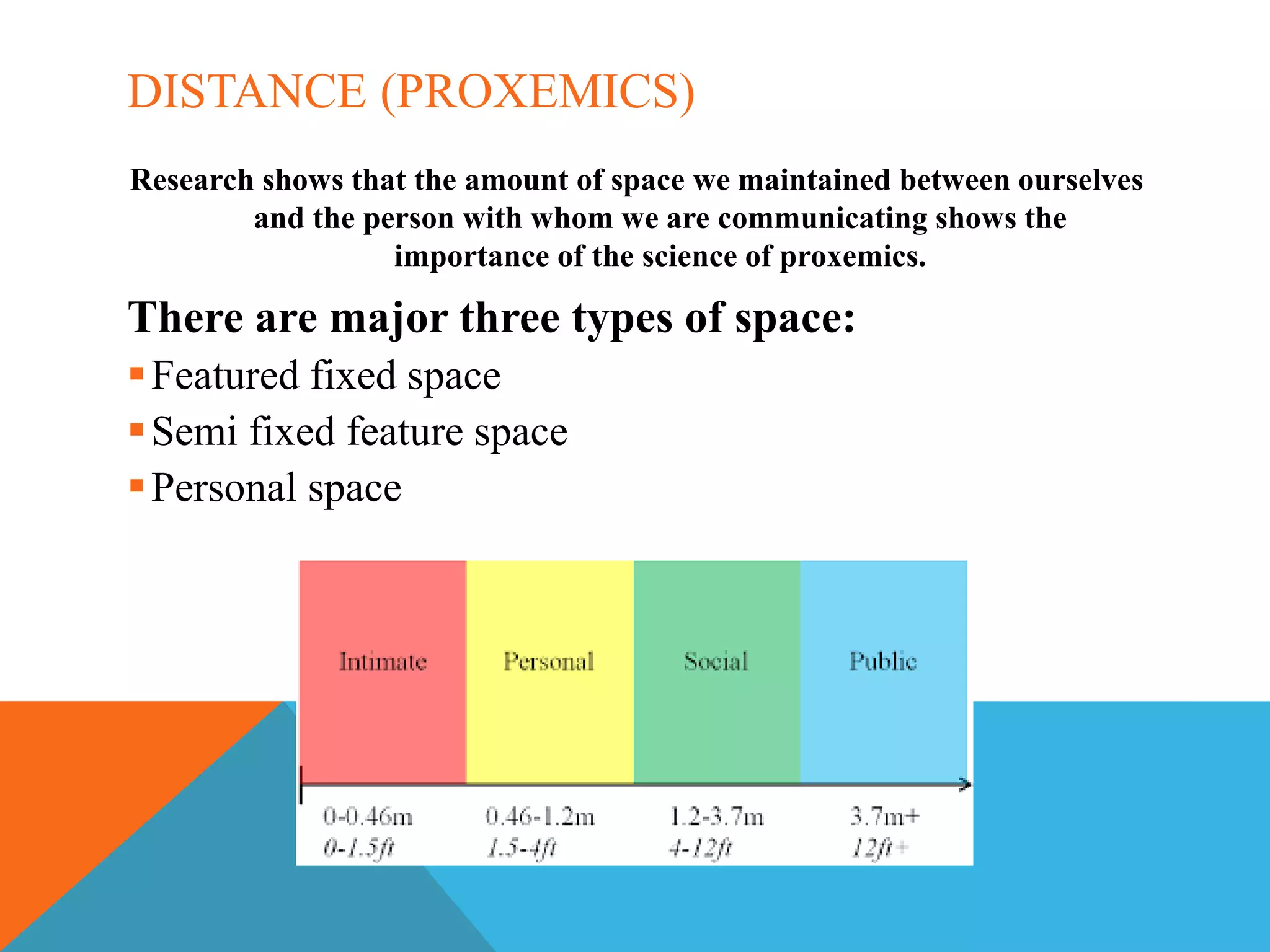
The document discusses non-verbal communication, which includes body language, posture, gestures, facial expressions, touch, paralanguage, physical context, personal space, and time language. It states that less than 35% of social meaning is conveyed through words, while at least 65% is conveyed non-verbally. Some key aspects of non-verbal communication covered include body language, gestures, the role of eyes and facial expressions, proxemics, and tips for effective non-verbal communication such as paying attention to signals and eye contact.