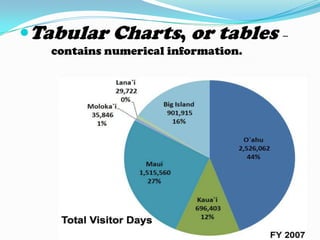
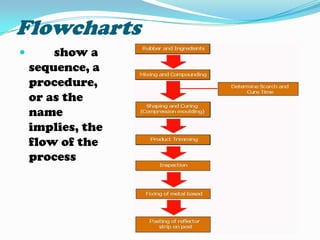
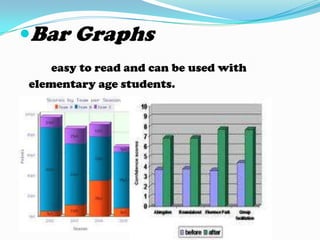
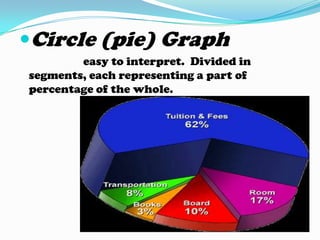
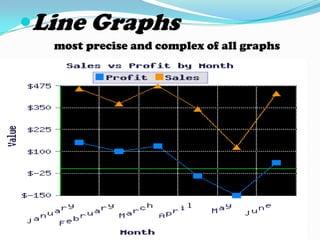
Non-projected visuals such as still pictures, drawings, charts, and posters can translate abstract ideas into more concrete representations. They allow instruction to move from verbal symbols to a more visual level. These visuals are inexpensive and easy to use without equipment in many instructional contexts and disciplines. They can stimulate creative expression and be used for testing and evaluation. Common types include still pictures, drawings, organizational charts, timelines, tables, flowcharts, graphs like bar graphs and line graphs, and posters.