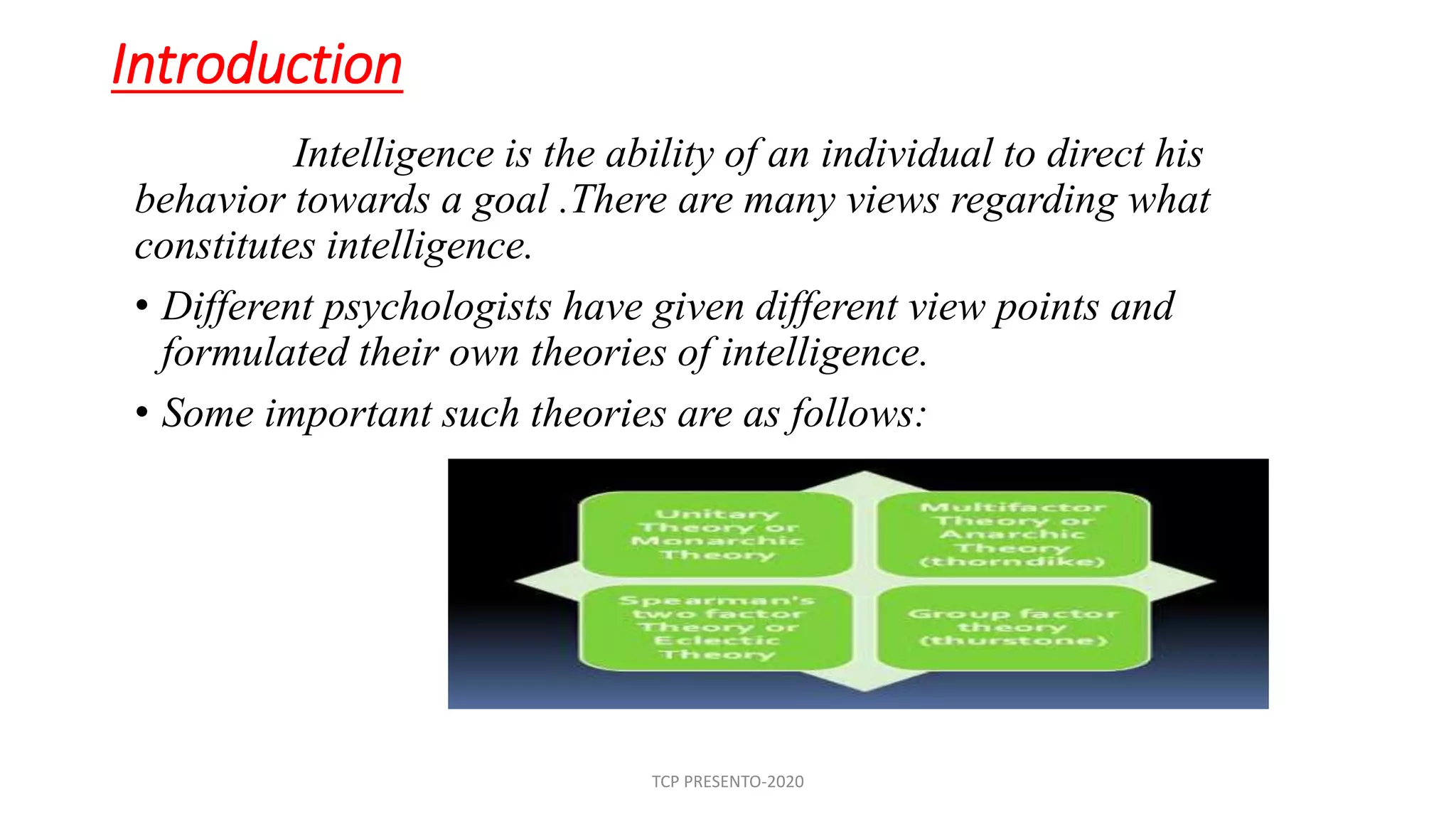
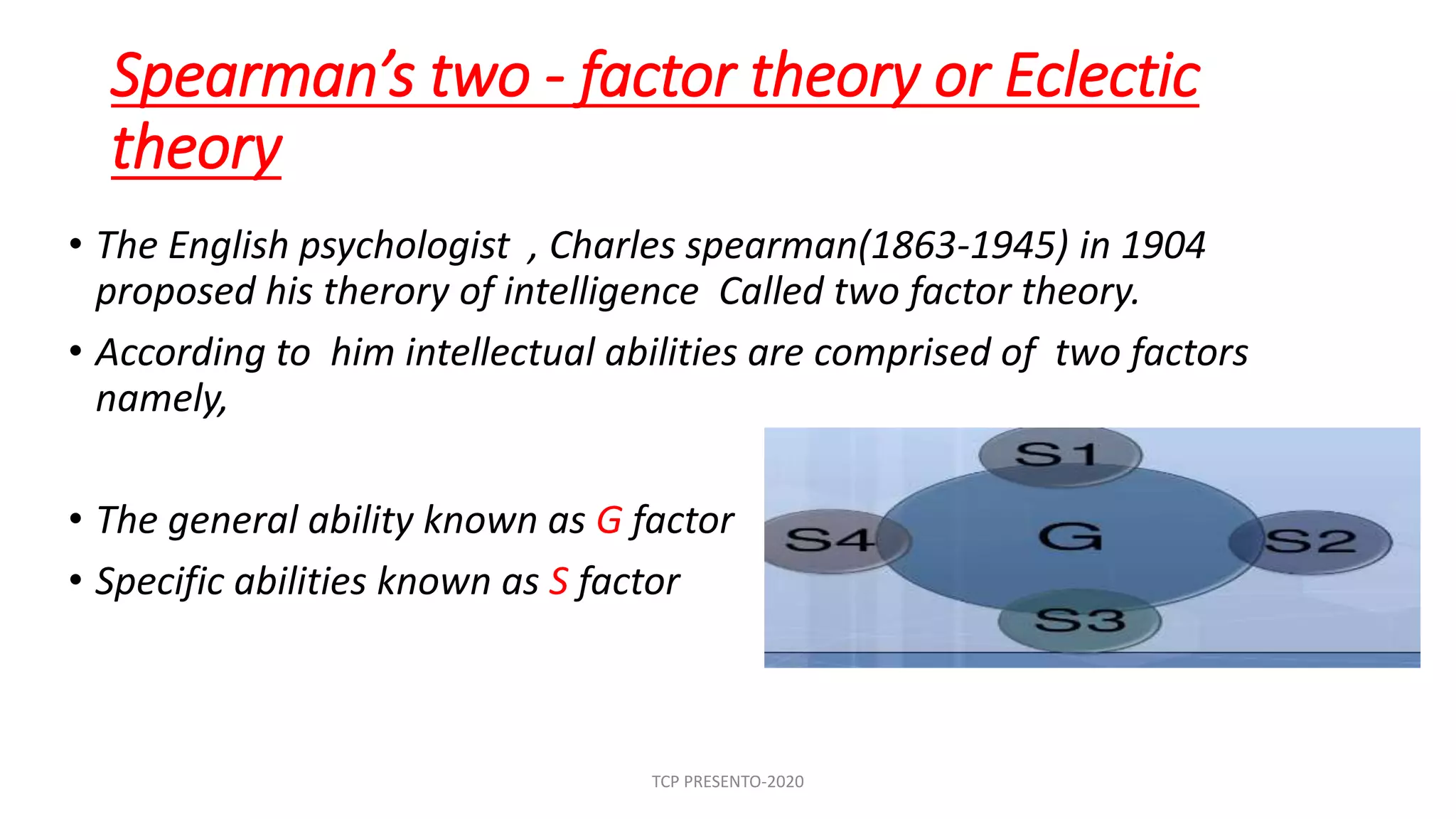
The document discusses various theories of intelligence proposed by different psychologists, highlighting key theories including Spearman's two-factor theory, Thorndike's multi-factor theory, Thurstone's group-factor theory, and Gardner's multiple intelligences theory. Each theory offers unique insights into understanding intelligence, such as distinguishing between general and specific abilities or recognizing diverse types of intelligences. Additionally, the document presents Guilford's structure of intellects, suggesting a complex interaction of cognitive processes and types of content that yield numerous mental abilities.