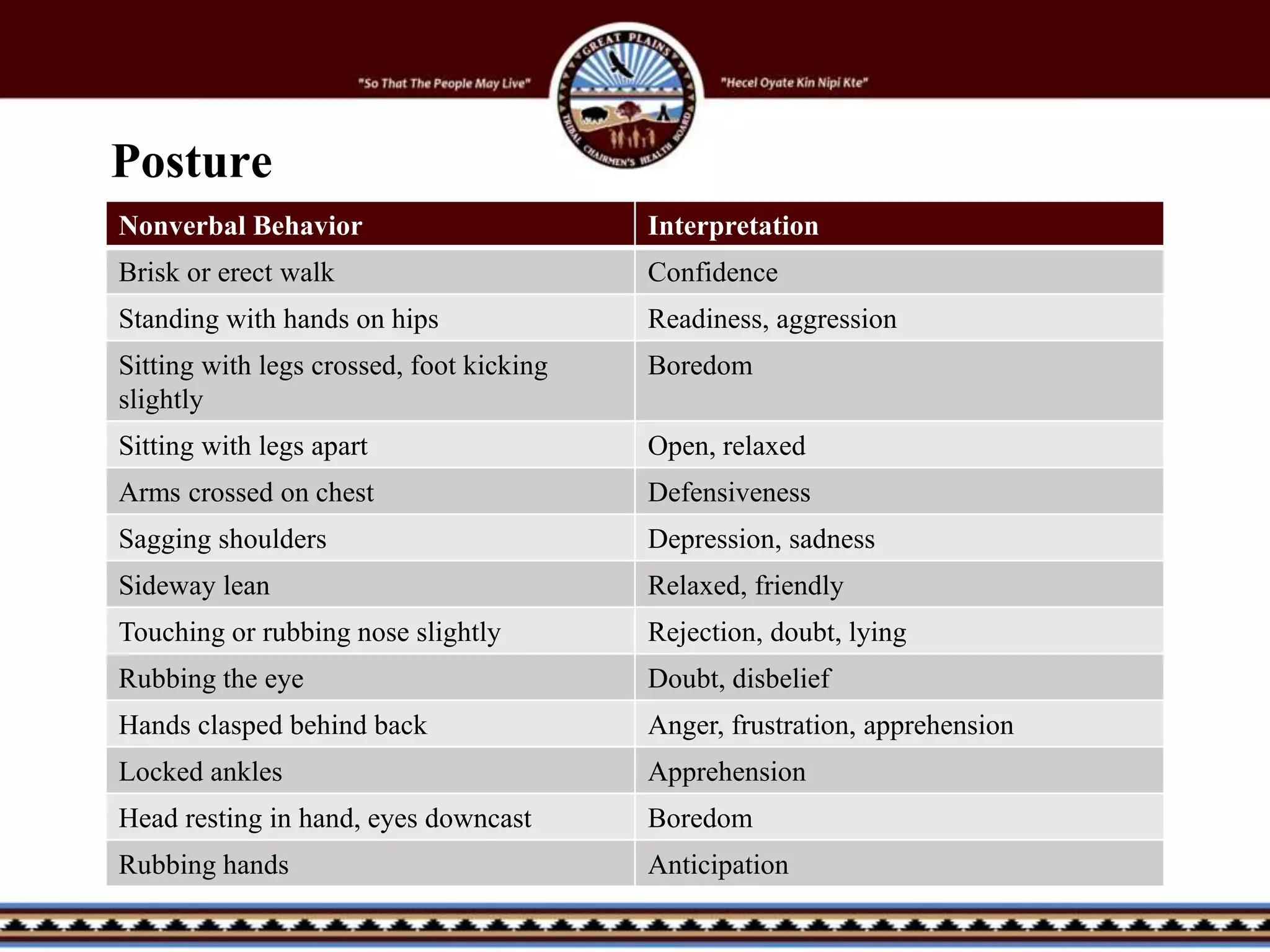
The document discusses effective communication skills. It covers defining communication, the communication process, barriers to communication, listening vs hearing, verbal and nonverbal communication, body language, personal space, and tools for effective communication such as being positive, a good listener, using clear pronunciation, and respecting others. The key aspects of communication covered are listening, speaking clearly, overcoming barriers, and ensuring messages are understood by both the sender and receiver.