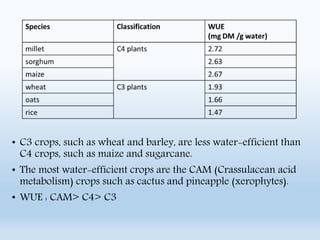
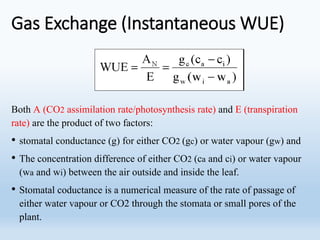
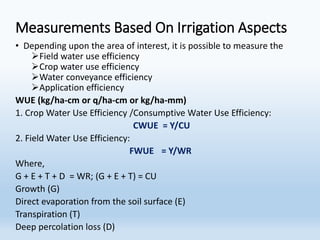
Water use efficiency (WUE) refers to the amount of plant material produced per unit of water used and can be measured at the leaf, plant, or ecosystem level. There are several approaches to measuring WUE including gravimetric methods, gas exchange measurements, carbon isotope discrimination analysis, and considerations of irrigation aspects. Higher WUE occurs when stomatal conductance and photosynthesis are lowest, ambient water vapor concentration is higher, leaf temperature is lower, or ambient CO2 concentration is increased. Studies have used relationships between WUE and carbon isotope discrimination to identify genotypes in crops like groundnuts and understand genetic control of WUE in plants like sunflower under drought conditions.












![IRMS
• The carbon isotopic ratio (R=13C/12C) of the samples (Rsample)
and standard (Rstandard) was determined using an Isotope Ratio
Mass Spectrometer (GD 150, MAT, Germany). R values were
converted to δ13C (in ‰ or per mil) using the relationship:
δ13C (‰) = [Rsample/Rstandard-1] x 1000.
• The standard is the CO2 obtained from a limestone from Pee Dee
Belmenite “PDB” formation in South Carolina, USA. The δ13C
values were converted to carbon isotope discrimination (Δ) values
using the relationship established by Farquhar et al., (1989):
Δ (‰) = (δ13Ca - δ13Cp) /(1 - δ13Cp/1000) ,
• where a and p represent air and plant, respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wateruseefficiencyfinaledited-200520062727/85/Water-use-efficiency-in-plants-15-320.jpg)