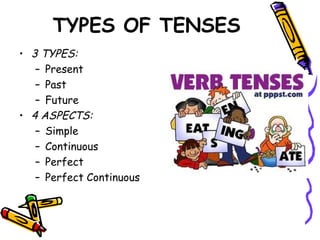
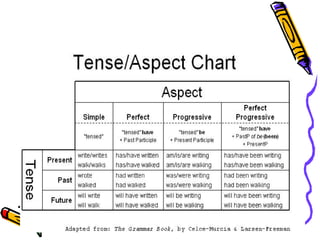
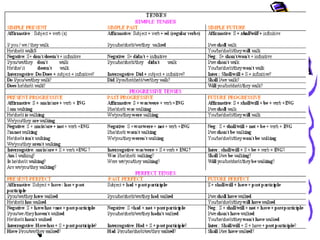
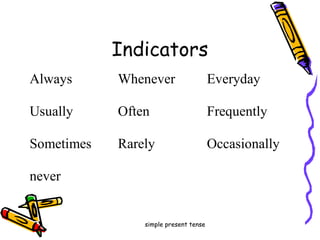
This document discusses verb tenses in English including past, present, and future tenses. It covers the three main tenses - present, past, and future - as well as four aspects - simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. For each tense, it provides examples, explanations of usage, and indicators to identify each tense. It discusses the simple present, present perfect, present progressive, past, past perfect, past progressive, future, future perfect, and future progressive tenses.