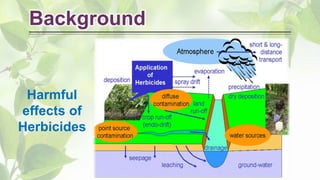
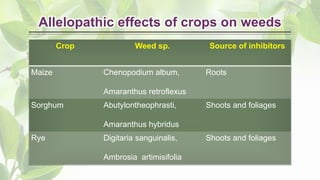
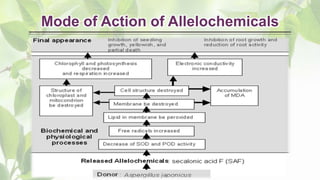
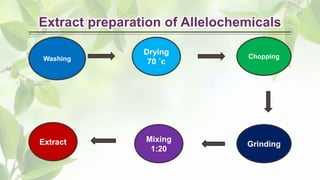
The document presents a detailed overview of allelopathy, emphasizing its definition, interactions, and chemical mechanisms that affect neighboring plant growth. It discusses various forms of allelopathy, ways of chemical release, and factors influencing these effects, as well as the advantages of employing allelopathic strategies in weed management. Additionally, the document outlines practical applications of allelopathy in sustainable agricultural practices, such as intercropping and straw mulching.