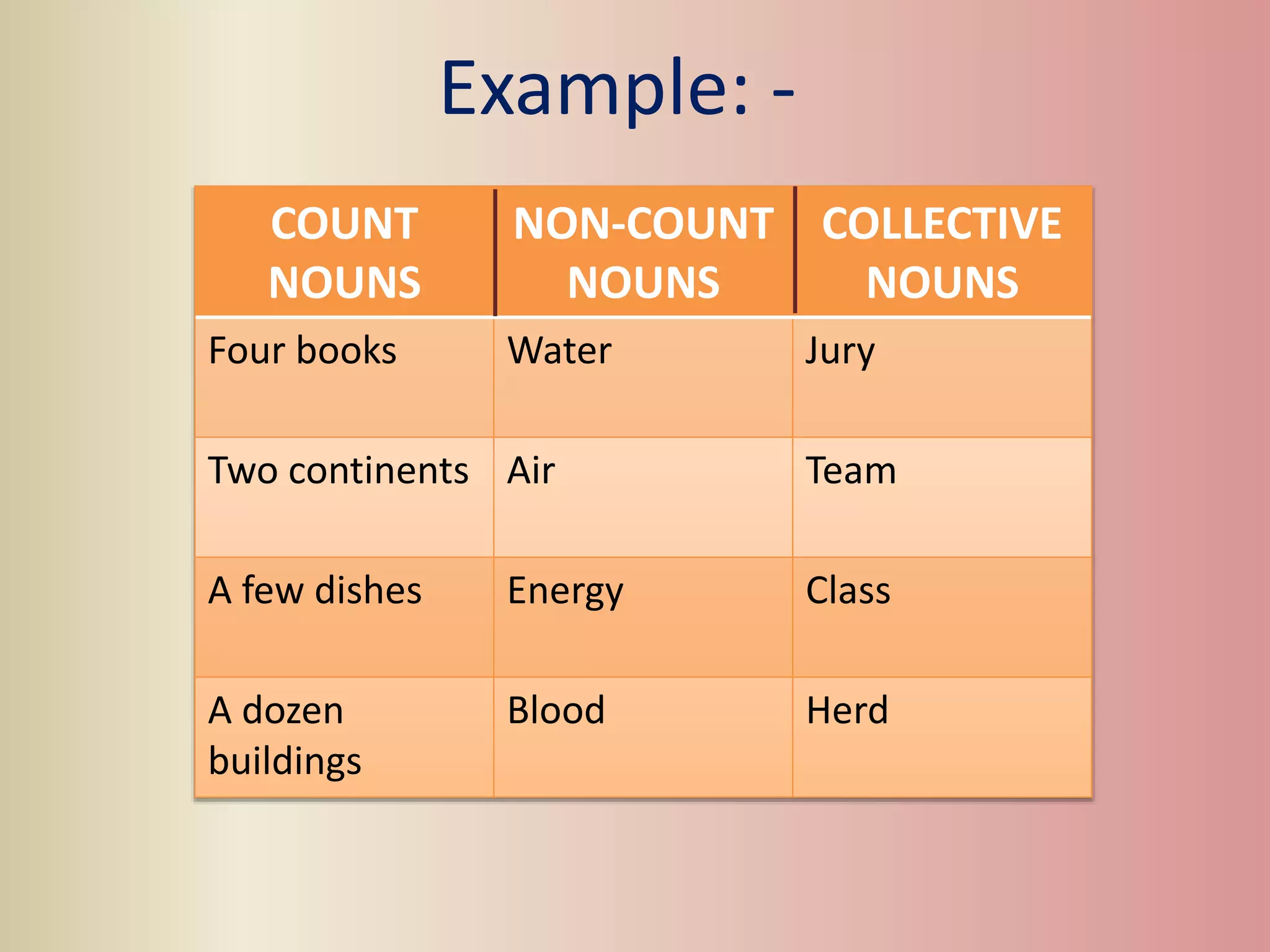
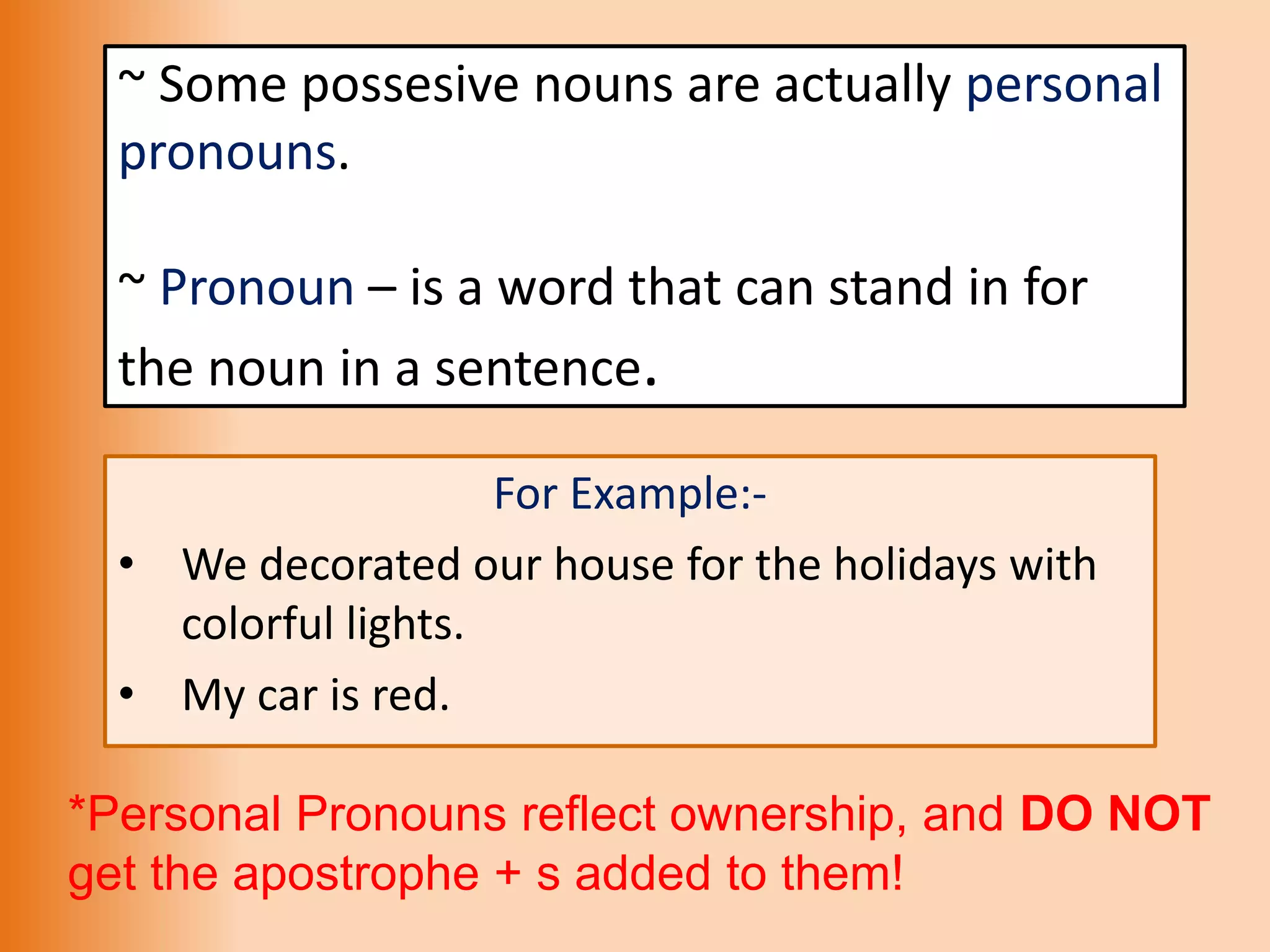
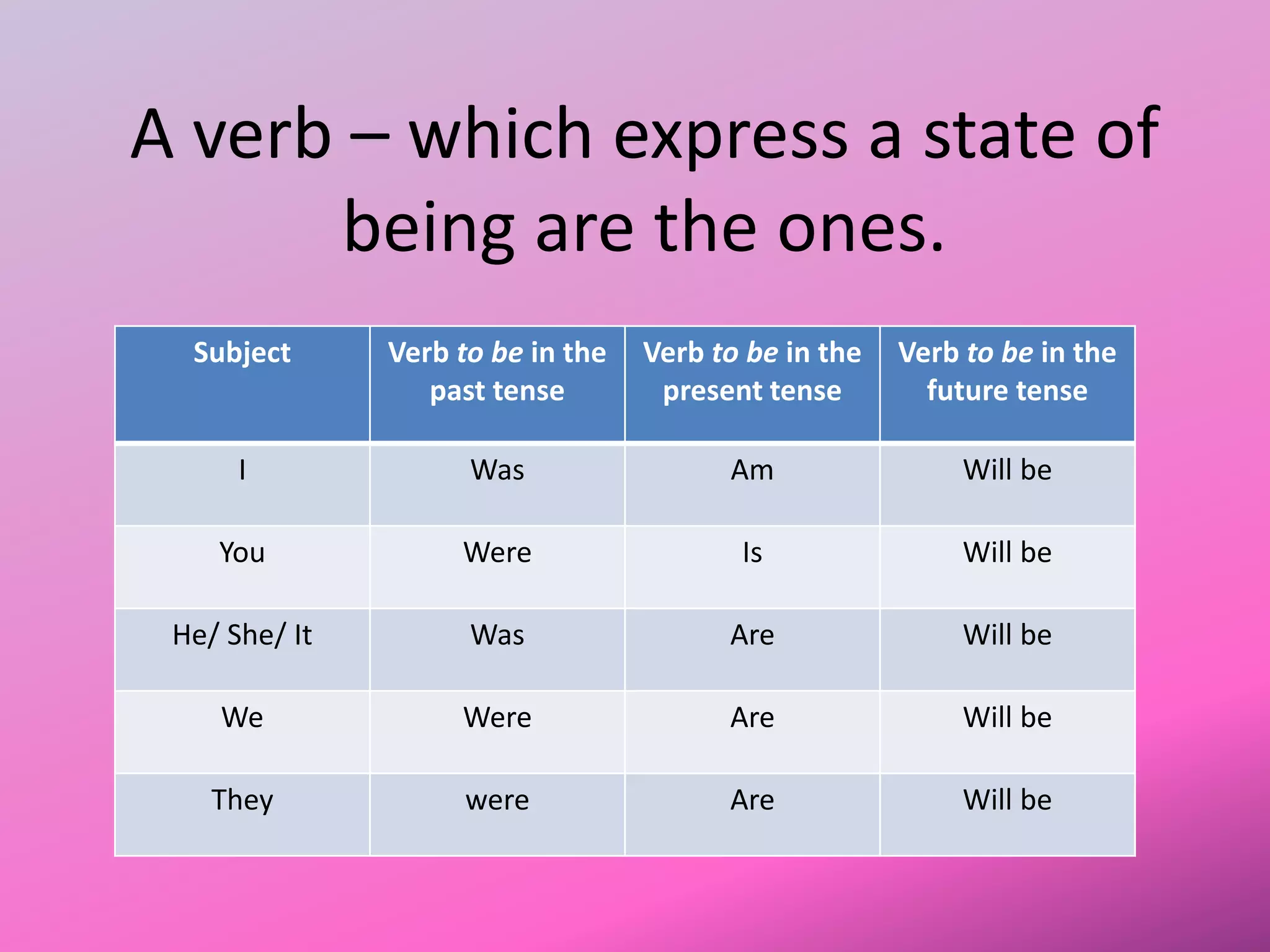
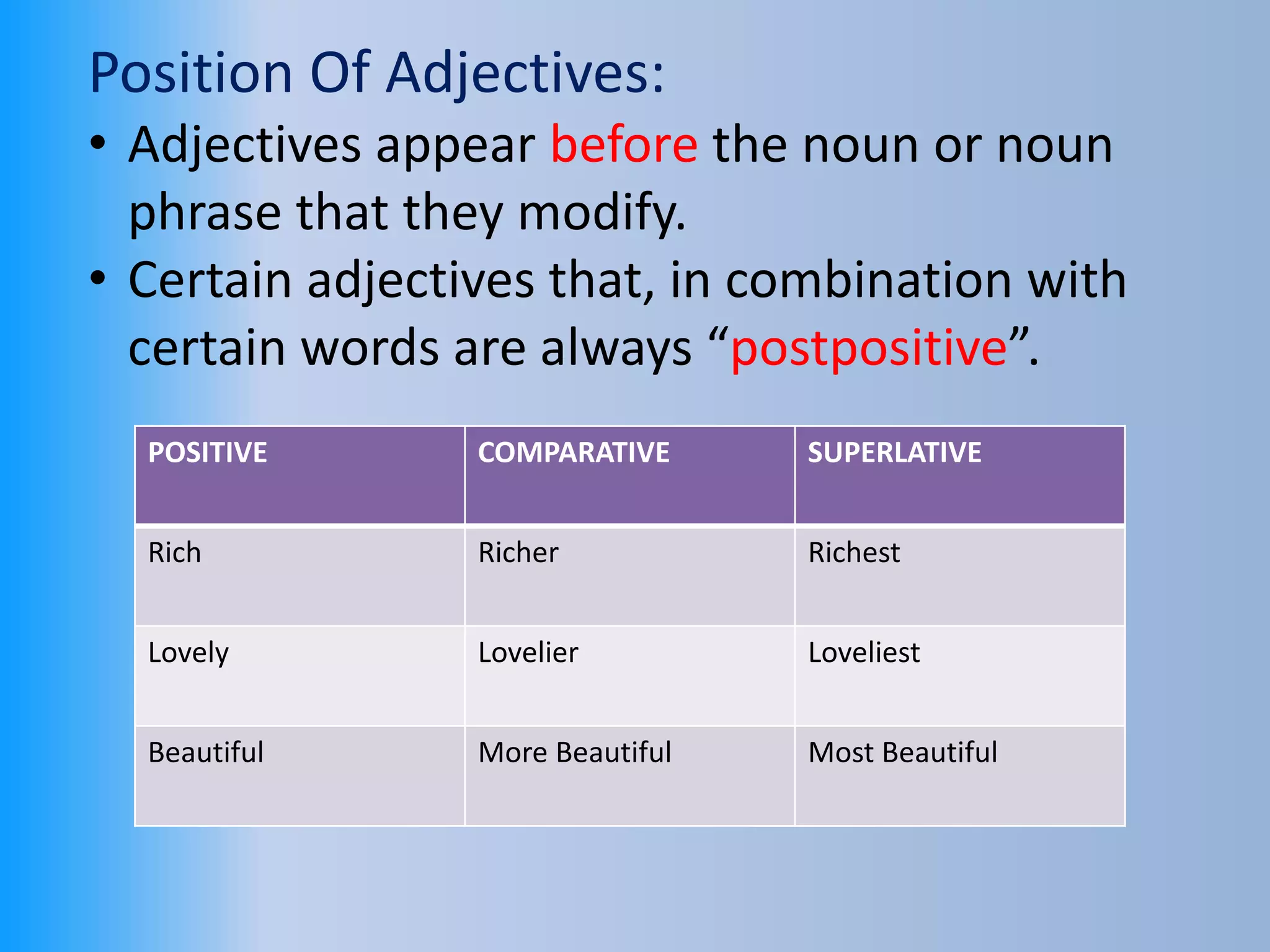
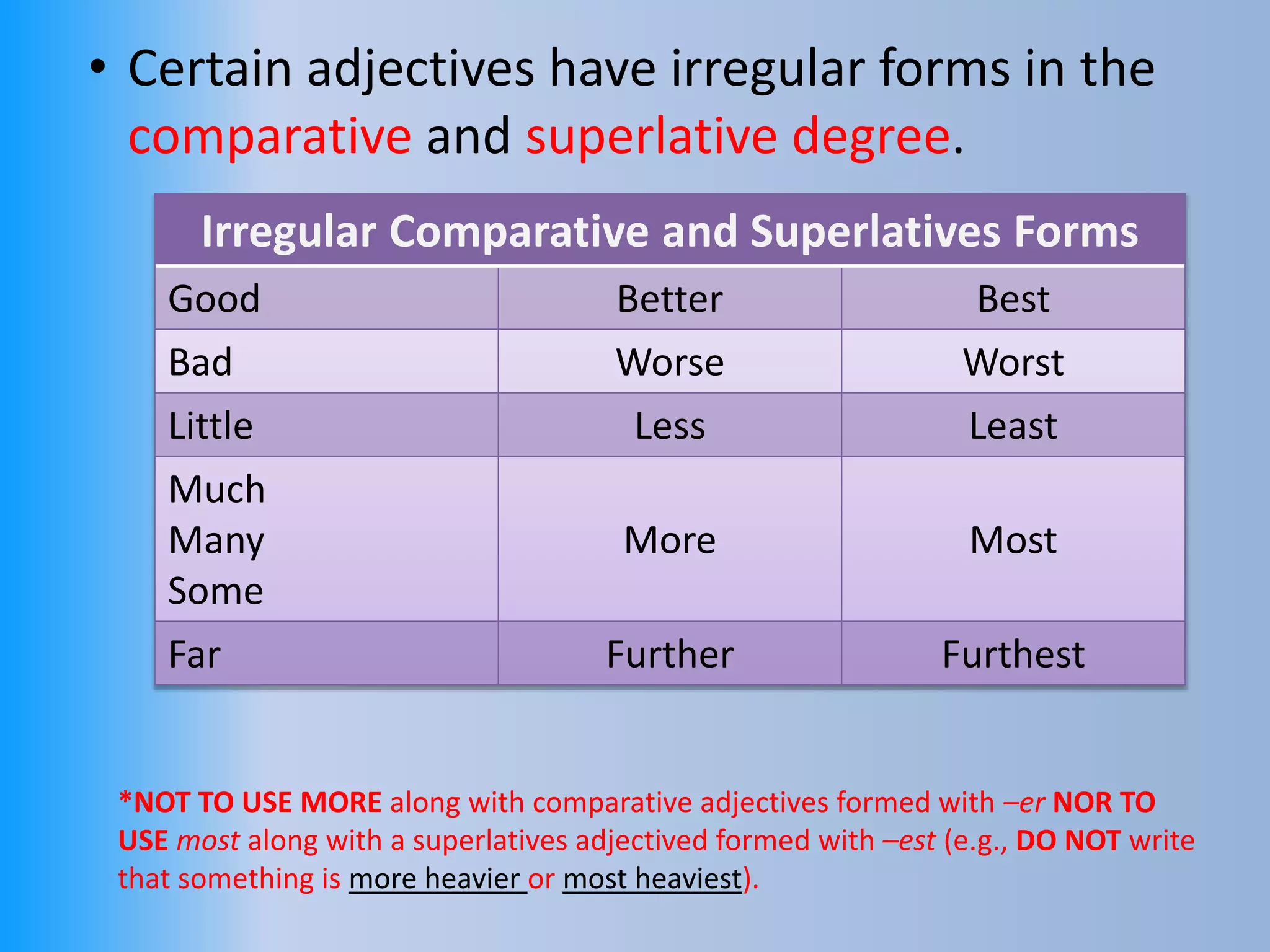
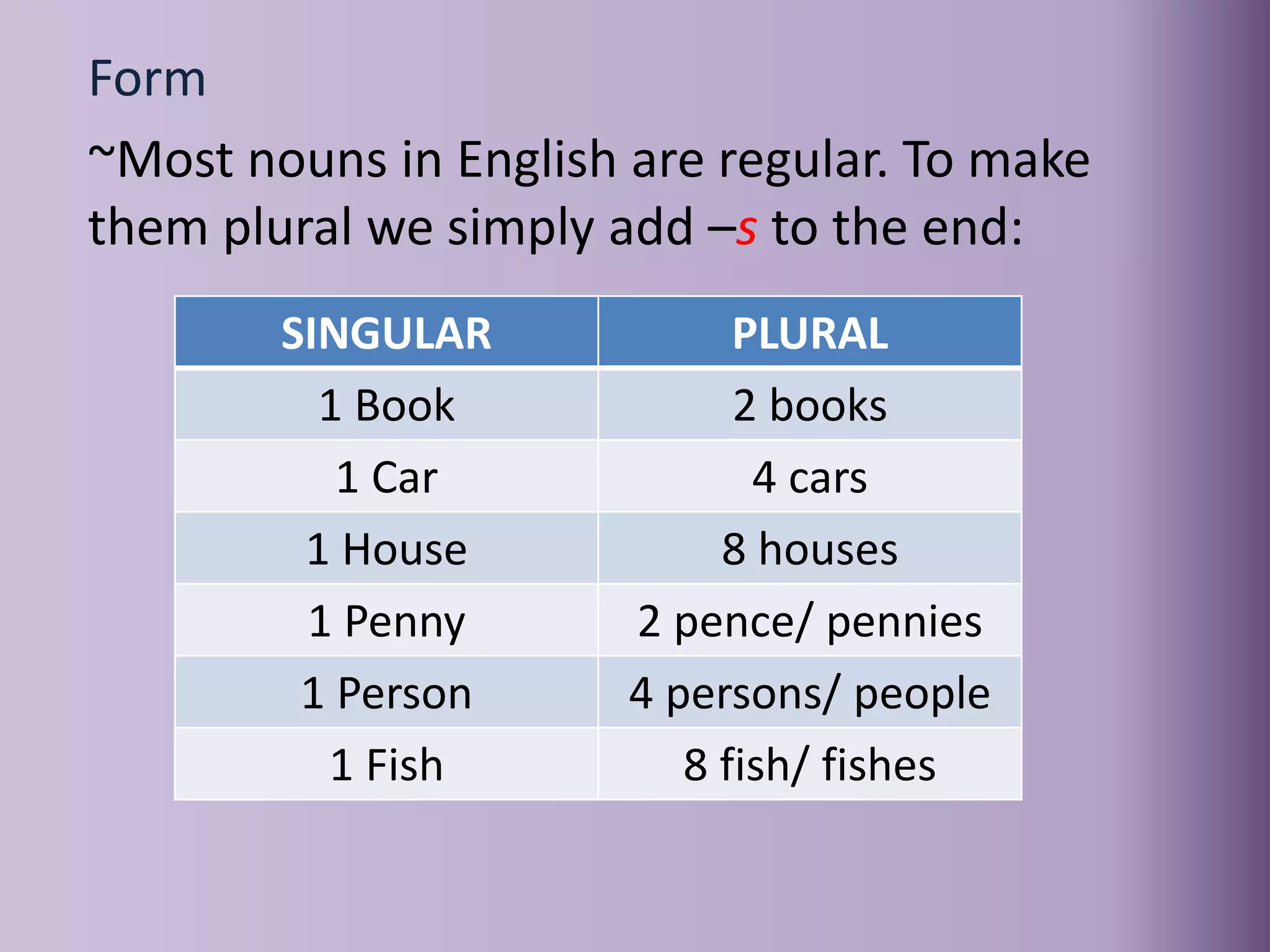
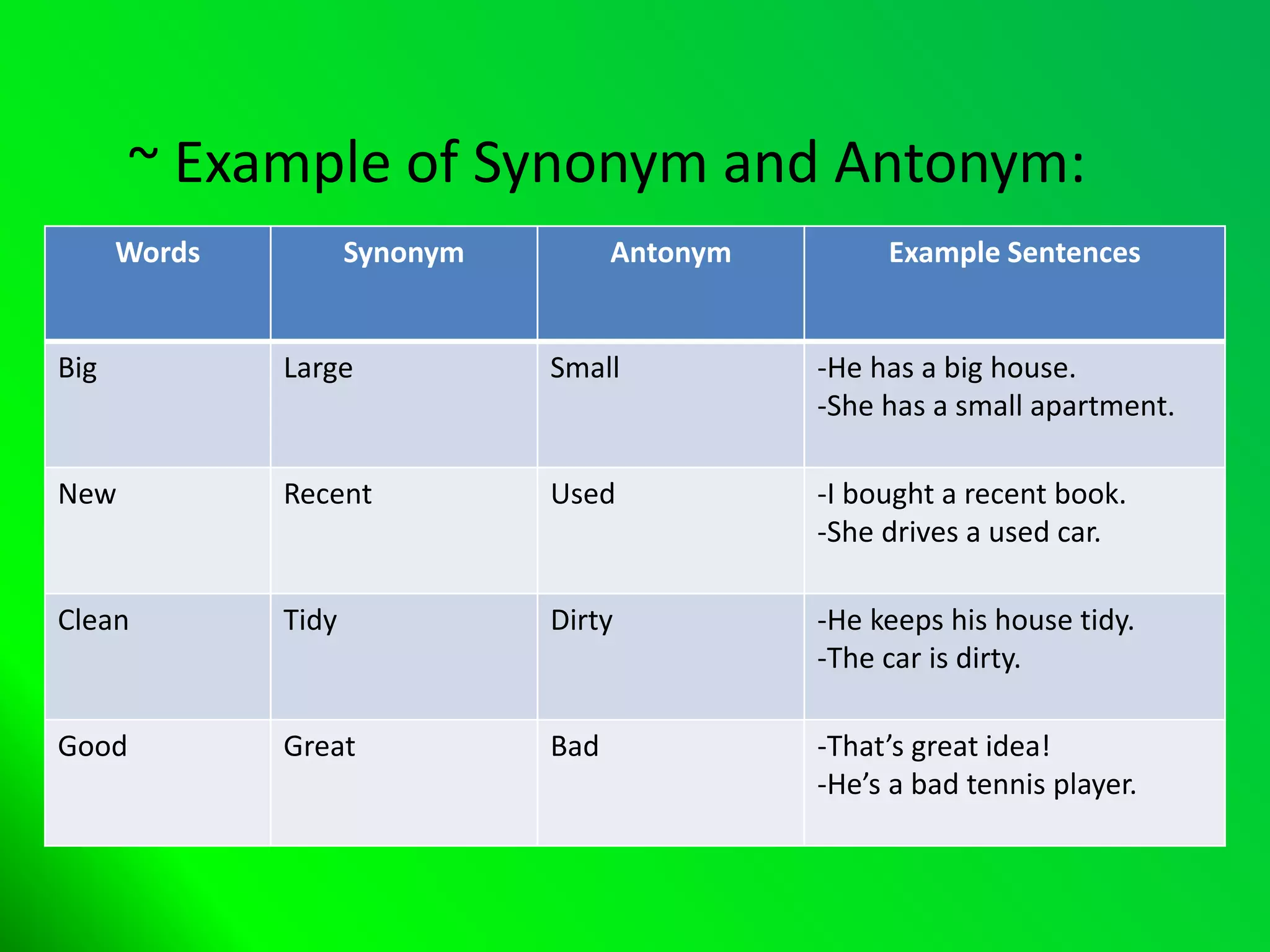
The document provides an overview of various parts of speech in English, including nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, conjunctions, and their functions with examples. It explains the categorization of nouns into proper, count, non-count, and collective nouns, as well as the rules for verb tenses and adjectives. Additionally, it discusses the distinction between countable and uncountable nouns, synonyms and antonyms, and common question words used in English.