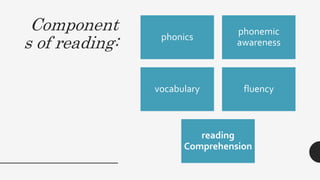
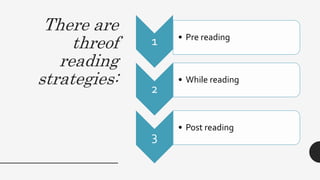
1. The document discusses various components and strategies of reading including phonics, phonemic awareness, vocabulary, fluency, comprehension, and pre-reading, while-reading, and post-reading strategies.
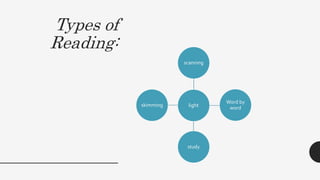
2. It describes different types of reading like scanning, skimming, light reading, word-by-word study, and study reading.
3. Barriers to reading comprehension are discussed such as inability to understand words, sentences, or how information fits together cohesively as well as lack of interest.